
Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

CLAN CARRUTHERS – OUR NORSE ANCESTORS
Ancient & Honorable Clan Carruthers – Promptus et Fidelis -Since 1983

Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.

The Vikings are known for their ferocity in battle, but among their ranks were a group of elite warriors known as the Úlfhéðnar or wolf warriors. The Úlfhéðnar were a special breed of Viking warrior who were feared and revered by their enemies. They were known for their savagery in battle, their use of wolf skins and their ability to channel the power of the Norse god Odin.

Photo by BRAYDEN
The term Úlfhéðnar translates to “wolf coat” in Old Norse, and it is said that these warriors wore the hides of wolves into battle. The Úlfhéðnar were renowned for their berserker rage, a state of mind that allowed them to fight with incredible ferocity and disregard for their own safety. It was said that in this state, they were immune to pain and were driven by an intense desire to kill their enemies.
The origins of the Úlfhéðnar are shrouded in mystery, but it is believed that they were a select group of warriors who were chosen for their strength and bravery. They were often associated with the god Odin, who was known as the god of war and death. It was said that Odin himself would select the warriors who would become Úlfhéðnar and that he would visit them in their dreams, offering them his protection and guidance.
The Úlfhéðnar were not just skilled warriors, but also practiced shamanism and were believed to have the ability to shape-shift into wolves. This belief was strengthened by their use of wolf skins, which they wore into battle as a symbol of their connection to the spirit of the wolf. Some accounts even suggest that the Úlfhéðnar would go into battle without weapons, relying solely on their wolf-like strength and ferocity to overpower their enemies.
Despite their fearsome reputation, the Úlfhéðnar were not invincible. In fact, it is believed that their berserker rage could sometimes lead to their downfall. In this state, they would often lose all sense of reason and would attack anyone in their path, including their own comrades. This could lead to confusion and disarray on the battlefield, and many Úlfhéðnar were killed as a result.
The stories of the Úlfhéðnar have been largely forgotten over time, but their legend lives on in Norse mythology and in the annals of Viking history. It is believed that the Úlfhéðnar were present at many of the most important battles of the Viking age, including the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, where they fought against the English army.
It is interesting to note that the practice of wearing wolf skins in battle was not unique to the Úlfhéðnar. In fact, it was a common practice among many Viking warriors, who believed that it would give them strength and protection in battle. This belief was based on the idea that the spirit of the animal would inhabit the warrior and imbue them with its strength and ferocity.
The use of berserker rage was also not unique to the Úlfhéðnar. It was a practice that was common among many Viking warriors, who believed that it would give them an advantage in battle. The berserker rage was often induced through the use of drugs or alcohol, which would alter the warrior’s state of mind and make them more susceptible to the influence of the Norse gods.
Today, the Úlfhéðnar have become a symbol of Viking strength and bravery, and their legacy can be seen in modern depictions of Vikings in popular culture. The use of wolf skins and the portrayal of berserker rage can be seen in movies, television shows, and video games that depict Vikings and their way of life.
In conclusion, the Úlfhéðnar were a unique and fearsome group of Viking warriors who were respected and feared by their enemies. Their use of wolf skins and their ability to channel the power of Odin made them a force to be reckoned with on the battlefield. While their stories may be shrouded in mystery, their legend lives on as a testament to the strength and bravery of the Viking people.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CAROTOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA

TAMMY WISE CHS
DR PATRICIA CARROTHERS


Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

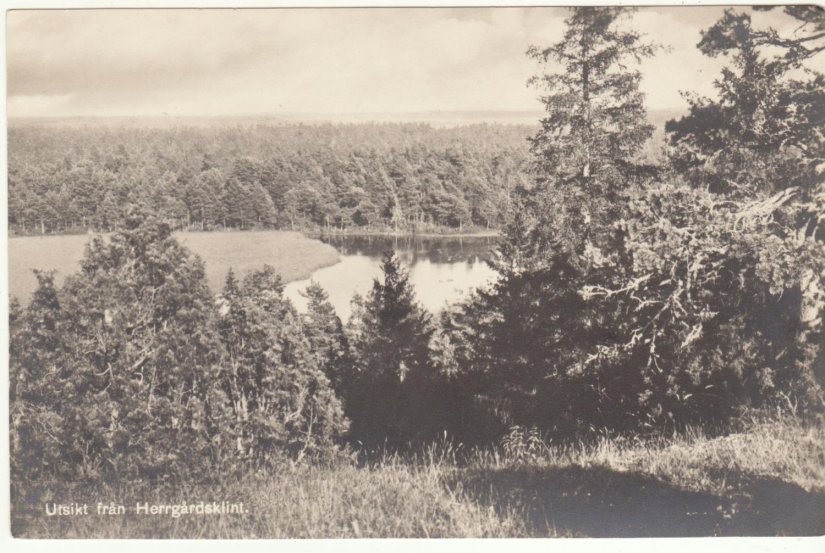
HERRGARDSKLING : FORTIFIED HILL-SITE ON GOTLAND
In this article, the author argues that the Gotlandic hilltop complex, Herrgårdsklint,
should be viewed as a fortiied hill-site (Sw. befäst höjdbosättning). This phenomenon
occured mainly on the East Middle Swedish mainland, where the fortiied hill-sites were
constructed by the late Early Iron Age period (AD 0–550) élite. The complex comprises
a 120 metre long and 2.5 metres high dry-stone wall of limestone built on a large cliff
and encloses an area of c. 1.5 ha, in which several signiicant house foundations of
limestone are visible even today. It was once given the antiquarian designation “clifffort”
(Sw. klintborg), a term which has contributed to a rather simplistic approach
from scholars. In past archaeological research, Herrgårdsklint, with the rest of the
constructions categorized as cliff-forts, has often been seen merely as a “temporary
refuge in times of unrest.” This perception has been challenged, however, by a new
approach that puts Herrgårdsklint in the spotlight of eastern Gotland during the Roman
Iron Age/Migration Period. A recently initiated project, which aims to remedy the weak
empirical situation regarding the diverse Gotlandic cliff-forts, has carried out new
analyses of the pottery and animal bone material found in a 1940s excavation of a
couple of the house foundations. Together with the observation of the architecturally
advanced stone wall’s entrance construction (which the author suggests is an imitation
of a clavicula-entrance of a sort used by the Imperial Roman army), the results indicate
that Herrgårdsklint should be viewed as a strongly fortiied permanent/semi-permanent
settlement, which controlled a large hinterland that specialized in beef production and
shows signs of close connections to R oman ideas.
288 Runsa Borg – Representative Life on a Migration Period Hilltop Site
Herrgårdsklint revisited: a fortiied hill-site on Gotland

Introduction
Situated on a remote clif in the eastern part of
the Baltic island of Gotland, a hilltop complex
built sometime during the late Early Iron Age
(AD 0–550) commands a view over what is
today a great woodland territory (ig. 2). An area
of c. 1.5 ha is enclosed by vertical precipices up
to 15 metres steep in the north, east and west,
as well as a 120 metre-long and 2.5 metre-high
transverse dry-stone wall in the south (igs. 1 and
8). Within this area, the remains of a number
of substantial stone-house foundations, similar
to those of the late Early Iron Age landscapes
of the rest of Gotland and the adjacent island,
Öland, are visible even today. his complex
is known as Herrgårdsklint (en. Clif of the
manor) and was once given the antiquarian
designation “clif-fort” (Sw. klintborg), a term
which will be shown to be anything but simple,
and seems to have been somewhat forgotten by
archaeologists. he following article is based
on results obtained from a recently initiated
archaeological project1, the aim of which is to
remedy the weak empirical situation and create
a more nuanced image of the diverse Gotlandic
clif-forts2. Below, I will argue that there
are several indications that Herrgårdsklint
might constitute a fortiied hill-site (Sw. befäst
höjdbosättning); a phenomenon that has
recently attracted archaeological attention,
formerly being mainly known, in Scandinavian
research, on the East Middle Swedish mainland.
If so, this hilltop complex would have been
central to the Gotlandic Early Iron Age élite.
Before a discussion of Herrgårdsklint in the
centuries following A.D. can begin, however, a
brief review of past research focuses within the
discourse, as well as a study of the terminology,
is necessary.

To deconstruct a cliff-fort
Traditionally, Gotland’s hill-forts have
been divided into three subgroups; clifforts
(Sw. klintborgar), lat ground-forts (Sw.
latmarksborgar) and bog-forts (Sw. myrborgar)
(Stenberger 1940a: 66). he irst subgroup
consists of remains which can be described as
the general idea of how a hill-fort is supposed
to be; great stone walls erected on an elevated
position which together completely enclose
an area (e.g. Torsburgen). But such an old
term also conceals constructions which are
made up of nothing more than a single row
of stones which seems to encircle a clif or a
hilltop in an almost symbolic way (e.g. Lärbro
RAÄ 17). Since few of the Gotlandic hill-forts
have been archaeologically excavated, the idea
that topographic and geographic location is
synonymous with function and dating has been
popular in modern archaeological research
(e.g. Cassel 1998, 2008). Furthermore, the
sheer absence of clif-forts afected by large
contract archaeological projects, usually the
result of the often extensive empirical data
associated with the types of investigations that
also serve as a catalyst for continued research
interest (Olausson 1995), simply do not exist.
his lack of empirical data might be one
factor contributing to why traditional ideas
concerning the clif-forts have been, for the
most part, unchallenged.
here have been two main ields of research
interest within the discourse. For the majority
of the 1900s, interpretations of the so-called
forts were dominated by expositions
of military strategies and various sorts of
fortiication, as a rule often combined with
accounts of the supposed unrest during
Roman Iron Age/Migration Period (e.g.
Nihlén and Boëthius 1933, Stenberger 1945;
1964, Lundström 1955, Manneke 1979,
Engström 1984). It was not until the 1990s
and early 2000s, as postmodern theories
began to inluence archaeological studies, that
alternative interpretations started to dispute the
“clif-fort as strictly a fort” paradigm. Instead
of accentuating the military aspects of the
constructions, they came to advocate an
understanding based on more symbolic
premises of the monuments. hus, the mental
and ritual nature of the clif-forts became the
focal point (e.g. Cassel 1998, 2008; Hegardt
1991a, 1991b; Swedish mainland material: see
Johansen 1997, Carlsson 2001, 2005, Wall
2003). Although these studies can be described
as a breath of fresh air in a ield of research
which, with few exceptions (e.g. Olausson
1995), can be described as stagnant for quite
some time, they had a tendency to theorize
outside the framework of the empirical data,
which, although meagre, nevertheless existed.
As I have previously shown, (Bornfalk-Back
2011) there are great variations within the
long-assumed homogeneous category of
“clif-fort”, and all attempts to come up with
a general explanation of these 28 Gotlandic
hilltop monuments have been fairly hopeless,
regardless of the theoretical approach (ig. 3).
Evidently, it is the generally weak empirical
knowledge that has contributed to these rather
one-dimensional attitudes towards the hilltop
sites. As a necessary start to a newly aware
discourse, then, it is critical to appreciate the
fact that within the antiquarian term “clif-fort”
(and indeed “hill-fort”!), there are a number
of diverse remains with various functions and
various dating (Bornfalk-Back 2011).
With this discussion in mind, the very
term clif-fort must be said to be poor as it
linguistically implies a construction associated
with fortiication and war, which might be true
for some of the remains, but far from all. I hope
to return with a more thorough terminological
discussion within the hill-fort ield elsewhere
and thus will here conine myself to the
suggestion that the most suitable term for
Herrgårdsklint is, for the moment, fortiied
hill-site, a descriptively acceptable term which
has been used for a special kind of defendable
aristocratic hilltop settlement from the late
Early Iron Age in the East Middle Swedish
mainland (see below).

Herrgårdsklint in previous
archaeological research
he stone wall and house foundations on the
clif are presently one of a kind on Gotland,
and the remains were noticed early by
antiquarians. he Swedish cultural historian
C.G.G. Hilfeling (1740–1823) paid a visit to
Herrgårdsklint in the 1790s and in addition to
documenting the dimensions of the remains,
he also suggested that the hilltop complex was
probably a place of refuge in times of unrest
(Hilfeling 1994: 236–7). he next visit nearly
80 years later, however, can be described as the
true birth of modern Swedish archaeological
hill-fort discourse. he archaeologist Fredrik
Nordin (1852–1920) not only described
Herrgårdklint and other clif-forts, but also
divided them into subgroups which resulted
in the publication Om Gotlands fornborgar
(1881). He visited Herrgårdsklint twice and
the eminent scholar stated that, based on the
substantial house foundations, the hilltop
complex was erected “not merely for the
moment” (Nordin 1881: 32).
Two minor archaeological excavations have
been carried out at Herrgårdsklint. In 1940,
the Swedish archaeologist Mårten Stenberger
excavated what turned out to be two of the
at least six stone house foundations (ig. 4),
whose wall dimensions (up to 1.75 metres in
width and a current height of up to 0.80 m)
appeared to be similar to those of other late
Early Iron Age house foundations across the
island, most of which date to AD 200–600
(Stenberger 1940b; Burenhult 1999:224).
Aside from two larger hearths, about 1500
sherds of plain Early Iron Age period pottery
and more than 18 kg of animal bone material
were found (Stenberger 1940b). A bridle,
probably from later re-use of the site, was
also found and could be dated to late Iron
Age (Biörnstad 1955: 949). In the beginning
of the 1980s, a smaller trench was put right
where the wall would have continued in the
south if it were not for modern removal of
stone for building material. he wall proved
to be constructed mostly of limestone, but no
datable artefacts were found (Engström 1982:
172, 1984:3).

Surprisingly little has been written about
Herrgårdsklint over the years, and I would argue
that what has been printed is not satisfactory,
but rather has had a tendency to simplify this
unique monument. For instance, the long widespread
idea that the Gotlandic clif-forts
were impermanent in character contributed to
the demotion of the at least six massive stone
house foundations to the status of simple wind
breakers (Biörnstad 1955: 916). his naturally
made the site less exciting to researchers overall.
Also, no one has ever studied Herrgårdsklint
from a local viewpoint, but rather as a mere
member of the artiicially constructed “cliffort
mass” (e.g. Cassel 1998: 132, 144; 2008:
90–93) or as a secondary element to other
archaeological phenomenon; e.g. part of a lank
defence to the gigantic hill-fort Torsburgen
(Engström 1984: 106). I would like to suggest
that a new approach that puts Herrgårdsklint
in the spotlight of eastern Gotland during late
Early Iron Age might bring together the site not
only with the surrounding landscape, but also
with the East Middle Swedish mainland.
A brief glance at
the Swedish mainland, and beyond…
As mentioned above, it is necessary to recognize
the diferences among constructions within
the “clif-fort mass”, and in the term fortiied
hill-site there are some speciic characteristics
which can be mentioned here. hese hilltop
complexes are all heavily defended by great
walls and inside the enclosure there are
buildings which were permanently inhabited.
It seems, at least in East Middle Sweden, that
these sites were established sometime during
the later part of the Early Iron Age (c. AD
200–550), though the precise nature of the sites,
as well as their relation to the surrounding
settlements, is still debatable. Although few
have been archaeologically excavated, there
are some constructions almost exclusively in
the East Middle Swedish mainland which
have been identiied as fortiied hill-sites,
which include sites around Mälaren (e.g.
Runsa, Darsgärde, Broborg), Södertörn (e.g.
Fållnäs) and Östergötland (e.g. Gullborg,
Boberget). One must keep in mind that even
if these constructions should be viewed as élite
residences, their function within society need
not have been identical in all matters (Olausson
2011a: 19).
Runsa borg is a very well fortiied hill-site in
Uppland, slightly north of Stockholm, and
through extensive excavations an aristocratic
milieu has been exposed with a hall building
and areas of handcraft, e.g. bronze casting, with
inds of, for instance, fragments of glass with
possible provincial Roman origin (Olausson
2011a, 2011b, 2009, 1996). he animal bone
material indicates luxury consumption and
since during the centuries following AD Runsa
borg was situated on a small island divided
from the mainland by a narrow inlet, the hillsite
was dependent on the control of a large
agrarian hinterland for goods and supplies
(Risberg 2011; Olausson 2011b: 237–8).
In the province of Östergötland, the existence
of fortiied hill-sites has also been recognized.
For instance, within the 350 metre-long and up
to 15 metre-wide dry-stone wall in Borgberget,
Kimstad parish, two substantial stone house
foundations have been observed. During a
minor excavation in the 1960s, inds such
as spindle whorls, whetstone and pots
herds date the remains to the late Early Iron Age
(Lindahl 1963). Another illustrative example
from Östergötland is the site Gullborg. Just
as at Runsa borg, extraordinary inds such as
an imported beaker from the Black Sea area
and a Roman glass bottle indicate a upper
class environment (Nordén 1938: 280–284;
Nielsen 1996: 87 with ref.). he occurrence
of imported Roman/Continental artefacts in
settings similar to Herrgårdsklint might be a
critical observation for the understanding of
the Gotlandic hill-site, which so far has no high
status inds.
At last, a region that would be exceptionally
exciting to study within the discourse is the
eastern part of the Baltic Sea area. If fortiied
hill-sites such as the ones recognized in East
Middle Sweden and now Gotland can be
identiied in this area, a whole new dimension
to the study of these remarkable remains would
be gained.

A revisit to Herrgårdsklint
A crucial task of the study of Herrgårdsklint
must, at this stage, be more precise dating. Until
new archaeological excavations are carried out,
the pottery inds from the 1940s excavation are
the only material available. However, it seems
to be diicult to get a speciic dating, other than
late Early Iron Age, from the plain fragmental
pieces (Stenberger 1955: 1173; Biörnstad 1955:
949). Still, other aspects are able to be clariied
by a new pottery analysis, since the original
one merely established the simple nature of
the sherds. Vessels for storage, preparations as
well as serving could be identiied among the
material. Several of the identiied lower parts
of the pots show evidence of an open angle
which would have been suitable for food,
which, in contrast to vessels used for storage
alone, were to be visualized and consumed
at once (Eriksson 2009: 160). Also, based on
reconstructions of the mouth diameter, several
pots had the mouth measurements of 25 cm,
and hence might have had the potential to
accommodate up to 20 litres of luid (Eriksson
2009: 83). he smaller pots should most likely be
understood as vessels used in food preparation.
Since there are indications that these fortiied
hill-sites were rather short lived, perhaps as
brief as only 3–4 generations as Runsa borg
(Olausson 2011b: 239), the total amount of
pottery (1500 sherds/c. 7 kg) combined with
the total amount of bone material (c. 18 kg)
found in the two houses suggest quite intensive
activity at Herrgårdsklint compared to the
material found in similar house foundations
on Gotland (e.g. Lundberg 1937, Stenberger
[ed.] 1955a: 100–254; 1955b: 863–976). hus,
based on the pottery, the overall picture must
at present be said to indicate that everyday
domestic chores such as cooking, serving and
the storage of food dominated these buildings,
which, based on the quantity, should be viewed
as intensely inhabited.
The animals from Herrgårdsklint
Osteologist Lisa Hartzell’s project performed a
thorough analysis of the animal bone material
found in two of the house foundations. he
majority of the material consists of an equal
amount of cattle, sheep and goat inds, with
single inds of horse and dog. he most striking
result was that while the bones of the sheep
and goats were consistent with the meat-rich
parts of the animals, as well as the waste, the
cattle bones found were 99 % waste material
(Bornfalk-Back 2013). his suggests that the
sheep and goats were slaughtered and consumed
at the site while the cattle was slaughtered and
dismembered at Herrgårdsklint, but then
consumed elsewhere. Where the consumption
took place is, of course, a central question.
Was the beef transported to a nearby location
for consumption or was it sold or traded
and, if so, to where and to whom? Another
important aspect to consider: the bone
material might give greater insight into the
question of the permanence of the settlement
at Herrgårdsklint. Based on the fragmentary,
yet rather large, animal bone material, a
cautious conclusion is that the site was perhaps
at least seasonally inhabited, since it would
seem that people found it meaningful to bring
cattle to the site with the intent of engaging in
specialized beef production.
To locate areas of more intense activity at
Herrgårdsklint a soil phosphate analysis
(citronsyrametoden) was carry out on the
site (Bornfalk Back 2013). East and south
of the house foundations no or extremely
thin soil layer prevented the sampling, which
concentrated to the northern parts of the
clif. he elevated values of the soil phosphate
sampling indicate activity in three places
within the sampling area . Obviously,
to clarify the nature of activity archaeological
excavations are necessary.
The Roman inluences
It is clear that people from what is today East
Middle Sweden interacted, to various degrees,
with the Roman Empire during the early
centuries AD. hrough trade and service within
the Roman military apparatus, ighting against
Roman troops, and indirect contact via non-
Roman people living close to Limes, new ideas
and artefacts found their way to Scandinavia
(e.g. Andersson 1991; Axboe 1991; Jørgensen et
al [red] 2003; Kalif and Sundqvist 2004). For
Gotland’s part, inds of Roman glass, solidi,
gold bracteates, as well as a recently recovered
Roman oicer’s parade mask dating to the
later part of 200 AD (Widerström 2012: 31)
tell us of intense contact between members of
the élite of the island and the Roman Empire.
Although there is an absence, at the moment,
of high status inds related to the settlement
on the clif, it is possible to distinguish other
features, which suggests that the architect of
Herrgårdsklint was an individual of means and,
for the region, a unique know-how. Bearing the
discussion of Roman connections in mind, the
best way to understand the extensive entrance
construction of the only opening to the stone
wall of Herrgårdsklint might be through the
“home-comer’s perspective”. he unusual
construction is made up of a curved wall section
continuing from the main wall of the eastern
part of the more than three metre-wide entrywith an opening in the west his once
dry-stone structure seems to have had the same
dimensions as the sections of the main wall (c.
4 metres wide), and a rectangular open space.
I would like to suggest that this architectural
construction indicates that the architects of
Herrgårdsklint were quite familiar with the
engineering methods used by the Imperial
Roman army.
he Roman castra (marching camps) were a
central part of the invasion tactic, and although
they could vary in size and layout, they were
all strongly fortiied, sometimes, especially
during the 1st and 2nd centuries A.D., with a
sort of defendable entrance construction called
clavicula (Johnson 1983: 50; Frere 1987: 211).
A clavicula was an arched extension of the defensive rampart and could be either external
or internal (ig. 7). he idea was to prohibit a
direct frontal assault at the gate by forcing the
enemy through a sideway where they were thus
more exposed to the defenders. It can also be
mentioned as a proof of its eiciency that this
defensive construction was utilized by the later
Byzantine army. It was not only described by
the emperor Maurices (A.D. 582–602) in his
Strategikon (trans. Dennis 1984: 164), but also
recommended by Byzantine military leaders
as late as in the tenth century A.D., as can be
seen in contemporary military texts (trans.
Dennis 1985: 251, 257–260). It is obvious that
the entrance construction at Herrgårdsklint
displays remarkable similarities to a Roman
clavicula in layout, and I would argue that
this particular defensive structure could only
be built with the help of the advanced level
of expertise that could only be provided by
a Germanic soldier returning from years of
service in the Roman military apparatus.
Previous discussions (Herschend 1985) of
constructional details of the entrances to the
Eketorp ring-fort on the island of Öland have
pointed towards Roman examples. Although
these ring-forts, which more or less can be
described as fortiied villages, and the fortiied
hill-sites are two separate phenomena, they
were in part contemporary with each other and
a cautious comparison is motivated. However,
it is crucial to emphasize that Herrgårdsklint
should not be viewed as an attempt to imitate a
castra in either function or design, nor should
one necessarily see the defendable nature of the
entrance construction as the key motivation.
Essential, I would say, is the Roman aspect:
by demonstrating a unique knowledge in
fortiication techniques obtained from thecontinent, additional prestige was gained,
justifying the lord of the clif’s position in the
social hierarchy.

Herrgårdsklint was built on a remote clif
relatively far from other Early Iron Age
settlement, with no cultivated land nearby
(ig. 2), and thus a signiicant question is:
why? At this stage, any ideas on the matter
must be described as speculative, but one
thought worth mentioning is the importance
of Herrgårdsklint potentially superb location
from a communicative standpoint. Since the
new results indicate that Herrgårdsklint was at
least semi-permanently inhabited, the people
living on the clif were dependent on a steady
supply of food and other goods from elsewhere,
much like Runsa Borg (see above). his, in
turn, implies that a large hinterland must have
been under the control of the residents of the
clif to secure this provision. Herrgårdsklint
is today situated only 5 km from Gotland’s
eastern coast, where good locations of Iron Age
ports have been discussed (Engström 1984:
99–103). Since a large part of Gotland’s lakes
and rivers were drained during the 1800s and
early 1900s for agricultural purposes, a possible
explanation worth studying is the occurrence
of now vanished navigable waterways. If these
were to connect Herrgårdsklint with the coast,
and a potential port, it would not have been
diicult to provide the site with both foodstuf
and commodities.
Future questions
Although the initiation of this project has
proven to be a productive irst step in the task of
generating a more solid empirical foundation,
as well as challenging traditional ideas withrespect to Gotlandic clif-forts, it has merely
scratched the surface. A central future task is to
obtain a more precise dating of Herrgårdsklint
and its phases. his can only be achieved by way
of new archaeological excavations. Questions
concerning precise time of establishment,
abandonment, re-use, relation to other
contemporary settlements in the area, the exact
nature of dwelling (permanent/seasonal use)
etc. can only be answered via such excavations.
From a local viewpoint, an exciting thought
is whether Herrgårdsklint is the only hill-site
on Gotland, and, if this is the case,
what does this mean for the island as a whole
during late Early Iron Age? In addition, the
relation between Herrgårdsklint and other
fortiied hill-sites on the Swedish mainland is
an interesting matter for future study. Also, if
fortiied hill-sites were to be identiied in the
adjacent eastern Baltic, it would be a crucial
task to study the relationship between areas
with the same aristocratic tradition.
Many thanks to homas Eriksson (SHM) for
making the pottery material available.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CAROTOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA

TAMMY WISE CHS


Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

HAAKON THE GOOD AND THE SONS OF GUNHILD
CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR
We have told how King Haakon succeeded his brother, Erik Blood-Axe, on the throne, and how, from his kindly and gentle nature, people called him Haakon the Good. There were other sons and several grandsons of Harold the Fair-Haired in the kingdom, but the new king treated them with friendliness and let them rule as minor kings under him.

He dealt with the peasants also in the same kindly spirit, giving them back their lands and relieving them of the tax which Harold had laid. But he taxed them all in another way, dividing the country into marine districts, each of which was required to supply the king, on his demand, with a fully equipped warship. Yet as this was for the defence of the country, the people did not look on it as oppressive. And as Norway had a long mountainous coast, and important events were often long in becoming known, he gave orders that the approach of an enemy should be made known by signal fires lighted all along the coast.
Haakon made other wise laws, in which he took the advice of the ablest men of the kingdom. But now we have to speak of the most striking event in the new king’s career. Norway at that time was a haunt of idolatry. Men worshipped Odin and a host of other gods, and there was not a Christian in the whole land except the king himself, who had been brought up in the new faith by his foster-father, King Athelstan of England.
An earnest Christian, he looked with sorrow on the rude worship and heathen belief of his people, but not until he had been many years on the throne did he venture to interfere with it. Then, about 950, when he had won the love of them all, he took steps to carry out his long-cherished desire.
Sending to England for a bishop and a number of priests, the king issued a decree in which the people were forbidden to make sacrifices to the old gods and ordered to accept the Christian faith.
This came like a thunderbolt to the worshippers of the old gods. To bid a whole nation to give up at a word the religion which they had cherished from childhood and which their fathers had held for generations before them was too much to demand. The king brought together a concourse of the people and spoke to them of his wish and purpose, but they had no answer to make except that the matter must be settled by their legal assembly.
When the thing, or assembly, was called into session, a great body of the people were present, for never had so important a question been laid before them. Earnest and imploring was the speech made by the king, in which he warmly asked them to accept the God of the Christians and give up their heathen idols of wood and stone.
These words were followed by an angry murmur from the multitude, and many dark looks were bent upon the rash monarch. Then a peasant leader, Aasbjörn of Medalhus, stepped out from the throng and spoke:
“When you, King Haakon, first called us here before you and we took you for our king, it was with deep gladness, as if heaven had opened to us. But was it liberty we gained, or do you wish to make thralls of us once more, that you ask us to give up the faith of our fathers and forefathers for the new and unknown one you offer? Sturdy men they were, and their faith did well for them and has done well for us. We have learned to love you well and have always kept and will always keep the laws made by you and accepted by us. But in this thing which you now demand we cannot follow. If you are so resolved upon it that your mind cannot be changed, then we shall be forced to part from you and choose a new chief who will support us in worshipping our fathers’ gods. Choose, O king, what you will do, before this assembly has dispersed.”
So loud were the shouts of approval with which this speech was greeted that not a word could be heard. Then, when quiet reigned again, Earl Sigurd, who had spoken aside with Haakon, rose and said that the king had no wish to lose their friendship and would yield to their wishes. This was not enough to overcome the distrust of the peasants. They next demanded that he should take part in the sacrifices to be given and in the feast to follow. This he felt obliged to do, though he quieted his conscience by making the sign of the cross.
When the next Yuletide sacrifice came Haakon was required to eat horse-flesh at the feast and this time was forbidden to make the sign of the cross when he drank the usual toasts to the ancient gods of Norway. This was a humiliation that cut the proud monarch deeply and it was with an angry soul he left, saying to his attendants that when he came back it would be with an army to punish those who had thus insulted his faith. Back he did not come, for new troubles were gathering around him.
To learn the source of these troubles we must return to the story of Erik Blood-Axe and Gunhild, his wicked wife. After Erik’s death that mischief-loving woman sought Denmark with her sons, who grew up to become brave warriors and daring viking rovers, infesting the coast of Norway and giving its king and earls all the trouble they could. At length, backed by Harold Bluetooth, the king of Denmark, their piratical raids changed to open war, and they invaded Norway, hoping to win their father’s old kingdom for themselves.
A crisis came in 955. In that year the sons of Erik appeared so suddenly with a large fleet that they took King Haakon by surprise. He had with him only a small force, the signal fires had not been lighted, and the enemy were close at hand before he could prepare to meet them.
“What shall we do?” he asked his men. “Shall we stay and fight, or draw back and gather men?”
The answer came from an old peasant, Egil Woolsack:
“Often have I fought, King Haakon, with King Harold, your father. Whether the foe was stronger or weaker the victory was always his. Never did he ask his friends if he should run; nor need you, for we are ready to fight and think that we have a brave chieftain for our leader.”
“You speak well and wisely, Egil,” said the king. “It is not my wish to run, and with your aid I am ready to face the foe.”
“Good words those!” cried Egil joyously. “It has been so long since I saw the flash of sword that I feared I would die in my bed of old age, though it has been my hope to fall in battle at my chieftain’s back. Now will my wish be gained.”
To land came the sons of Erik, having six men to Haakon’s one. Seeing how great were the odds, old Egil tried strategy, leading ten standard-bearers to a hidden spot in the rear of the hostile army and leaving them there in ambush. When the armies had met and the fighting was under way, he led these men up a sloping hill until the tops of their standards could be seen above its summit. He had placed them far apart, so that when the Danes saw the waving banners it looked like a long line of new troops coming upon them. With sudden alarm and a cry of terror they fled towards their ships.
Gamle, their leader, was quick to discover the stratagem, and called on them to stop, that it was all a trick; but nothing could check their panic flight, and he was swept along with them to the beach. Here a stand was made, but Haakon rushed upon them in a furious attack in which old Egil had his wish, for he fell in the storm of sword blows, winning the death he craved. Victory rested on the king’s banners and his foes fled to their ships, Gamle, their leader, being drowned in the flight.
For six years after this the land lay at peace. King Haakon continued a Christian and many of his friends joined him in the new faith. But he was too wise and gentle to attempt again to force his belief upon his people and the worship of the heathen gods went on. All the people, nobles and peasants alike, loved their king dearly and he would have ended his reign in a peaceful old age but for his foes without the kingdom. This is the way in which the end came.
In the summer of the year 961, when Haakon had been twenty-six years on the throne, he with many guests was at feast in the royal mansion of Fitje, in Hördaland. While at table a sentinel brought in the alarming news that a large fleet of ships was sailing up the fiord.
By the king’s side sat Eyvnid, his nephew, who was a famous scald, or bard. They rose and looked out on the fiord.
“What ships are they, of friends or of foes?” asked the king.
The scald replied in a verse, in which he sang that the sons of Erik were coming again.
“Once more they take us unawares,” said Haakon to his men. “They are many and we are few. Never yet have we faced such odds. The danger lies before you. Are you ready to meet it? I am loath to flee before any force, but I leave it to the wise among you to decide.”
Eyvnid sang another verse, to the effect that it would be ill counsel to advise a man like King Haakon to flee from the sons of Gunhild the sorceress.
“That is a man’s song,” cried the king, “and what you say is what I wish.”
All around him the warriors shouted their war-cry, and while they ran for their weapons he put on his armor, seized his sword and shield, and placed on his head a golden helmet that shone brightly in the sun. Never had he looked more like a born king, with his noble and inspired countenance and the bright hair streaming down from under his helmet.
The battle that followed was fierce and bloody. Harold, Gunhild’s third son, commanded the invaders, who far outnumbered Haakon’s small force. And now there was no Egil to defeat the foe by stratagem, but the battle was hand to hand and face to face, with stroke of sword and thrust of spear, the war-shout of the fighters and the death-wail of the fallen.
King Haakon that day showed himself a true and heroic warrior. As the battle grew fiercer his spirit rose higher, and when Eyvnid the scald greeted him with a warlike verse, he answered with another. But the midsummer heat growing hard to bear, he flung off his armor and fought with only his strong right arm for shield. The arrows had now been all shot, the spears all hurled, and the ranks met hand to hand and sword to sword, in desperate affray.
In the front rank stood the king, his golden helmet making him a shining mark for the warriors of the foe.
“Your helmet makes you a target for the Danish spears,” cried Eyvnid, and he drew a hood over it to hide its gleam. Skreyja, Harold’s uncle, who was storming onward towards the king, now lost sight of him and cried out:
“Where is the Norse king? Has he drawn back in fear? Is he of the golden helmet a craven?”
“Keep on as you are coming, if you wish to meet the Norsemen’s king,” shouted Haakon, throwing down his shield and grasping his sword with both hands, as he sprang out before them all. Skreyja bounded towards him and struck a furious blow, but it was turned aside by a Norse warrior and at the same instant Haakon’s sword cleft the foeman’s head down to the shoulders.
This kingly stroke gave new spirit to the Norsemen and they rushed with double fury upon the foe, whom the fall of their best warrior filled with fear. Back to the beach they were pressed, many being slain, many drowned, a few only, Harold among them, reaching the ships by swimming.
The Norsemen had won against fearful odds, but their king was in deadly peril. In the pursuit he had been struck in the right arm by an arrow with an oddly-shaped head, and do what they would, the flow of blood could not be stopped. It was afterwards said that Gunhild the sorceress had bewitched the arrow and sent it with orders to use it only against King Haakon.
In those days it was easy to have men believe tales like that, but, witchcraft or not, the blood still ran and the king grew weaker. As night came death seemed at hand and one of his friends offered to take his body to England, after his death, that he might be laid in Christian soil.
“Not so,” said Haakon. “Heathen are my people and I have lived among them like a heathen. See then that I am laid in the grave like a heathen.”
Thus he died, and he was buried as he wished, while all men mourned his death, even his foes; for before breathing his last he bade his men to send a ship after the sons of Gunhild; asking them to come back and rule the kingdom. He had no sons, he said, and his daughter could not take the throne.
Thus death claimed the noblest of the Norsemen, at once heathen and Christian, but in his life and deeds as in his death a great and good man.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CAROTOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA

Dr Tim Fraser SCOTLAND CHS
Reviewed by : Tammy Wise USA CHS


Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

HAROLD FAIR HAIRED FOUNDS THE KINGDOM OF NORWAY
CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR
To the far-off island of Iceland we must go for the story of the early days of Norway. In that frosty isle, not torn by war or rent by tumult, the people, sitting before their winter fires, had much time to think and write, and it is to Iceland we owe the story of the gods of the north and of the Scandinavian kings of heathen times. One of these writers, Snorri Sturlasson by name, has left us a famous book, “The Sagas of the Kings of Norway,” in which he tells of a long line of ancient kings, who were descended from the gods. Here are some of their names, Aun the Old, Ingjald Ill-Ruler, Olaf the Wood-Cutter, Halfdan Whiteleg, and Halfdan the Swarthy. There were others whom we need not name, and of these mentioned the names must suffice, for all we know of them is legend, not truth.
In those times there was no kingdom of Norway, but a number of petty provinces, ruled over by warriors who are spoken of as kings, but whose rule was not very wide. Most powerful among them was Halfdan the Swarthy, who was only a year old in 810 when his father was killed in battle.
He lived for many years, and he and his wife Ragnhild had strange dreams. The queen dreamed that a thorn which she took out of her clothes grew in her hands until one end of it took root in the ground and the other shot up into the air. It kept on growing until it was a great tree, so high that she could barely see its top. The lower part of it was blood-red, higher up it was bright green, and the spreading branches were white as snow. So widely they spread that they seemed to shade the whole country of Norway.
King Halfdan did not like it that his wife had such strange dreams and he had none. He asked a sage why this was so, and was told that if he wanted to have dreams as strange he must sleep in a pig-sty. A queer recipe for dreams, one would think, but the king tried it, and dreamed that his hair grew long and beautiful and hung in bright locks over his shoulders, some of them down to his waist, and one, the brightest and most beautiful of all, still farther down.
When he told the sage of this dream, the wise man said it meant that from him was to come a mighty race of kings, one of whom should be the greatest and most glorious of them all. This great hero, Snorri tells us, was supposed to be Olaf the Saint, who reigned two hundred years later, and under whom Christianity first flourished in Norway.
Soon after these dreams a son was born to the queen, who was named Harold. A bright, handsome lad he grew to be, wise of mind and strong of body and winning the favor of all who knew him. Many tales which we cannot believe are told of his boyhood. Here is one of them. Once when the king was seated at the Yuletide feast all the meats and the ale disappeared from the table, leaving an empty board for the monarch and his guests. There was present a Finn who was said to be a sorceror, and him the king put to the torture, to find out who had done this thing. Young Harold, displeased with his father’s act, rescued the Finn from his tormentors and went with him to the mountains.
On they went, miles and leagues away, until they came to a place where a Finnish chief was holding a great feast. Harold stayed there until spring, when he told his host that he must return to his father’s halls. Then the chief said:
“King Halfdan was very angry when I took his meat and ale from him last winter, and now I will reward you with good tidings for what you did. Your father is dead and his kingdom waits for you to inherit. And some day you will rule over all Norway.”
Harold found it to be as the Finn had said, and thus in 860, when he was only ten years old, he came to the throne. He was young to be at the head of a turbulent people and some ambitious men there were who sought to take advantage of his youth, but his uncle guardian fought for him and put them all down. Harold was now the greatest among the petty kings of Norway and a wish to be ruler of the whole land grew up in his soul.
Here comes in a story which may not be all true, but is pretty enough to tell. It is to the effect that love drove Harold to strive for the kingdom. Old Snorri tells the story, which runs this way.
King Erik of Hördaland had a fair daughter named Gyda, the fame of whose beauty reached Harold’s ears and he sent messengers to win her for himself. But the maid was proud and haughty and sent back word:
“Tell your master that I will not yield myself to any man who has only a few districts for his kingdom. Is there no king in the land who can conquer all Norway, as King Erik has conquered Sweden and King Gorm Denmark?”
This was all the answer she had for the heralds, though they pleaded for a better answer, saying that King Harold was surely great enough for any maid in the land.
“This is my answer to King Harold,” she said. “I will promise to become his wife if for my sake he shall conquer all Norway and rule it as freely as King Erik and King Gorm rule their kingdoms. Only when he has done this can he be called the king of a people.”
When the heralds returned they told the king of their ill success and advised him to take the girl by force.
“Not so,” Harold replied. “The girl has spoken well and deserves thanks instead of injury. She has put a new thought into my mind which had not come to me before. This I now solemnly vow and call God to witness, that I will not cut or comb my hair until the day when I shall have made myself king of all Norway. If I fail in this, I shall die in the attempt.”
![[Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris [Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris](https://www.heritage-history.com/books/morris/scandinavian/zpage035.gif) HOUSE OF PARLIAMENT, NORWAY |
Such is the legend of Gyda and the vow. What history tells us is that the young king set out to bring all Norway under his rule and prospered in the great enterprise. One after another, the small kings yielded to his power, and were made earls or governors under him. They collected taxes and administered justice in his name. All the land of the peasants was declared to be the property of the king, and those who had been free proprietors were now made the king’s tenants and were obliged to pay taxes if they wished to hold their lands. These changes angered many and there were frequent rebellions against the king, but he put them all down, and year after year came nearer the goal of his ambition. And his hair continued to grow uncut and uncombed, and got to be such a tangled mass that men called him Harold Lufa, or Frowsy-Head.
There was one great and proud family, the Rafnistas, who were not easily to be won. To one of them, Kveld-Ulf, or Night-Wolf, Harold sent envoys, asking him to enter his service, but the chief sent back word that he was too old to change. Then he offered Bald Grim, old Night-Wolf’s son, high honors if he would become his vassal. Bald Grim replied that he would take no honors that would give him rank over his father.
Harold grew angry at this, and was ready to use force where good words would not prevail, but in the end the old chief agreed that his second son Thorolf might be the king’s man if he saw fit. This he agreed to do, and as he was handsome, intelligent and courtly the king set much store by him.
Not only with the Norway chiefs, but with the king of Sweden, Harold had trouble. While he was busy in the south King Erik invaded the north, and Harold had to march in haste to regain his dominions. But the greatest danger in his career came in 872, when a number of chiefs combined against him and gathered a great fleet, which attacked Harold’s fleet in Halfrs-Fjord. Then came the greatest and hottest fight known to that day in Norway. Loudly the war-horns sounded and the ships were driven fiercely to the fray, Harold’s ship being in the front wherever the fight waxed hottest. Thorolf, the son of Night-Wolf, stood in its prow, fighting with viking fury, and beside him stood two of his brothers, matching him blow with blow.
Yet the opposing chiefs and their men were stout fighters and the contest long seemed doubtful, many brave and able men falling on both sides. Arrows hissed in swift flight through the air, spears hurtled after them, stones were hurled by strong hands, and those who came hand to hand fought like giants. At length Harold’s berserkers—men who fought without armor, replacing it with fury of onslaught—rushed forward and boarded the hostile ships, cutting down all who opposed them. Blood ran like water and the chieftains and their men fell or fled before this wild assault. The day was won for Harold, and with it the kingdom, for after that fatal fray none dared to stand up before him.
His vow accomplished, all Norway now his, Harold at last consented to the cutting of his hair, this being done by Ragnvald, the earl of Möre. The tangled strands being cut and the hair deftly combed, those who saw it marvelled at its beauty, and from that day the king was known as Harold the Fair-Haired. As for Gyda, the maid, the great task she set having been accomplished, she gave her hand to Harold, a splendid marriage completing the love romance of their lives.
This romance, however, is somewhat spoiled by the fact that Harold already had a wife, Aasa, the daughter of Earl Haakon, and that he afterwards married other wives. He had his faults and weaknesses, one of these being that he was not faithful to women and he was jealous of men who were growing in greatness. One of the men whom he began to fear or hate was Thorolf, who had aided him so mightily in battle and long stood highest in his favor.
Thorolf married a rich wife and grew very wealthy, living like a prince, and becoming profuse in his hospitality. He was gracious and liberal and won hosts of friends, while he aided the king greatly in collecting taxes from the Finns, who were not very willing to part with their money. Despite this service Harold grew to distrust Thorolf, or to hate him for other reasons, and the time came when this feeling led to a tragedy.
Thorolf had been made bailiff of Haalogaland, and when Harold came to this province his bailiff entertained him with a splendid feast, to which eight hundred guests were invited, three hundred of them being the king’s attendants.
Yet, through all the hilarity of the feast, Harold sat dark and brooding, much to his host’s surprise. He unbent a little at the end and seemed well pleased when Thorolf presented him with a large dragon ship, fully equipped. Yet not long afterwards he took from him his office of bailiff, and soon showed himself his deadly foe, slandering him as a pretext for attacking him on his estate.
The assailants set fire to Thorolf’s house and met him with a shower of spears when he broke out from the burning mansion. Seeing the king among them Thorolf rushed furiously towards him, cut down his banner-bearer with a sword blow, and was almost within touch of the king when he fell from his many wounds, crying: “By three steps only I failed.”
It is said that Harold himself gave the death blow, yet he looked sadly on the warrior as he lay dead at his feet, saying, as he saw a man bandaging a slight wound: “That wound Thorolf did not give. Differently did weapons bite in his hand. It is a pity that such men must die.”
This would indicate that King Harold had other reasons than appears from the narrative for the slaughter of his former friend. It must be borne in mind that he was engaged in founding a state, and had many disorderly and turbulent elements with which to deal, and that before he had ended his work he was forced to banish from the kingdom many of those who stood in his way. We do not know what secret peril to his plans led him to remove Thorolf from his path.
However that be, the killing of the chief sent his father to his bed sick with grief, and he grew content only when he heard that the king’s hand had slain him and that he had fallen on his face at his slayer’s feet. For when a dying man fell thus it was a sign that he would be avenged.
But the old man was far too weak to attack Harold openly, and was not willing to dwell in the same kingdom with him; so he, with his son Bald Grim and all his family and wealth, took ship and set sail for Iceland. But long he lingered on Norway’s coast, hoping for revenge on some of Harold’s blood, and chance threw in his way a ship containing two cousins of the king. This he attacked, killed the king’s cousins, and captured the ship. Then Bald Grim, full of exultation, sang a song of triumph on the ship’s prow, beginning with:
|
“Now is the Hersir’s vengeance On the king fulfilled; Wolf and eagle tread on Yngling’s children.” |
There were other chieftains who sought refuge abroad from Harold’s rule, men who were bitterly opposed to the new government he founded, with its system of taxation and its strict laws. They could not see why the old system of robbing and plundering within Norway’s confines should be interfered with or their other ancient privileges curtailed, and several thousand sailed away to found new homes in the Orkneys, the Hebrides, and Iceland.
One of the chief of these, Rolf, or Rollo, son of the king’s friend, Ragnvald of Möre, defied Harold’s laws and was declared an outlaw. His high birth made the king more determined to punish him, as an example to others, and no influence could win forgiveness for Rolf the Walker, as men called him, saying that he was so tall and heavy that no horse could carry him.
We must follow the outlaw in his journey, for it was one destined to lead to great events. Setting sail with a fleet and a large number of followers, he made his way to the coast of France, and fixed himself there, plundering the people for several years. Charles the Simple, king of France, finding that he could not drive the bold Norseman off, at length gave him a large province on condition that he would become a Christian, and hold his land as a vassal of the king. The province was given the name of Normandy, and from Rollo descended that sturdy race of kings one of whom conquered England in the following century. Thus the exile of Rollo led to events of world-wide importance.
When the proud Norseman was asked to kiss King Charles’s foot in token of fealty to him, he answered: “I will never bend my knee before any man, nor will I kiss any man’s foot.”
He could hardly be persuaded to let one of his men kiss the king’s foot as a proxy for him. The man chosen strode sturdily forward, seized the foot of the king, who was on horseback, and lifted it to his lips so roughly that the poor king turned a somersault from his horse. The Norsemen laughed in derision while the king’s followers stood by grim and silent.
But despite his unruliness at home, Rollo, when he got a kingdom of his own, ruled it with all the sternness of King Harold, hanging all robbers that fell into his hands, and making his kingdom so secure that the peasants could leave their tools in the fields at night without fear of loss. Five generations after him came to the throne William the Conqueror, who won himself the kingdom of England.
To go back to Harold, the builder of the kingdom of Norway, we shall only say in conclusion that he built his rule on sure foundations and kept a court of high splendor, and died without a rebel in his realm in 933, seventy-three years after he succeeded his father as ruler of a province.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CARATOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA



Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

HOW KING ROLF WON HIS WIFE
At one time very many centuries ago, we cannot say just when, for this was in the days of the early legends, there reigned over Upsala in Sweden a king named Erik. He had no son and only one daughter, but this girl was worth a dozen sons and daughters of some kings. Torborg she was named, and there were few women so wise and beautiful and few men so strong and valiant. She cared nothing for women’s work, but was the equal of any man of the court in riding, fighting with sword and shield, and other athletic sports. This troubled King Erik very much, for he thought that the princess should sit in her maiden chamber like other kings’ daughters; but she told him that when she came to succeed him on the throne she would need to know how to defend her kingdom, and now was the time for her to learn.
That she might become the better fitted to rule, she asked him to give her some province to govern, and this he did, making her queen of a third of his kingdom, and giving her an army of stout and bold warriors. Her court was held at Ulleraker in Upland, and here she would not let any one treat her as a woman, dressing always in men’s clothing and bidding her men to call her King Torborg. To fail in this would be at risk of their heads. As her fame spread abroad, there were many who came to court her, for she was at once very beautiful and the heiress of a great kingdom. But she treated all such with laughter and contempt. It is even said that she put out the eyes of some, and cut off the hands and feet of others, but this we do not like to believe. At any rate, she drove away those who troubled her too much with lance and spear. So it was plain that only a strong and bold man could win this warlike maiden for his wife.
At that time King Götrik who ruled in Gothland, a country in southern Sweden, had sent his younger son Rolf to be brought up at the court of his foster-brother King Ring of Denmark. His elder son Kettil he kept at home, but did not love him much on account of his pride and obstinacy. So it happened that when Götrik was very old and like to die, he decided that Rolf, who was very tall and strong, and very fit and able, should succeed him, though he was the younger son. All agreed to this, even Kettil, so Rolf was sent for and made king of Gothland, which he ruled with skill and valor.
One day Rolf and Kettil, who loved each other as brothers should, were talking together, and Kettil said that one thing was wanting to the glory and honor of Rolf’s rule, and that was a queen of noble birth and goodly presence.
“And whom have you in mind?” asked Rolf.
“There is Torborg, the king of Upsala’s daughter. If you can win her for wife it will be the greatest marriage in the north.”
To this advice Rolf would not listen. He had heard of how the shrewish Torborg treated her suitors, and felt that wooing her would be like taking a wild wolf by the ears. So he stayed unmarried for several years more, though Kettil often spoke of the matter, and one day said to him contemptuously:
“Many a man has a large body with little courage, and I fear you are such a one; for though you stand as a man, you do not dare to speak to a woman.”
“I will show you that I am a man,” said Rolf, very angry at these words.
He sent to Denmark for his foster-brother Ingiald, son of King Ring, and when he came the two set out with sixty armed men for the court of King Erik in Upsala.
One morning, about this time, Queen Ingerd of Upsala awoke and told King Erik of a strange dream she had dreamed. She had seen in her sleep a troop of wolves running from Gothland towards Sweden, a great lion and a little bear leading them; but these, instead of being fierce and shaggy, were smooth-haired and gentle.
“What do you think it means?” asked the king.
“I think that the lion is the ghost of a king, and that the white bear is some king’s son, the wolves being their followers. I fancy it means that Rolf of Gothland and Ingiald of Denmark are coming hither, bent on a mission of peace, since they appear so tame. Do you think that King Rolf is coming to woo our daughter, Torborg?”
“Nonsense, woman; the king of so small a realm would show great assurance to seek for wife so great a princess as our daughter.”
So when Rolf and his followers came to Upsala King Erik showed his displeasure, inviting him to his table but giving him no seat of honor at the feast. Rolf sat silent and angry at this treatment, but when Erik asked him why he had come, he told him courteously enough the reason of his visit.
“I know how fond you Goths are of a joke,” said Erik, with a laugh. “You have a way of saying one thing when you mean another. But I can guess what brings you. Gothland is little and its revenues are small and you have many people to keep and feed. Food is now scarce in Gothland, and you have come here that you may not suffer from hunger. It was a good thought for you to come to Upsala for help, and you are welcome to go about my kingdom with your men for a month; then you can return home plump and well fed.”
This jesting speech made Rolf very angry, though he said little in reply. But when the king told Queen Ingerd that evening what he had said she was much displeased.
“King Rolf may have a small kingdom,” she said, “but he has gained fame by his courage and ability, and is as powerful as many kings with a wider rule. You did not well to mock him.”
The next day Erik, thus admonished, begged Rolf’s pardon, saying that the ale had made him speak foolishly, and thus he became reconciled with his guest. As for Rolf’s desire to win his daughter, he would first have to gain Torborg’s consent, which would be no easy matter. The king promised not to interfere but would do no more.
Soon after this Rolf and his men arrived at Ulleraker, reaching there when the whole of Torborg’s court were assembled in the great hall. Fearing a hostile reception, Rolf took wary precautions. He choose twelve of his stoutest men, with himself and Ingiald at their head, to enter the court with drawn swords in their hands. If they were attacked, they were to go out backward fighting, but they were bidden to conduct themselves like men and let nothing alarm them. The others remained outside, keeping the horses in readiness to mount.
When the party entered the hall, Rolf at their head, all there were struck with his great size and noble aspect. No one assailed them and he walked up the hall, on whose high seat at the front he saw what seemed a tall and finely formed man, dressed in royal robes. Knowing that this must be the haughty princess whose hand he had come to seek, he took off his helmet, bowed low before her, and began to tell what brought him to her court.
He had scarcely begun when she stopped him. She said that he must be joking; that she knew his real errand was to get food and that this she would give him; but he must apply for it to the chief of the kitchen, not to her.
Rolf had not come so far to be laughed out of the court, and he sturdily went on with what he had to say, speaking to her as a woman, and demanding her hand in marriage. At this she changed her jesting manner, her cheeks grew red with anger, and springing up, she seized her weapons and called upon her men to lay hold upon and bind the fool that had dared affront their monarch. Shouting and confusion followed and a sharp attack was made on the intruders, but Rolf put on his helmet and bade his men to retire, which they did in good order. He walked backward through the whole hall, shield on arm and sword in hand, parrying and dealing blows, so that when he left the room, though no blade had touched him, a dozen of the courtiers lay bleeding. But being greatly overmatched, he ordered his men to mount, and they rode away unscathed.
Back to West Gothland they went and told Kettil how poorly they had fared.
“You have suffered a sore insult and affront at a woman’s hand,” said Kettil, “and my advice is that it be speedily avenged,” but Rolf replied that he was not yet ready to act.
Torborg had not taken the trouble to ask the name of her wooer, but when she learned who it was she knew very well that the matter had not reached its end and that her would-be lover would return stronger than before. As she did not want him or any man for husband she made great preparations for an attack, gathering a large body of warriors and having a wall of great strength and the finest workmanship built round the town. It was so high and thick that no battering ram could shake it, while water-cisterns were built into it to put out the fire if any one sought to burn it. From this we may judge that the wall was of wood. This done, Torborg made merry with her court, thinking that no lover in the wide world would now venture to annoy her.
She did not know the kind of man she had to deal with in King Rolf. He had fought with men and fancied he was fit to conquer a woman. The next summer he had a battle with Asmund, son of the king of Scotland, and when it was over they became friends and foster-brothers and went on viking cruises together. Next spring Rolf armed and manned six ships and, taking Kettil and Ingiald and Asmund with him, set sail for Upsala. He proposed now to woo the warrior princess in another fashion.
Queen Ingerd about this time dreamed again, her dream being the same as before, except that this time there were two white bears, and a hog which was small but spiteful, its bristles pointing forward and its mouth snarling as if ready to bite anything that came before it. And the bears did not look as gentle as before, but seemed irritated.
She interpreted this dream to mean that Rolf was coming again to avenge the affront he had received, and that the fierce hog must stand for Kettil, of whose character she had been told.
When Rolf now arrived King Erik received him with honor, and again agreed to remain his friend, no matter how stormy a courtship he might have. From Upsala he set out for Ulleraker and sent a herald to Princess Torborg, asking speech with her. She presented herself at the top of the wall, surrounded by armed men. King Rolf renewed his suit, and told her plainly that if she did not accept his proposal he had come to burn the town and slay every man within its walls.
“You shall first serve as a goatherd in West Gothland before you get any power over me and mine,” answered Torborg haughtily.
Rolf lost no time in assailing the walls, but found them stoutly defended. The Swedes within poured boiling water and hot pitch on their assailants, threw down stones and beams, and hurled spears and arrows from the wall. For fourteen days the siege continued without effect, until the Goths, weary of their hard fighting and the mockery of the defenders, began to complain and wanted to return home. The townspeople derided them by showing costly goods from the ramparts and bidding them come and take them, and ridiculed them in many other ways.
King Rolf now saw that he must take other measures. He had a cover constructed of boards and brushwood and supported by stout beams, making a strong roof which was set against the wall and defied all the boiling water and missiles of the Swedes. Under its shelter a hole was dug through the wall and soon the Goths were in the queen’s citadel.
To their surprise they found it empty. Not a soul was to be seen, but in every room they found well-cooked food and many articles of value.
“This is a fine capture,” said Kettil. “Let us enjoy ourselves and divide the spoil.”
“Not so,” said Rolf. “It is a lure to draw us off. I will not rest till I have the princess in my power.”
They sought the palace through and through, but no one was there. Finally a secret passage was discovered, leading underground, and the king entered it, the others following. They emerged in a forest where they found Torborg and all her men and where a sharp battle began. No warrior could have fought more bravely than the man-like princess, and her men stood up for her boldly, but they gradually gave way before the onset of Rolf and his tried warriors.
Rolf now bade Kettil to take Torborg prisoner, but not to wound her, saying that it would be shameful to use arms against a woman. Kettil sprang forward and gave the princess a sharp blow with the flat of his sword, reviling her at the same time with rude words. In return, Torborg gave him so hard a blow on the ear with her battle-axe that he fell prostrate, with his heels in the air.
“That is the way we treat our dogs when they bark too loud,” she said.
Kettil sprang up, burning with anger, but at the same moment Rolf rushed forward and grasped the warlike princess in his powerful arms, so that she was forced to surrender.
He told her that she was his prisoner, but that he did not wish to win a wife in the viking manner and that he would leave it to her father to judge what should be done. Taken captive in his arms, there was nothing else for her to do, and she went with him to Upsala, where King Erik was delighted at Rolf’s success. As for the warlike princess, she laid down her arms at her father’s feet, put on a woman’s garments, and seemed glad enough to have been won as a bride in so warlike a manner and by so heroic a wooer.
Soon after this the marriage took place, the festivities being the grandest the court could afford and lasting for fourteen days, after which Rolf and his followers returned home, his new queen with him. The sagas say, as we can well believe after so strenuous a wooing, that afterwards King Rolf and Queen Torborg lived a long and happy life.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CARATOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA



Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR
 Randver was a legendary Danish king. In Nordic legends, according to Sögubrot and the Lay of Hyndla, he was the son of Ráðbarðr the king of Garðaríki and Auðr the Deep-Minded, the daughter of the Danish-Swedish ruler Ivar Vidfamne. In these two sources, Auðr had Randver’s brother, Harald Wartooth, in a previous marriage.
Randver was a legendary Danish king. In Nordic legends, according to Sögubrot and the Lay of Hyndla, he was the son of Ráðbarðr the king of Garðaríki and Auðr the Deep-Minded, the daughter of the Danish-Swedish ruler Ivar Vidfamne. In these two sources, Auðr had Randver’s brother, Harald Wartooth, in a previous marriage.
One of the genealogies in Hversu Noregr Byggðist seems to say that he is the son of Hrœrekr slöngvanbaugi and the brother of Harald Wartooth. Hrœrekr was, according to Sögubrot, a Danish king on Zealand who was killed by Ivar Vidfamne.
According to Hervarar saga both Randver and Harald Wartooth were the sons of Valdar and Alfhild, the daughter of Ivar Vidfamne. This saga relates that Ivar appointed Valdar as the king of Denmark, and when Valdar died, he was succeeded by Randver. Randver married Åsa Haraldsdottir of Agder (in other sagas said to be the wife of Gudrød the Hunter of Vestfold), who gave birth to a son, Sigurd Hring. After his brother Harald had reclaimed Götaland (or Gotland depending on the manuscript), Randver fell in battle in England.
The Hervarar saga says that Randver was succeeded as Danish king by his son Sigurd Hring (probably as Harald’s viceroy). However, Sögubrot says that Harald Wartooth elevated Sigurd Hring as sub-king of Sweden and Västergötland.The Danish chronicle of Saxo Grammaticus (c. 1200) does not clearly mention Randver, but rather asserts that Hring was the son of the Swedish king Ingjald and an unnamed sister of Harald Wartooth.
The Danish scholar Gudmund Schütte drew a parallel between the pair Ráðbarðr – Randver in Langfeðgatal and the pair Rædhere – Rondhere that is mentioned in line 123 in the Anglo-Saxon poem Widsith (7th century?). Schütte’s argument was that lists of heroic figures found in Widsith were reflected in the ordering of names in some later medieval sagas and chronicles.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
SCOTTISH CLAN – IRISH CLAN – NORSE CLAN


Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci

By the end of Procopius’ Book VI on the Gothic War in Italy, he loses interest in the war and writes instead about the Heruli, who was part of Belisarius’ army. He recounts among other things a decisive battle between Heruls and Langobards, which took place north of the Danube – possibly quite far north:
Reconstruction of the Langobards’ migrations – Langobards had given name to the region around Milan, Lombardy – Paul the Deacon mentions that the Lombards came from Scandia, but elsewhere he writes that they were not so numerous, because they came from only a small island, and this does not fit with Scandia. – Wikimedia Commons.
“And when the two armies came close to one another, it so happened that the sky above the Lombards was obscured by a sort of cloud, black and very thick, but above the Eruli it was exceedingly clear. And judging by this one would have supposed that the Eruli were entering the conflict to their own harm; for there can be no more forbidding portent than this for barbarians as they go into battle. However, the Eruli gave no heed even to this, but in absolute disregard of it, they advanced against their enemy with utter contempt, estimating the outcome of the war by mere superiority of numbers. But when the battle came to close quarters, many of the Eruli perished and Rodolphus himself also perished, and the rest fled at full speed, forgetting all their courage. And since their enemy followed them up, the most of them fell on the field of battle and only a few succeeded in saving themselves.”
“When the Eruli, being defeated by the Lombards in the above-mentioned battle, migrated from their ancestral homes, some of them, as has been told by me above, made their home in the country of Illyricum, but the rest were averse to crossing the Ister River, but settled at the very extremity of the world; at any rate, these men, led by many of the royal blood, traversed all the nations of the Sclaveni one after the other, and after next crossing a large tract of barren country, they came to the Varni, as they are called. After these, they passed by the nations of the Dani, without suffering violence at the hands of the barbarians there. Coming thence to the ocean, they took to the sea, and putting in at Thule, remained there on the island.”
Procopius was Belisarius’ secretary through three wars: against the Persians in Syria, against the Vandals in Africa and against the Goths in Italy. In all three wars, Heruls had been part of the Roman army. We must believe that Procopius had a very intimate relationship with them and that he had his information from the Heruli themselves. It is assumed that he published his reports on Emperor Justinian’s wars around 550 AD in Constantinople.
It is known from the Gothic chancellor Cassiodorus’ letters that the Goths in Italy tried to create an alliance with the Heruli, Thuringi and Varni against the Franks. Since he does not mention the Saxons, that we otherwise would expect, we must believe that Varni was an early name for the Saxons. We can imagine that the Saxons originally were called Varni and later got their name from their favorite weapon, the short single-edged sword, the sax; in the same way as the Langobards originally were called Vinil, but later was named after their favorite weapon, the long ax, langobard – bard as in the Danish name for halberd, hellebard.
 |
Reconstruction of the Germanic tribes following Tacitus. He did not create any map himself, but many writers have sought to place the tribes on a map following his description. As it can be seen Jutland and North West Germany are somewhat crowded at the expense of other areas. Tacitus mentions Varini after Anglii, and that is probably an error by Tacitus, who had all information on second hand. Varini must be the Saxons. From “The Spoils of Victory. The North in the Shadow of the Roman Empire”. Edited by L. Jorgensen, B. Storgaard and L.G. Thomsen. Nationalmuseet, Copenhagen.
In that case, the Herulian travel party had followed the Rhine or more likely the Elbe, crossed “a large distance of barren land”, perhaps Luneburger Heide, then traveled through the land of the Varni that most likely was Saxony, and from there through “the nations of the Dani” – notice that they are in plural – which must have been Jutland. Then they crossed the sea and landed in Thule, which is the Scandinavian Peninsula. As they traveled through Jutland through several of the Danes’ nations, we must believe that they traveled a good distance up in Jutland, before they sailed over to Halland and Scania.
The earliest mention of Varni is by Tacitus in “Germania”, in which he wrote: “Then follows in sequence and Reudignians, Aviones and Angles and Varinians and Eudoses and Suardones and Nuithones; all defended by rivers or forests.” This means that the Varinians were neighbors to the Angles, which fits very well with the idea that they were a kind early Saxons and lived south of the “the nations of the Dani”. Alternatively, it is suggested that Varni lived at the river Warnow and the city of Warnemünde, it would then lead to that the returning Heruls sailed from northern Germany to perhaps Blekinge and Scania, and that they not – as reported – “passed by the nations of the Dani” before they “took to the sea, and putting in at Thule”.

Coin with a portrait of Odovacar issued in Ravenna in 477 AD. He has a mustache following barbaric custom and maybe hair done up in a pillow. He was in all probability a Scirii, a Gothic-speaking people, but Consularia Italica calls him King of Heruli. Consularia Italica is a collection of documents published by Theodore Mommsen in 1892. Other sources claim he was of Gothic origin. But Heruls constituted a large part of his men, and he was Rex Italia, therefore he was actually King of Heruli, though he himself was not a Herul. Moreover, Scirii was a kind of Goths, and as Odovacar was a Scirii, one can also say that he was a Goth. Thus, all statements are true. Odovacar deposed the last Western Roman emperor, Romulus Augustulus, in 476 AD. Jordanes wrote about Odovacar: “Now that Augustus was appointed emperor in Ravenna by his father Orestes, it did not last long before Odoacer, King of Torcilingi (Thuringi), invaded Italy, as leader of Sciri, Heruli and allies of various races” – Photo Wikipedia.
In Procopius’ report on the Heruls, they assure him several times that they lived in their original homeland when they fought their destiny battle against the Longobards. They did not tell Procopius that they originated from Scandia or another island, as Jordanes says. However, the term “passed the nations of the Dani, without suffering violence at the hands of the barbarians there” reveals, however, a somewhat tense relationship with the Danes, which suggests that Jordanes was right. Perhaps it was too humiliating for them to admit to Procopius that they two times had been expelled.
Following Paul the Deacon, the Rugi who lived north of the Danube opposite the Roman province Noricum, were defeated by Odoacer, who reigned in Italy. This happened 487-88 AD. He says that the victor led the Rugians away in large quantities, and the Longobards moved into the now almost uninhabited Rugiland, which must have been northern Austria, some believe Moravia. Here they were attacked by the Heruli, who, however, lost the fateful battle that followed, so that they were forced to leave their own country, as they told Procopius. This battle must most likely have taken place around the year 500 AD – and according to Paul in an area immediately north of the Danube.
As previously explained, it is likely that some Heruls were expelled from Scandinavia by Dani maybe around 200-300 AD The returning Heruls thus came back through “the nations of the Dani” 200-300 years after they had been expelled the first time.

OFFICIAL AND REGISTEREDL CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
SCOTTISH CLAN – IRISH CLAN – NORSE CLAN


GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Socie

If you think of a Viking warband, the modern image would be one of men armed mainly with swords. However when you read Old Norse literature, the predominate weapon mentioned is the spear or more often, something usually translated as a “halberd”. In the original Old Norse, however, we find a variety of intriguingly named weapons being translated to that one term.

The usual Old Norse word for spear is geirr. Another common term often used is a kesja. The saga’s also name other, now obscure varieties of blades mounted on sticks, including atgeirr, höggspjót, brynþvarar and bryntroll.
That all of these are a type of blade on a stick, something we would otherwise call a “spear”, is not in doubt. However their use and appearance in medieval literature is sufficiently different to what our notion of a spear is to warrant translators from Victorian times to use a different term, usually “halberd” or “bill”.
This is itself raises an issue, as halberds, pikes and other pole-arms developed in the later middle ages, so were anachronistic to the Viking age when the characters in the sagas are described as wielding them. So the possibility exists that these are types of weapons now lost to history.
The saga writers have a frustrating tendency not to describe these weapons, hinting that they were very familiar to the audience they were writing for. However it means the we are left to seek for clues amid the texts for what they really were.
The atgeirr is probably the most famous of these. It was the weapon of choice for Gunnar Hámundarson, the Icelandic warrior and main character of Njal’s Saga, one which he uses to devastating affect on many characters in the saga. Apart from using it as a vaulting pole to leap, Lone Ranger-like, onto his horse for a quick get away, Gunnar kills many men with his atgeir.
Compared with sword and axe, the spear was relatively cheap and effective to produce. Because of its length, it was probably the most important weapon in close combat. Together with arrows it also posed a big threat when it was thrown.
At one point in the saga Gunnar hoists an adversary impaled on the atgeirr aloft. When his enemies gang up on him and one tries to sneak onto the roof, Gunnar shoves his atgeirr out the window, catching Thorgrim in the stomach. The unfortunate man tumbles off the roof. His comrades ask him if Gunnar is at home.

“You can find that out for yourselves,” said Thorgrim; “but this I am sure of: His atgeirr is at home,” and with that he fell down dead.
Thorgrim’s last words, so typical of the black humour of the Sagas, also hint at the regard in which Gunnar’s weapon was held. Gunnar’s weapon is referred to as atgeirinn – “The atgeir”, which suggests it was a unique, special item – a magic weapon worthy of a Dungeons and Dragons quest – however atgeirrs are named in Laxdœla Saga and the Eyrbyggja Saga too. Gunnar’s was rumoured to have a life of its own, the blade ringing when it was lifted off its bracket on the wall if it was to taste blood soon.
But what was it? Geirr is simply a very old word for spear, so as Jan H. Orkisz points out, the importance must lie in the “at” part of its name. The common interpretation of “at” appears to be as “excellent” or “very” – hence perhaps “most excellent” or “best” spear. However Orkisz points out that this ultimately derives from a Latin prefix ad-, and Old Norse had a poetic use of at- to denote fight, clash or attack. Hence atgeirr would be “battle spear” or “fighting spear”. The way Gunnar and others use it in the saga point towards a heavy spear used in hand-to-hand fighting, perhaps like a heavy board spear, rather than a javelin hurled at the enemy while they are still at a distance.
The höggspjót is another weapon appearing in the sagas. Spjót is again just another word for spear. Högg is a form of the verb höggva which means “to strike, to smite”. It’s tempting to again translate this as another “battle spear”, however the verb is often used in the context of cutting down a tree or wielding an axe, so the name “Hewing spear” might be more appropriate. Some of the descriptions of its use correlate with the idea of a long, heavy blade mounted on a pole, capable of slicing through shields and the flesh and bone of the unfortunates holding them. Egil Skallagrimsson carries a höggspjót on his ill-fated meeting with Rognvald, ( CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR) the young son of King Eirik Bloodaxe ( CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR) of Norway.
Egil’s Saga also mentions another weapon, the brynþvarar and gives quite a detailed description of it. Thorolf strides into the Battle at Brunanburgh “armed like this”:
Kesju hafði hann í hendi. Fjöðrin var tveggja álna löng ok sleginn fram broddr ferstrendr, en upp var fjöðrin breið, falrinn bæði langr ok digr, skaftit var eigi hæra en taka mátti hendi til fals ok furðuliga digrt. Járnteinn var í falnum ok skaftit allt járnvafit. Þau spjót váru kölluð brynþvarar.
“He had a kesja [spear] in his hand…the feather-formed blade was two ells long, ending in a four-edged spike; the blade was broad above, the socket both long and thick. The shaft stood just high enough for the hand to grasp the socket, and was remarkably thick. The socket was fitted with an iron prong on the shaft, which was also wound round with iron. Such spears [spjót] were called brynþvarar.”
 In the middle, a large bayonet-spear from the Gournay-sur-Aronde sanctuary in northern France.
In the middle, a large bayonet-spear from the Gournay-sur-Aronde sanctuary in northern France.
An ell was the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger, about 18 inches. Therefore at 2 ells the blade of this weapon was about 36 inches long, or 3 feet, which is impressive for a spear. It would seem that this weapon has a short, thick shaft, and the impression is some sort of short implement, mostly blade, specifically designed for piercing mail. Though perhaps not very short. Later in the battle, gripped by berserker rage, Thorolf does a Vlad Tepeș. He lunges at an enemy Jarl’s chest with the brynþvarar, “driving it right through mail-coat and body, so that it came out at the shoulders; and he lifted him up on the halberd over his head, and planted the butt-end in the ground”. Ouch.
The Old Norse word spjót (spear) is related to the Old French word espiet which means “the spy, one who stares from a long distance”.
The bryn part of the name refers to the brynja, the Old Norse name for a mail shirt. My Old Norse dictionary lists þvari as meaning a “bolt or spear”. In other words this was a special type of spear, specifically designed for piercing mail. Possibly closely related to the brynþvarar we have the bryntroll. We’ve already covered that bryn means mail and troll speaks for itself. It’s a monster, an enemy, a creature that destroys, so the weapon is a troll or moster for mail shirts. The effectiveness of medieval spears against mail is demonstrated in this video:
There was also the rather horrible sounding “Hooked Spear”, the Krókspjót, a weapon so nasty a law was passed forbidding its use.
So at the end of the day these all appear to be varieties of spear. That they were not swords is underlined by the way in many sagas the hero is specifically mentioned as having a sword as well, either at his belt or, in Egil’s case, tied to his wrist.
That spears would be important to pagan Scandinavians should not be that surprising. The spear was the weapon sacred to the God Odin. Battles were traditionally started by one side hurling a spear over their opponents and yelling “Óðinn á yðr alla” – Odin owns you all. Being transfixed by a spear while also being hung appears to have been the way to sacrifice a human being to Odin.
Another other possibility is that these are all anachronisms. Medieval saga writers could have been giving impressive modern (for them) weapons to their heroes to make them look cool to a contemporary audience, or to use terms they were familiar with.


TODD HODKINSON
http://timhodkinson.blogspot.com/2019/09/mail-trolls-and-atgeirs-mysterious.html?m=1
Reviewed by Tammy Wise CHS- CHAIRMAN – Indiana USA
CLAN SEANACHAIDHI
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST

GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society
References:

The weapons found at Viking sites tend to be swords, axes, spears and bows – warriors were buried with their weapons. Interestingly, we have less evidence from Denmark because their earlier adoption of Christianity stopped this practice, which continued for a longer period in Sweden and Norway.
The Sword
Viking swords were long, straight and double-edged (over 2,000 found in Scandinavia) Viking swords were not particularly sharp at the end as some varieties were, as they were used primarily for hacking and slashing, not for stabbing.

There were local variants of the longsword – the long-sax which was around 3 feet long and single edged.
Swords were very expensive and so poorer freemen would have an axe or spear. However, raiding was so lucrative for the Vikings that after one raid, anyone would have enough to afford their own sword. As such, most raiders in a Viking warband would carry their own sword. The wealth and status was then demonstrated not by owning a sword, but by how decorated it was – different metals inlaid on the pommel for example.
The Axe

Aswell as swords, axes were decorated to reflect the status of its owner. As with most romanticised periods, there are some embellishments in popular culture and the huge two handed, double or wide bladed axe was not a common weapon through much of the period and was a specialised fighting implement. By the end of the Viking era though, they were a distinguishing mark of the Huscarls who would use them to fight against the mail-clad soldiers of their adversaries.
The Spear
Tim Hodkinson, author of Odin’s Game shared this brilliant blog post he wrote on the use of spears and polearms, check it out here!
The Bow
The bow was used by Vikings fairly commonly, though you don’t hear as much about them with the focus on their axes. Vikings utilised both long and shortbows, and they are mentioned in the sagas. If you look to the right on the below image (of the Bayeux Tapestry) you can see the anglo-saxon shieldwall, flanked by a bowman. This is generally the technique used by the Vikings too, as supporting troops to back up the shield wall. An arrow was often fired over the heads of the enemy troops on Viking battles to signify the start of the battle.


OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
SCOTTISH CLAN – IRISH CLAN – NORSE CLAN

Reviewed by Tammy Wise CHS – Indiana USA
CLAN SEANACHAIDHI
CLAN CARRUTHERS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST


GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society