
ERIC BLOODAXE AND EGIL THE ICELANDER
CARRUTHERS ANCESTOR
 In the year 900 Harold the Fair-Haired, the famous monarch who made a kingdom of Norway, passed a law which was to work mischief for centuries to come. Erik, his favorite son, was named overlord of the kingdom, but with the proviso that his other sons should bear the kingly title and rule over provinces, while the sons of his daughters were to be made earls. Had the wise Harold dreamed of the trouble this unwise law was to make he would have cut off his right hand before signing it. It was to give rise to endless rebellions and civil wars which filled the kingdom with ruin and slaughter for many reigns and at last led to its overthrow and long disappearance from among the separate nations of the earth.
In the year 900 Harold the Fair-Haired, the famous monarch who made a kingdom of Norway, passed a law which was to work mischief for centuries to come. Erik, his favorite son, was named overlord of the kingdom, but with the proviso that his other sons should bear the kingly title and rule over provinces, while the sons of his daughters were to be made earls. Had the wise Harold dreamed of the trouble this unwise law was to make he would have cut off his right hand before signing it. It was to give rise to endless rebellions and civil wars which filled the kingdom with ruin and slaughter for many reigns and at last led to its overthrow and long disappearance from among the separate nations of the earth.
A bold and daring prince was Erik, with the old viking blood in his veins. When only twelve years of age his father gave him five ships, each with a sturdy crew of Norsemen, and sent him out to ravage the southern lands, in the manner of the sea-kings of those days. Many were the perilous exploits of the young viking admiral and when he came back to his father’s halls and told him of his daring deeds, the old king listened with delight. So fierce and fatal were many of his fights that he won the name of Blood-Axe, but for this his father loved him all the more and chose him to be his successor on the throne.
Before his father died Erik had shown what was in him, by attacking and killing two of his brothers. But despite all that, when the old king was eighty years of age he led Erik to the throne and named him as his successor. Three years later Harold died and Norway fell under the young sea-king’s hand—a brave, handsome, stately ruler; but haughty, cruel, and pitiless in his wrath, and with the old viking wildness in his blood.
He had married a woman whom men called a witch—cruel, treacherous, loving money and power, and with such influence over him that she killed all the good in his soul and spurred him on to evil deeds.
Strange stories are told of the wicked Queen Gunhild. It was said that she had been sent to Finland to learn the arts of sorcery, in which the Finns of those days were well versed. Here Erik met her in one of his wanderings, and was taken captive by her bold beauty. She dwelt with two sorcerers, both bent on marrying her, while she would have neither of them. Prince Erik was a suitor more to her liking and she hid him in her tent, begging him to rescue her from her troublesome lovers.
This was no easy task, for sorcerers have arts of their own, but Erik proved equal to it, cut his way through all the difficulties in his path and carried Gunhild away to his ships, where he made her his wife. In her he had wed a dragon of mischief, as his people were to learn.
She was of small size but of wonderful beauty, and with sly, insinuating ways that fitted her well to gain the mastery over strong men. But all her arts were used for evil, and she won the hatred of the people by speaking words of ill counsel in her husband’s ears. The treachery and violence he showed were said to be the work of Gunhild the witch, and the nobles and people soon grew to hate Erik Blood-Axe and his cruel wife, and often broke out in rebellion against them.
His brothers, who had been made kings of provinces, were not ready to submit to his harsh rule, and barely was old King Harold dead before Halfdan the Swarthy—who bore the name of his grandfather—claimed to be monarch in Tröndelag, and Olaf, another brother, in Viken. Death came suddenly to Halfdan—men whispered that he had been poisoned by the queen—but his brother Sigfrid took his place and soon the flame of rebellion rose north and south. Erik proved equal to the difficulty. Sigfrid and Olaf were in Tunsberg, where they had met to lay plans to join their forces, when Erik, whose spies told him of their movements, took the town by surprise and killed them both.
Thus, so far, Erik Blood-Axe was triumphant. He had killed four of his brothers—men said five—and every one thought that Gunhild would not be content until all King Harold’s brood except her own husband were in the grave.
Trouble next came from a region far away, the frost-king’s land of Iceland in the northern seas, which had been settled from Norway in the early reign of Harold the Fair-Haired, some sixty years before. Here lived a handsome and noble man named Thorolf, who had met Erik in his viking days. He was the son of the stern old Icelander Bald Grim, and nephew of the noble Thorolf who had been basely slain by King Harold.
Bald Grim hated Harold and all his race, but Thorolf grew to admire Erik for his daring and made him a present of a large and beautiful ship. Thus Erik became his friend, and when Thorolf came to Norway the young prince begged his father to let him dwell there in peace. When he at length went home to Iceland he took with him an axe with a richly carved handle, which Erik had sent as a present to his father.
Old Bald Grim was not the man to be bought over by a present. The hate he felt for Harold he transferred to his son, and when Thorolf set sail again for Norway his father bade him take back the axe to the king and sang an insulting song which he bade him repeat to Erik. Thorolf did not like his errand. He thought it best to let the blood-feud die, so he threw the axe into the sea and when he met the king gave him his father’s thanks for the fine gift. If Thorolf had had his way the trouble would have been at an end, but with him came Egil, his younger brother, a man of different character.
Stern old Bald Grim seemed born again in his son Egil. A man of great size, swarthy face, harsh of aspect, and of fierce temper, in him was the old, tameless spirit of the Norse sea-kings, turbulent, passionate, owning no man master, he bent his strong soul to no man’s rule. Rash and adventurous, he had a long and stormy career, while nature had endowed him with a rich gift of song, which added to his fame. Such was the type of men who in those days made all Europe tremble before the Norsemen’s wrath, and won dominion for the viking warriors in many lands.
Thorold when in Norway before had gained powerful friends in the great nobles, Thore Herse and Björn the Yeoman. On this visit the brothers became Thore’s guests, and Egil and Arinbjörn, Thore’s son, became warm friends. The young Icelander’s hot temper soon brewed trouble. Sickness kept him from going with Thorolf to the house of Björn the Yeoman, whose daughter, Aasgard, he was to marry; but he soon got well and went on a visit to Baard, a steward of the king. As fortune decreed he met there King Erik and Queen Gunhild.
Egil was not the man to play the courtier and his hot blood was under little control. When Baard neglected him in favor of his royal visitor, he broke into such a rage that the queen, to quiet him, tried one of her underhand arts. She bade Baard to mix sleeping herbs with his beer.
Suspecting treachery from the taste of the beer Egil flung his flagon to the floor, struck Baard dead in his fury, and, fleeing for his life, swam to an island in the neighboring stream. When men were sent to search the island and capture him he killed some of them, seized their boat, and made his escape.
King Erik was furious, but Thore Herse got him to accept a money payment for Baard’s death—as was then the custom of the land—and he agreed to let Egil dwell in Norway unharmed.
This was not to the queen’s liking. She was fond of Baard and was deeply incensed at Egil for his murderous act, and she stormed at the king for his mildness of temper till he broke out:
“You are forever egging me on to acts of violence; but now you must hold your peace, for I have given my kingly word and cannot break it.”
Gunhild, thus repulsed, sought other means of revenge. A great feast of sacrifice to the old heathen gods was to be held at the temple of Gaule, and at her instigation her brother, Eyvind Skreyja, agreed to kill one of Bald Grim’s sons. Finding no opportunity for this, he killed one of Thorolf’s men, for which act Erik outlawed him.
The remainder of the story of Egil’s career is largely that of a viking, that is, a piratical rover, bent on spoil and plunder and the harrying of sea-coast lands. With Thorolf he took to the sea and cruised about in quest of wealth and glory, finally landing in England and fighting in a great battle under the banner of King Athelstan. He made his mark here, but Thorolf was slain, so Egil went back to Norway, married his brother’s widow, and sailed for his old home in Iceland, which he had not seen for twelve years.
Iceland was too quiet a land to hold the stirring sea-king long and news from Norway soon made him take ship again. Björn the Yeoman, his wife’s father, had died, and Queen Gunhild had given his estate to Berg-Anund, one of her favorites. Storming with rage, he reached Norway and hotly pleaded his claim to the estate before the assembly or thing at Gula, Erik and Gunhild being present. He failed in his purpose, the thing breaking up in disorder; and Egil, probably finding Norway too hot to hold him, went back to Iceland.
If King Erik now fancied he was rid of the turbulent Icelander he was mistaken. Rankling with a sense of injury and borne onward by his impetuous temper, Egil was soon in Norway again, sought the Björn estate, surprised and killed Berg-Anund, and went so far in his daring as to kill Ragnvald, the king’s son, who was visiting Berg. Carried to extremes by his unruly temper he raised what was called a shame-pole, or pole of dishonor, on a cliff top, to the king and queen. On it he thrust the head of a dead horse, crying out:
“I turn this dishonor against all the land-spirits of this land, that they may all stray bewildered and none of them find his home until they have driven King Erik and Queen Gunhild out of this land.”
This message of defiance he cut in runes—the letters of the Northland—into the pole, that all might read it, and then sailed back to Iceland.
Egil had not long to wait for his curse to take effect, for Erik’s reign was soon threatened from a new source. He had not killed all his brothers. In the old days of King Harold, when near seventy years old, he had married a new wife, who bore him a son whom he named Haakon,—destined in later life to reign with the popular title of Haakon the Good. This boy, perhaps for his safety, had been sent to England and given over to King Athelstan, who brought him up almost as his own son.
Erik had been four years on the throne when Haakon came back to Norway, a handsome, noble youth, kind of heart and gentle in disposition, and on all sides hailed with joy, for Erik and his evil-minded wife had not won the love of the people. Great nobles and many of the people gathered around Haakon, men saying that he was like King Harold come back again, gentler and nobler than of old and with all his old stately beauty and charm.
The next year he was crowned king. Erik tried to raise an army, but none of the people were willing to fight for him, and he was forced to flee with his wife and children. Only a few of his old friends went with him, but among them was Arinbjörn, Egil’s former friend.
Sudden had been King Erik’s fall. Lately lord of a kingdom, he had now not a foot of land he could call his own, and he sailed about as a sea-robber, landing and plundering in Scotland and England. At length, to rid himself of this stinging hornet of the seas, King Athelstan made him lord of a province in Northumberland, with the promise that he would fight for it against other vikings like himself. He was also required to be baptized and become a Christian.
Meanwhile Egil dwelt in Iceland, but in bitter discontent. He roamed about the strand, looking for sails at sea and seeming to care little for his wife and children. Men said that Gunhild had bewitched him, but more likely it was his own unquiet spirit. At any rate the time came when he could bear a quiet life no longer and he took ship and sailed away to the south.
Misfortune now went with him. A storm drove his ship ashore on the English coast at the mouth of the Humber, the ship being lost but he and his thirty men reaching shore. Inquiring in whose land he was, people told him that Erik Blood-Axe ruled that region.
Egil’s case was a desperate one. He was in the domain of his deadly foe, with little hope of escape. With his usual impetuous spirit, he made no attempt to flee, but rode boldly into York, where he found his old friend Arinbjörn. With him he went straight to Erik, like the reckless fellow he was.
“What do you expect from me?” asked Erik. “You deserve nothing but death at my hands.”
“Death let it be, then,” said the bold viking, in his reckless manner.
Gunhild on seeing him was eager for his blood. She had hated him so long that she hotly demanded that he should be killed on the spot. Erik, less bloodthirsty, gave him his life for one night more, and Arinbjörn begged him to spend the night in composing a song in Erik’s honor, hoping that in this way he might win his life.
Egil promised to do so and his friend brought him food and drink, bidding him do his best. Anxious to know how he was progressing Arinbjörn visited him in the night.
“How goes the song?” he asked.
“Not a line of it is ready,” answered Egil. “A swallow has been sitting in the window all the night, screaming and disturbing me, and do what I would I could not drive it away.”
At that Arinbjörn darted into the hall, where he saw in the dim light a woman running hastily away. Going back he found that the swallow had flown. He was sure now that Queen Gunhild had changed herself into a swallow by sorcery, and for the remainder of the night he kept watch outside that the bird should not return. When morning broke he found that Egil had finished his song.
Determined to save his friend’s life if he could, he armed himself and his men and went with Egil to the palace of the king, where he asked Erik for Egil’s life as a reward for his devotion to him when others had deserted him.
Erik made no reply, and then Arinbjörn cried out:
“This I will say. Egil shall not die while I or one of my men remain alive.”
“Egil has well deserved death,” replied Erik, “but I cannot buy his death at that price.”
As he stopped speaking Egil began to sing, chanting his ode in tones that rang loudly through the hall. Famed as a poet, his death song was one of the best he had ever composed, and it praised Erik’s valor in all the full, wild strains of the northern verse.
Erik heard the song through with unmoved face. When it was done he said:
“Your song is a noble one, and your friend’s demand for your life is nobler still. Nor can I be the dastard to kill a man who puts himself of his own will into my hands. You shall depart unharmed. But do not think that I or my sons forgive you, and from the moment you leave this hall never come again under my eyes or the eyes of my sons.”
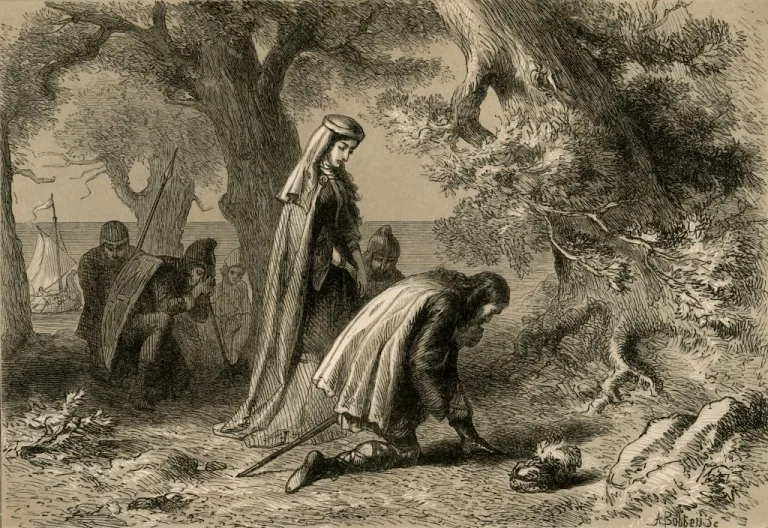
Egil thus won his life by his song, which became known as the “Ransom of the Head.” Another of his songs, called “The Loss of the Son,” is held to be the most beautiful in all the literature of Iceland. He afterwards lived long and had many more adventures, and in the end died in his bed in Iceland when he was over ninety years of age. Erik died in battle many years earlier, and Gunhild then went to Denmark with her sons. She was to make more trouble for Norway before she died.

OFFICIAL AND OLDEST SCOTTISH CLAN CARRUTHERS
SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
MERITED TO CHIEF CAROTOCUS 10AD
PRESENT CHIEF : PAT E CARROTHERS USA

CHARLES MORRIS
TAMMY WISE CHS USA
CLAN CARRUTHERS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST


Preserving Our Past, Recording Our Present, Informing Our Future
Ancient and Honorable Clan Carruthers
clancarruthers1@gmail.com

You can find us on our main facebook pages at :
SILVER WINGS-https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClanLLC/
GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
COPPER WINGS https://www.facebook.com/ClanCarruthers1/
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Soci
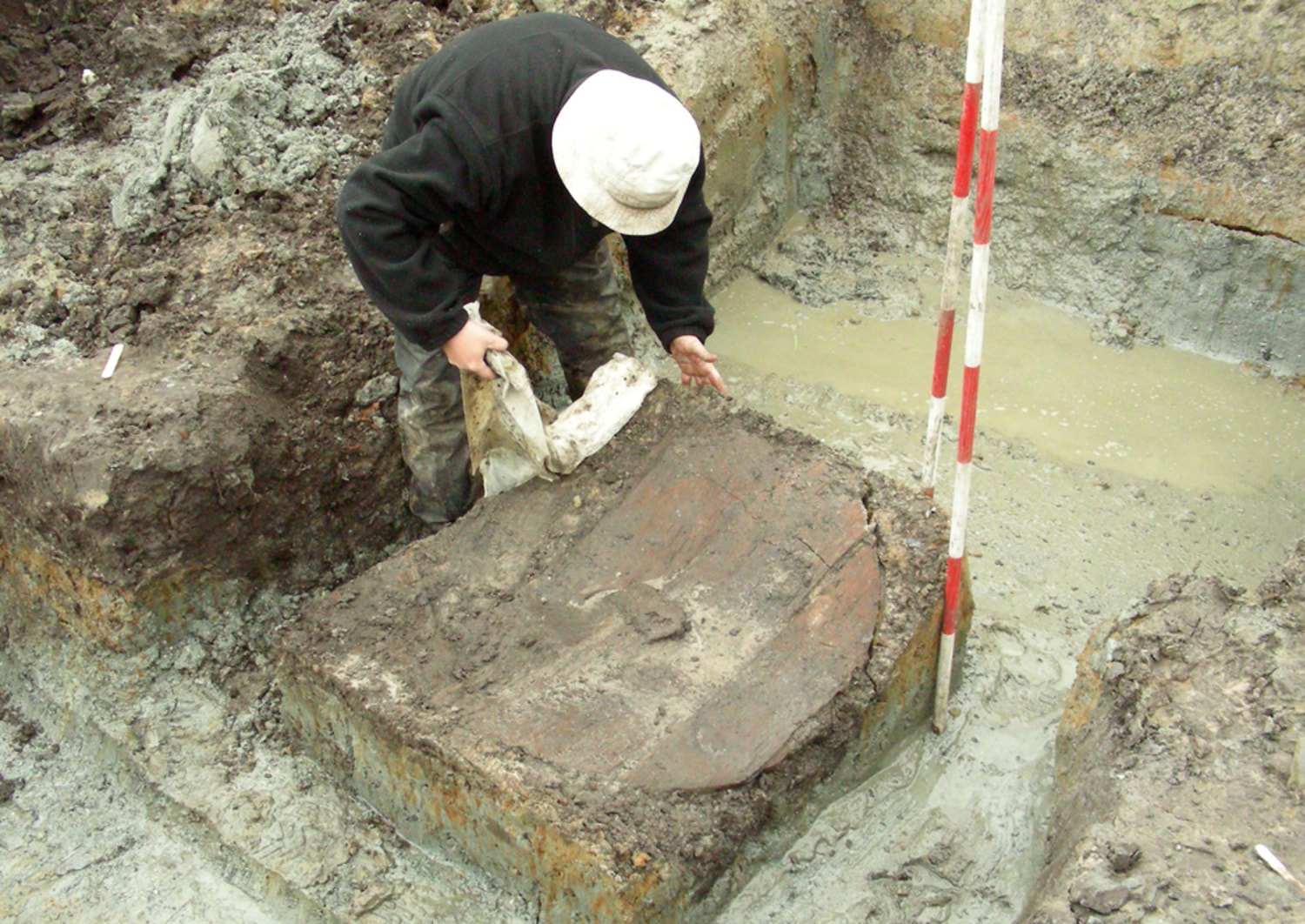
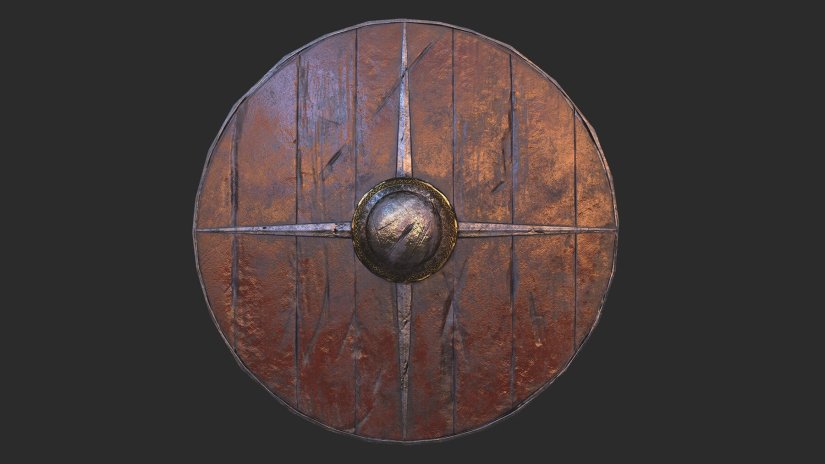













 In the year 900 Harold the Fair-Haired, the famous monarch who made a kingdom of Norway, passed a law which was to work mischief for centuries to come. Erik, his favorite son, was named overlord of the kingdom, but with the proviso that his other sons should bear the kingly title and rule over provinces, while the sons of his daughters were to be made earls. Had the wise Harold dreamed of the trouble this unwise law was to make he would have cut off his right hand before signing it. It was to give rise to endless rebellions and civil wars which filled the kingdom with ruin and slaughter for many reigns and at last led to its overthrow and long disappearance from among the separate nations of the earth.
In the year 900 Harold the Fair-Haired, the famous monarch who made a kingdom of Norway, passed a law which was to work mischief for centuries to come. Erik, his favorite son, was named overlord of the kingdom, but with the proviso that his other sons should bear the kingly title and rule over provinces, while the sons of his daughters were to be made earls. Had the wise Harold dreamed of the trouble this unwise law was to make he would have cut off his right hand before signing it. It was to give rise to endless rebellions and civil wars which filled the kingdom with ruin and slaughter for many reigns and at last led to its overthrow and long disappearance from among the separate nations of the earth.![[Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris [Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris](https://www.heritage-history.com/books/morris/scandinavian/zpage050.gif)

![[Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris [Illustration] from Historical Tales - Scandinavian by Charles Morris](https://www.heritage-history.com/books/morris/scandinavian/zpage035.gif)


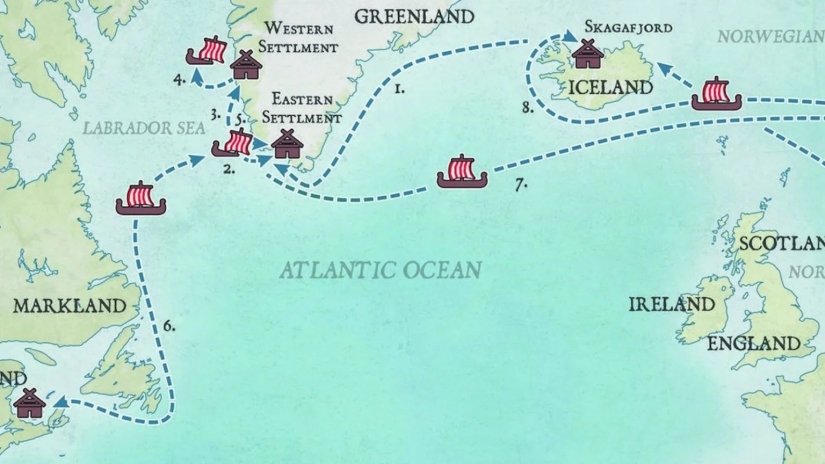

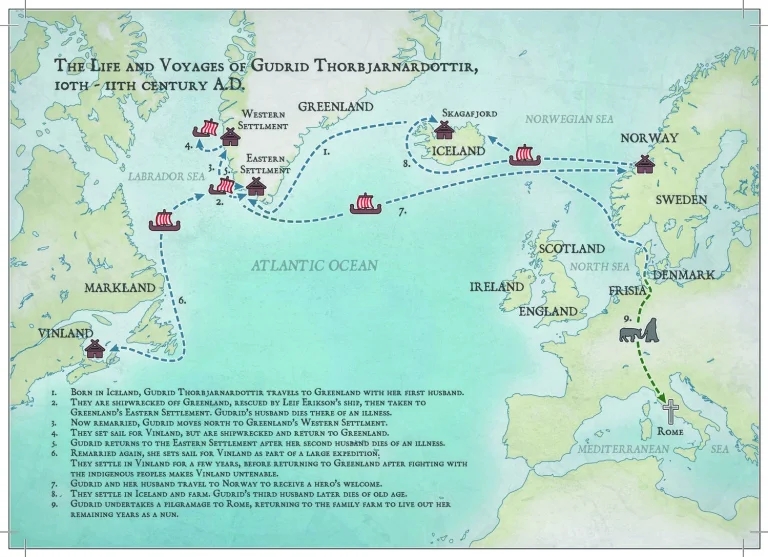

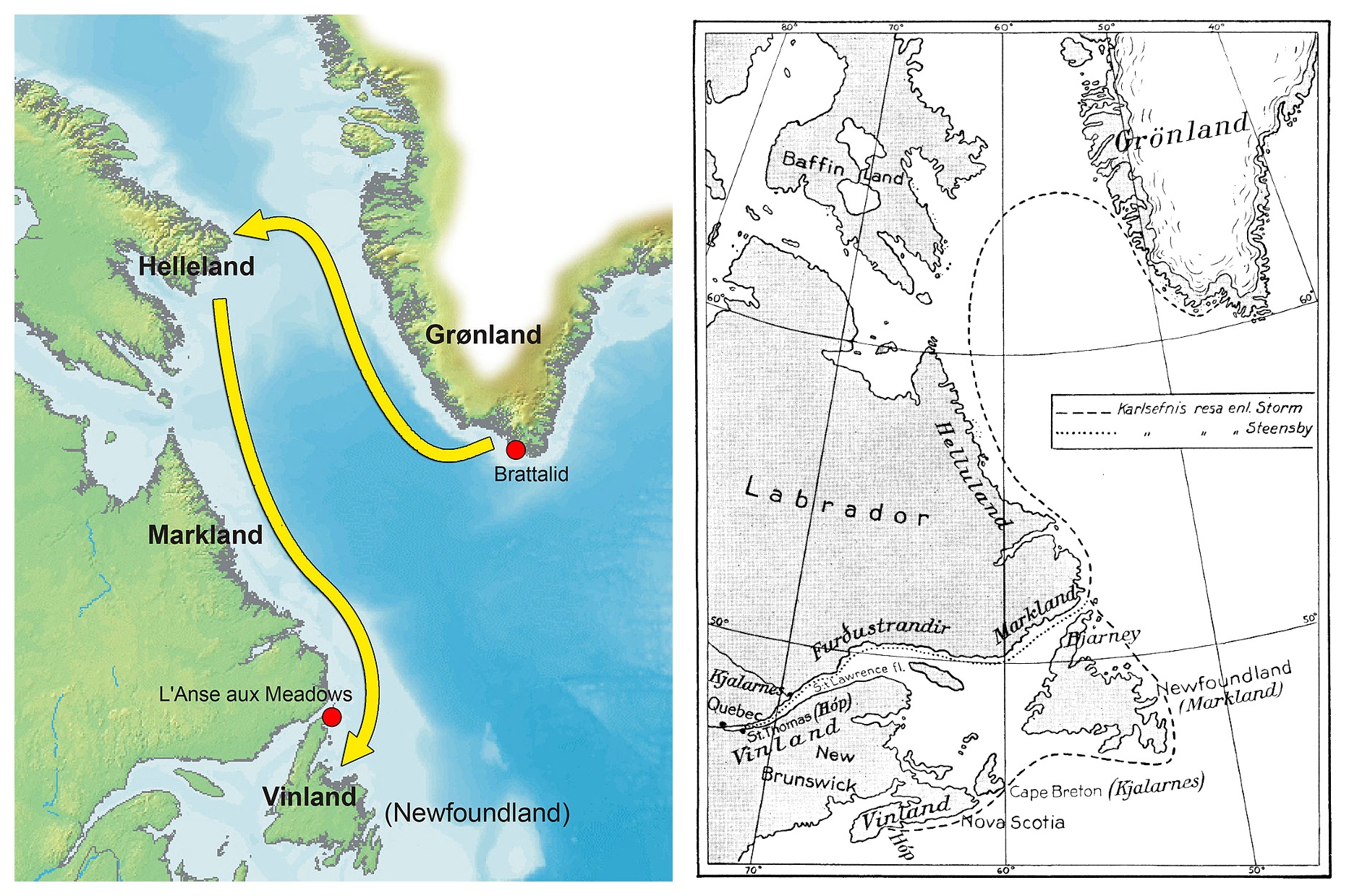










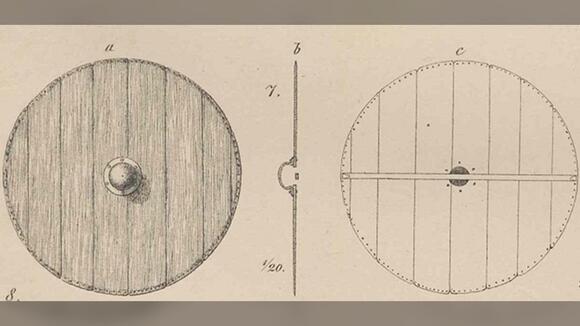
 Randver was a legendary Danish king. In Nordic legends, according to Sögubrot and the Lay of Hyndla, he was the son of Ráðbarðr the king of Garðaríki and Auðr the Deep-Minded, the daughter of the Danish-Swedish ruler Ivar Vidfamne. In these two sources, Auðr had Randver’s brother, Harald Wartooth, in a previous marriage.
Randver was a legendary Danish king. In Nordic legends, according to Sögubrot and the Lay of Hyndla, he was the son of Ráðbarðr the king of Garðaríki and Auðr the Deep-Minded, the daughter of the Danish-Swedish ruler Ivar Vidfamne. In these two sources, Auðr had Randver’s brother, Harald Wartooth, in a previous marriage.
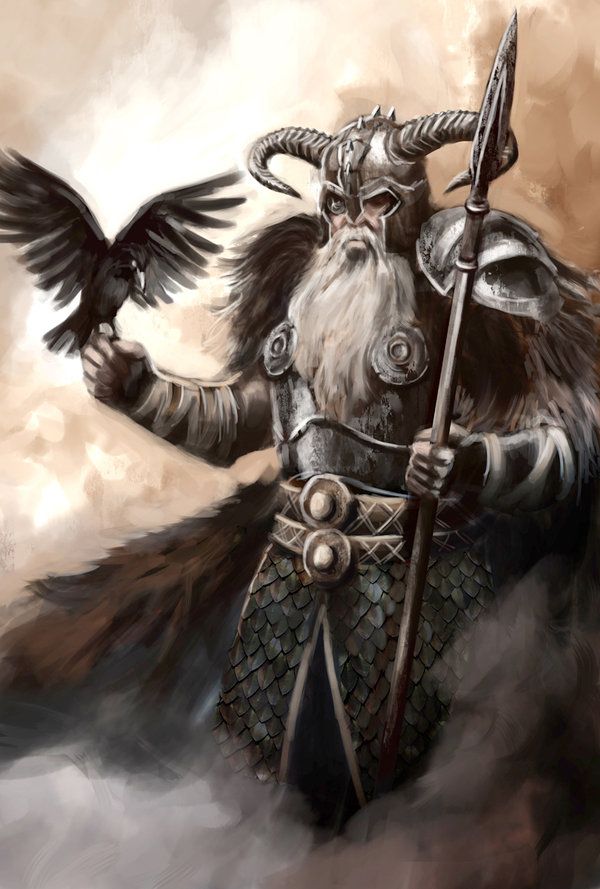


 There are many other interesting legends in the Norse sagas, such as Thor conquering a serpent- monster, while dying in the process. This was prophesied of Israel’s Messiah in GENESIS 3:15, who conquered the serpent’s seed by his own death. Other Norse religious traditions come from the Old Testament, as well. As an example, Odin is referred to as “the law-giver.” This is a title our heavenly father, Yahveh, could well claim, who gave Moses upon Mount Sinai the laws for the nation.
There are many other interesting legends in the Norse sagas, such as Thor conquering a serpent- monster, while dying in the process. This was prophesied of Israel’s Messiah in GENESIS 3:15, who conquered the serpent’s seed by his own death. Other Norse religious traditions come from the Old Testament, as well. As an example, Odin is referred to as “the law-giver.” This is a title our heavenly father, Yahveh, could well claim, who gave Moses upon Mount Sinai the laws for the nation.







