
AN ISLAND IN THE MIDDLE OF AN ISLAND- GOTLAND/GUTLAND
On Cult, Law s and Authority in Viking Age
** Our norse ancestors came from the Island of Gotland, east of Sweden. They were considered Christians from the earliest times. Please notice the acceptance of monastery’s, meeting places on the west coast of Scotland, and the fact that they had Clans and used the term Chieftain . Some will say that their are only clans in Scotland, and we know that is not truthful. ***
The present-day small village of Roma on Gotland in the Baltic Sea was the
physical and symbolic centre of the island in the Iron Age and into Medieval
times (Fig. 1). The Cistercian monastery and the meeting place of the island’s
assembly, the all-thing, two well-known features of medieval Roma, have often
been taken as indications of an egalitarian and non-stratified society on Gotland during the Viking Age and Middle Ages. It is here proposed, however,
that an older Iron Age cult site at Roma eventually came under the control of
a chieftain or major landowner who introduced Christianity, founded a monastery and inaugurated the thing in Roma in Viking or early medieval times,
just as his equals did elsewhere in Scandinavia. While the later medieval thing
was probably located near the monastery, an alternative site is suggested for
the older all-thing.
T he A ll -thin g of Gotland
In Medieval times (i.e. from c. 1100 onwards in local terms) Gotland was organised into 20 thing districts. These legal entities are mentioned in the Guta
Lagh (Gotlandic Law) and Guta Saga (printed edition Gannholm 1984), which
were written down at the beginning of the 13th century (but may contain older
strata, see Kyhlberg 1991). It is not certain whether the things were prehistoric
or belonged to an early medieval re-organisation of the island (Steffen 1943,
pp. 3 ff, 48 f; Hyenstrand 1989, pp. 15f , 108 ff; Rönnby 1995, p. 103),

but they served as means of organizing both societal relations and the physical space.
Lag means ‘law’, but was also used for the community of people who lived by
a given law, and for the physical area in which this community lived (Gurevich
1985, p. 157; Brink 2002, p. 99). As the judicial entities in that sense also constituted social and territorial boundaries, they thus defined much of the human movement that took place within the local society
The all-thing of Gotland, the island’s central assembly and supreme legal
instance, is of particular interest since it has been suggested (notably by Yrwing 1940, 1978) that its existence points to an egalitarian society of free farmers on Gotland during the Viking Age and Middle Ages.
This picture of the internal organisation of the island has been questioned on several occasions (e.g. Carlsson 1983; Hyenstrand 1989; Rönnby 1995), but it is still common and
is continuously being communicated to the public. The existence of a central
assembly on the island is mentioned in the Guta Lagh and Guta Saga (e.g. GL
§31, GS §9), and it is also likely by analogy with the medieval organization of
other Scandinavian-dominated areas such as Iceland. The image of Gotland as
an egalitarian farming and trading society nevertheless needs to be called into
question once more.
The area of Roma in the centre of the island was first named as the site of
the Gotlandic all-thing assemblies in the 1401 translation of the Guta Lagh
into German: “gutnaldhing das ist czu Rume” (Pernler 1977, p. 61; Yrwing 1978,
p. 80), while according to taxation records for 1699, some of the land around
the monastery of Roma may have belonged to several things (Östergren 1990,
2004) (Fig. 2). That this was the place where the Medieval all-thing gathered
might also be indicated by the name of the Cistercian monastery founded
there in 1164, Sancta Marie de Guthnalia, as suggested by Lindström (1895).
In his interpretation, Guthnalia could be a Latinized form of *gutnalþing, the
all-thing of the Gutar (Gotlanders), so that the name of the monastery was
derived from the all-thing itself, which may indeed have initiated the foundation of the monastery (Lindström 1895, p. 170 ff ). This suggestion and interpretation could imply that the all-thing took an active interest in the introduction of Christianity to Gotland, and thus may bear witness to the democratic character of early medieval Gotlandic society.
The endowment of land for the monastery could have been made out of land held in common by the Gotlanders and thus controlled by the all-thing (Östergren 2004, p. 44).
It should be remembered, however, that Christianization and the foundation of churches and monasteries were in all other cases initiated and dominated by individuals, normally major landowners or petty kings. The interpretation is thus based on a pre-supposed difference between Gotland and the rest of Scandinavia, namely the existence of a particularly egalitarian society on Gotland. Since this hypothesis or presupposition relies to an extent on the fact that it is used to explain, we are here dealing with a classic example of a circular argument. Luckily, archaeology can provide some more input that should be taken into consideration when discussing this matter.
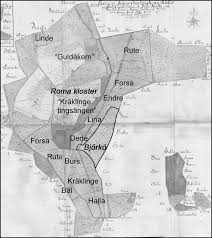
Guldåkern and Kräklige Tingsäng
The 1699 taxation map shows several plots of land with names referring to
things surrounding the monastery of Roma (Fig. 4), and Östergren suggests
that this was where the representatives attending the thing slept and kept their
animals during the meetings. Thus the area around the Roma monastery may
have been land held in common, where the different things held rights over
certain areas. In order to be at the centre of these dwelling places, the all-thing
itself must have assembled within the area of the later monastery (Östergren
1990, 2004, p. 40 ff ).
About 600 m northeast of the monastery lies the Guldåkern (the ‘Golden
Field’, named after three solidi coins found there in 1848, Fig. 2). This area, c. 200 x 300 m in size, was investigated with metal detectors in 1990 and was interpreted as a Viking Age trading place on the basis of finds of silver fragments, silver coins and weights, most of the material being from the 10th century AD.
The adjacent Kräklinge tingsängen (meadow of the Kräklinge thing)
was investigated on the same occasion and yielded silver coins, melted silver
and bronze, fragments of bronze jewellery and a casting cone, indicating metalworking at the site, and was considered to be a farmstead from the Vendel
or Viking period (Östergren 1992, p. 42 f ). Roman denarii were found at both
sites, indicating that they were connected in terms of their use during the period prior to the Vendel and Viking ages (all the Roman coins probably ended
up there during the fourth century AD). Unfortunately, the area was much
disturbed during the Second World War and it is thus difficult to say exactly
how and where the artefacts were initially deposited.
Guldåkern, Kräklinge tingsängen, and the other plots with thing names, are
all interesting sites, but neither has been suggested as the actual location of the
thing itself. The thing was not the scene of either trade or metalworking, nor
did people live there. It has been suggested that the Vendel and Viking Age
material found on Guldåkern and Kräklinge tingsängen results from the fines
and fees paid and exchanged during negotiations at the thing (Domeij 2000, p.
36 f ). If this is so, it would be the most tangible proof so far for a pre-medieval
thing actually having been located in the area.
The central location of the monastery within the semi-circle of properties
named after things may be a result of the monastery having been founded on
land held in common, and would thus indicate that this land was given to the
Cistercians by the things in 1164. But the distribution of these properties may
just as well result from their being secondary to the monastery, and demonstrate
that the monastery is the older feature and the localizing factor.
T he G u tnal þ in g
The word Gutnalia in the name of the Cistercian monastery at Roma first
appeared in written sources in the 13th century and was subsequently used
on the seals of the monastery and its abbot (Ortved 1933, p. 305), so that the
place-names Roma and Gutnalia are used interchangeably in the documents
(Lindström 1895, p. 171; Ortved 1933, p. 304 f ). It has been suggested that this
(Latinized) name of the monastery refers to the all-thing. But why would the
monastery take its name from an administrative assembly? And if the thing
was indeed so important, why is the place not named ‘Allthingia’? One significant point is that the Guta Saga does not actually read gutna alltþing, but gutnal þing (e.g. GS §9), as pointed out by Hjalmar Lindroth (1915) while discussing the linguistic basis of the name Gutnalia.
He concluded that Gutnal is an independent place-name, Gutna al (al of the Gotlanders) (Lindroth 1915, p.66 f ). Most Cistercian monasteries and churches were dedicated to the Virgin Mary, and thus the epithet “…de Gutnalia” served to distinguish the monastery of Roma from its sister institutions. The name Gutnalia itself, though,
must have been derived from a place-name containing the element -al.
A place denoted by al should be understood as a ‘protected area’, but there
is also a connection between al and assembly places (Vikstrand 2001, p. 192
ff ). Most al names denote natural features, but a few may have a cultic or
sacral meaning: Götala, Gutnal, Fröjel, Alsike and a few others. These names
derive from the Germanic alh-, ‘protection’ (Brink 1992, p. 111 ff ). The word
has connotations such as ‘defended’, ‘shielded’, ‘consecrated’ and ‘sanctified’.
Furthermore, al is apparently found where there was a building of great social
distinction (ibid, p. 116). In German non-religious texts the word was used in
the sense of ‘house’, ‘protection’, ‘a fenced, protected area’ or ‘a legally protected
place’ (settlement) (Schmidt-Wiegand 1967, 1989). It is known through texts
such as a runic inscription in Oklunda that cultic places were under some kind
of legal protection (see below), and also from passages in the Guta Lagh and
Guta Saga (GL §13, GS §11). The notion is also found in a Christian context,
in the idea that the sanctity of churches should not be violated.
The gutn(a) part of Gutnalia ties the name and the place to the Gotlandic
people. In that sense the interpretation of a pre-Christian cultic al-place of
importance to the Gotlanders does not disagree with the notion of the name
being connected with the all-thing. Cults and legal/regal authority may have
been even more intertwined in earlier times than later during the Medieval
period. The difference is that in one case, Latinized Gutnalia would refer to al,
the physical ‘(cult-? central-? thing-?) place of the Gutar’, perhaps connected
with a prominent house or hall. In the other case, the name Gutnalia would
refer to all as in the all-thing (‘-thing’ simply being omitted from the name)
and would imply that the thing wanted to found a Christian monastery, and
had the authority to do so. I will proceed to argue that the first explanation is
the more likely one.
The setting of the all -thin g

The exact locations of ancient thing assemblies are rarely known, but in several cases there is at least some information deriving from historical sources, folk
tradition or place-names. Such assemblies were often thought to have been held at prehistoric monuments such as great mounds, or ‘judge’s rings’ (Sw.
domarring, an Iron Age grave type consisting of a circle of boulders or vertical stones). But more frequently the meeting places are hard to identify, and
it is generally difficult to determine the age of a thing site or to locate it by
archaeological means (cf. Sanmark 2004).

The Law Ting Holm in Loch Tingwall, Shetland, Scotland
Prehistoric assembly places are generally found in areas with a high concentration of rune-stones and prehistoric graves, often on the “periphery” of a settled area. Also, assembly places were often moved on one or more occasions in the later Middle Ages (although, as far as is known, never more than 10 km) to comply with new situations or
demands on accessibility, but the old locations apparently influenced the allocation of later assembly places up until late historical times (Sanmark 2008, p. 15). Thing sites were often not situated near settlements, but rather at communication nodes in the landscape (Vikstrand 2001, p. 412; cf. Wilson 1994,
p. 67).
 The morphology of thing sites also shows much variation: open places,
The morphology of thing sites also shows much variation: open places,
mounds, or a rectangular stone-setting such as Arkil’s thing site in Uppland
(Nordén 1938; Lönnroth 1982). The excavated remains of Þingnes in Iceland
revealed a concentric circular structure surrounded by farmhouses (Ólafsson
1987, p. 343 ff ).
 The physical assembly place has thus often been connected with prehistoric
The physical assembly place has thus often been connected with prehistoric
monuments and manifest remnants such as procession roads, both prehistoric
and Medieval. The majestic Anundshög [Anund’s mound] in Middle Sweden
is one well-known example where a great mound, a procession road flanked
by large stones, and several monumental prehistoric graves (stone ships) are
combined, making a profound impression on the visitor even today. There is
no real proof, however, that these “thing” mounds were indeed once settings
for prehistoric assemblies. That may well be an invention of later times, connecting the impressive monuments with the forefathers and people of the past.
It is simply difficult to tell which one was the localizing factor: the thing site
for the monument, or the monument for the idea of how a thing was staged?
The known thing sites suggest there was in reality a considerable amount of
morphological variation.
Islands as settings for things
 There are similar traditions attached to thing and assembly places in northern
There are similar traditions attached to thing and assembly places in northern
Britain and in Scandinavia, with mounds or stone circles being identified as
gathering places (Driscoll 2004). On Islay, off the west coast of Scotland, an
important medieval meeting place was situated on a small island in a lake
(Eilean na Comhairle, ‘the council isle’, in loch Finlaggan).
 During the negotiations the lord and his attendants would live on a larger island nearby, just off the shore, in a royal complex that included a monastery (Caldwell 2003). On
During the negotiations the lord and his attendants would live on a larger island nearby, just off the shore, in a royal complex that included a monastery (Caldwell 2003). On
Shetland, the Law Ting Holm in the lake of Tingwall was a small island close
to the shore which was used for assemblies in the Norse (Viking/Medieval)
period . The most important medieval church of Shetland was on the
shore, and both Eilean na Comhairle and Law Ting Holm were connected to
the shore by a causeway.

Islands, an islet or holm as it may have been, have so far not been much
discussed as possible thing sites in a Scandinavian context. Þingnes in Iceland
was apparently situated on a promontory or peninsula (also reflected in its
name), but I have found no discussion on ‘island’ settings as such. Still, bearing
in mind the similarities between the assembly place traditions of the (Norsedominated) British Isles and Scandinavia in other respects, the suggestion can
be put forward that islets or small peninsulas should be evaluated in a new
light in the search for the elusive Scandinavian thing sites of the Late Iron Age
(Viking Age) and early medieval times.
Before and during the Iron Age the whole area of present-day Roma was in
the nature of a promontory, surrounded partly by wetlands and partly by open
water , and it was probably possible to reach the Roma area by boat all
the way from both coasts. At the south end of the complex of waterways surrounding Roma is the narrowest point, a small strait, with Gotland’s largest Iron Age burial ground (Broa, in the parish of Halla) and the Viking or Medieval fortifications of Hallegårda just across the water.
To the northwest and southeast the land is much higher, and the area of Roma thus lay ‘sunk’ between the two halves of Gotland. The peninsula of Roma was like an ‘island in
the middle of the island’ which had to be passed through no matter whether
one was travelling in a north-south or east-west direction, on land or by boat.
Roma parish church, a prominent three-aisled hall church erected in the mid-13th century, is situated on a high point north of the monastery and by a crossroads. It was preceded by a stone church from the 12th century (which was already there when the monastery was founded), which in its turn was perhaps preceded by a wooden church.
Broa (‘the bridge’) about 1.5 km southwest of the Roma monastery on the
other side of the bog, is the largest burial ground on Gotland and one of the
best sources of material of a typical high-status character. The cemetery was in
use from the Roman Iron Age to the Viking period, and the artefacts found
include numerous weapons and four prestigious helmets from the Vendel period as well as an equestrian grave from the early Viking period. In particular
the helmets indicate connections with high-status graves outside Gotland,
such as those of Vendel in Central Sweden or the British Sutton Hoo ship
burial. This distinguishes the Broa area from the other large centres and burial
grounds on northern and southern Gotland. The area stretches away on both
sides of the road southeast of the present bridge, and along the road running
north to Halla and Hallegårda (Fig. 4). The latter is a fortification of concentric circular walls with a stone building inside, probably of late Viking or early Medieval origin and has been interpreted as a centre inhabited by a local chieftain (Broberg et al. 1990).
This complex is situated south and southeast of the Roma monastery, on the other side of the wetland. There was once a small island or islet, Björkö, in the northeast mouth of the
strait, a feature which is still visible on late 19th-century maps drawn before
the draining of the bog began. The name of the island incites curiosity, since
Björkö is also the present name of the famous Viking Age town of Birka in
Lake Mälaren. In medieval Scandinavia the word Birka (Bjärka, Björkö) denoted a certain type of legislation, Bjärköarätt (the early legislation of many
early towns), and more generally ‘special jurisdiction’ (KHL, p. 656, entry Bjärköarätt). This may have nothing to do with the small island near Roma, but the
island is still interesting in its own right. Considering the similar traditions
surrounding thing and other assembly places in northern Britain and in Scandinavia, one may wonder if we are not looking here at a Scandinavian parallel
to the islands in the Finlaggan and Tingwall lakes.
The British examples of island thing sites, with churches, manors and accommodations for the attending parties on the shore, evoke the question of
whether the semicircle of properties bearing the names of things to be found
around the Roma monastery was in fact not relating to the waterfront at the
time, and that they faced the islet of Björkö rather than the monastery. It may
indeed be suggested that, at least in prehistoric and early Medieval times, the
assemblies may have been held on Björkö rather than in an area now beneath the monastery ruins or in any of the adjacent meadows. The Broa cemetery and
perhaps also the Hallegårda fortifications behind the island would have been
clearly visible from the shore, offering a view of the centre of power and the
resting place of the great forefathers as a background.
Unfortunately there is nothing left to prove that Björkö was an assembly
place, since the islet itself has been almost totally destroyed through draining
and digging in the bog during the past decade. There are now dams where the
island was until the beginning of the last century. This hypothesis will thus
remain unconfirmed unless new evidence is uncovered to prove it. This setting
for the assembly place makes far more sense, however, and conforms better to
other historically known settings such as Þingnes or Law Thing Holm than
does the previously proposed location on the site later taken over by the monastery.
The staging of the thing
According to written sources such as the Icelandic Sagas, negotiations at a
thing took place within a demarcated area and most of the agents attached to
the assembly had to remain outside. The law-court was probably marked out
with vébond, strings or ropes tied between rods stuck into the ground, or running through iron rings attached to the rods, as seems to have been the case at
the recently excavated site of Ullevi in central Sweden (Blomkvist & Jackson
1999, p. 21; Vikstrand 2001, p. 332; Brink 2002, p. 90; Svenska Dagbladet June
22 2008, p. 24 f ).
The word vébond is connected to the concept of vi, appearing
as a place-name in itself or as part of one (as in Ullevi, meaning ‘the Vi of
the god Ull’). ‘Vi’ denotes a protected area where there was a right of asylum
(Vikstrand 2001, p. 323 ff ), and has been interpreted as meeting place consecrated to the supernatural powers, an arena for cult and common ritual under
divine protection (ibid, p. 332). ‘Vi’ often appears in pairs with the toponym
lund [grove]¸ which denotes the cultplace proper, the sacrificial grove (a famous Lunda excavated recently outside Strängnäs in central Sweden, yielded
spectacular finds of gold figurines and more than 4 kilogrammes of burnt and
crushed human bones; see Andersson 2003, 2004). The locations for meetings
of a thing thus seem to have been very complex places, including several nodes
and combining legal actions with various cult and ritual elements.
Concepts of peace and inside/outside were also connected with the assembly place and with the ideology of the thing, as also with the vi. Inside
the vébond sphere there was friðr (‘peace’), and outside there was úfriðr (‘unpeace’) (Blomkvist & Jackson 1999, p. 21 f ). This was manifested through the demarcation of an area. The concept was not exclusive to the thing, but an individual could also legally seek asylum and protection by drawing a ‘circle of peace’ for himself. This is described in the medieval Gotlandic Guta Lagh (GL§13), but was probably also a legal feature in other parts of Scandinavia much earlier than the 13th century. Such an event is described in a 9th-century runic inscription in Oklunda (Sweden) (Lönnqvist & Widmark 1997, p. 151; Gustavson 2003, p. 187), where one Gunnar states that he has fled to this vi, inside
the circle of peace. This runic inscription may be regarded as a legal document
(Brink 2002, p. 96) but it may also have had a magical meaning, since the carving is shaped like a tied bond (Lönnqvist & Widmark 1997, p. 156 f ).
The vébond strings served a double purpose: they created a restricted area
where peace had to be kept, and they divided the lawmen from the ordinary
delegates during the meeting. The apparent tension between these two groups,
as reflected in the Icelandic law compilation Grágás, Egils saga Skallagrimsónar,
and Viga-Glúms saga, for example (Holmgren 1929, pp. 22, 25 ff ), may have
been due to the innate tension between those who enforced the law and siðr
(old custom) and those who had to accept their judgements. Respect for the
law-courts was just as fundamental as it is today, and infringement of it was
punishable by exile in Iceland (ibid, p. 25). Runes on a large 9th-century ring
from Forsa in northern Sweden (interpreted as an oath ring for use at the
thing) describe what will happen to the one who fails to respect the law-courts
and the asylum granted by the vi. This involved fines and the suspension of
property rights (Ruthström 1990; Brink 2002, p. 97 f; cf. Myrberg 2008, p.
146).
Rings were obviously important within the context of the thing, as indicated by the phrase ‘bringing something a þing ok a ring [to the thing and to the
ring]’ which is found in medieval laws (Holmgren 1929, p. 22 ff; Blomkvist &
Jackson 1999, p. 21). This may be a reference to an oath ring, kept in the temple
and brought out by the cult leader during legal negotiations (cf. Habbe 2005, p.
134 f ), such as the Forsa ring, or to the numerous smaller rings found on Ullevi
and originally probably attached to poles around the sacred area. “All is bound
in rings” the Guta Saga states solemnly, probably giving some kind of authentication to the text. References to band, ring and baugr (ring) in the sagas may
have a religious and/or judicial significance (Blomkvist & Jackson 1999, p. 20
ff ), and the tying of knots and giving away of rings are accordingly frequent
themes in the mythology and sagas as metaphors for the giving of promises or
establishment of relations.
The staging, ritual and ideology of the prehistoric or early medieval thing
thus seem to be much concerned with concepts of peace, inside/outside and rings, as well as with social reproduction, the community and the maintenance
of old customs, siðr. Ritual meals and communal feasting are thought to have
been part of the thing meetings and of the associated cultic activity (e.g. the
sjudning, ritual meals consumed with one’s suþnautar, ‘cooking brothers’, described in the Guta Saga (GS §5; cf. Yrwing 1951, p. 13; 1978, p. 82).
The thing may have represented a social ideology of equality in a time that otherwise
demonstrated great social differences. As a parallel, one may look at Iceland,
where the early laws and sagas helped to create and maintain a mythology and
ideal of an equal society which was not the real situation even in the earliest
landnám period (Rafnsson 1974, p. 187 f; Durrenberger 1992; Meulengracht
Sørensen 1993, p. 149; Smith 1995).
Gutnal , the monastery , and the all -thin g of Roma
It is easy to imagine that the low-lying promontory surrounded by lakes and
bogs in the middle of the island held a particular fascination for the people
of Gotland, especially at a time when waterfronts and bogs were of central
importance for cultic and votive activities, as seems to have been the case for
example at Tuna, southwest of Roma, and in the Roma mire itself. Gold and
wild boar tusks were found in the Roma mire during drainage work in the
1930s (SHM 17815, SHM 32811). Tuna has yielded a number of spectacular
finds, such as Roman coins, gold bracteates and a mass of golden rings, mostly
belonging to the Migration period, c. 400–550 AD (Hildeberg 1999, p. 24),
although the Roman denarii point to use of the site having begun around AD
300 (Roman Iron Age).
If the promontory was indeed an Iron Age al place, this would have sustained its function as a central meeting place for many centuries. But the archaeological and historical evidence also demonstrates the influence of local chieftains, as visible in matters ranging from burials and the deposition of Iron Age valuables in these to the building of private churches and the granting of land for a monastery. Explicitly referred to as a ‘chieftain’ can be detected in the written documents concerned with the founding of the monastery, and the initiative and endowment for all the other Swedish monasteries is known to have come from a major landowner or petty king with ambitions.
The role of a bishop in the process may have been decisive in some cases (Nyberg 2000, p. 211 f ), but this usually resulted from the bishops’ close family
connections with the nobility. The building of churches and monasteries was a
means by which the elite could act like continental kings and associate themselves with the expanding Church, and thus legitimize their claims to power
and retain their ideological influence within society (cf. Nyberg 2000, p. 81 ff;
Tagesson 2002, p. 237).
Such elite figures or chieftains are detectable in the Gotlandic archaeological record, and are also mentioned in the Guta Saga, being described as rich
landowners or lawmen, as being ‘wise’, or as acting as emissaries abroad. A
few kilometres northwest of Roma one still finds Akebäck and Kulstäde , where, according to the Guta Saga (§10), the first church on the island was
built by a private patron, probably in the 11th century.
This patron, Botair, actually had two churches built, since the people of the island burned the first one down, and tried to burn the second one as well. Botair was sufficiently influential, however, to build his churches in two prominent places: one (Kulstäde)

within a few kilometres of the Gutnal, and the other at Vi (often interpreted as
the present-day Visby). The prominence and significance of vi places has been
pointed out above. It may be that Botair’s self-confidence was partly based on
the fact that he was the son-in-law of Likair the Wise, a man who according to
the Guta Saga “reth mest um than tima” (ruled/advised most in that time) (GS
§11). Likair was thus either a petty king or the island’s highest legal authority,
and Botair must accordingly have been considered a mighty person himself to
conclude such a good marriage. Apparently he controlled land very close to
the Gutnal, most likely through inheritance, and it was there that he built his
first church.

The period of Botair, and of the Iron Age-medieval centre of Broa-Hallegårda, is close to the time when the monastery in Roma was established.
That is, to the time when the all-thing is thought to have been in command
of the land in the Roma area. Yet close to the monastery there was land in
one direction that was controlled by one of the most influential (and probably wealthiest) men on the island (Botair), and in another direction there
was the (now anonymous) owner of the fortified Hallegårda.
‘Botair’ may be only an imaginary figure in the saga, but the Hallegårda-Broa complex bears archaeological witness to the fact that such persons must have existed there at
the time. At least the early 13th-century author of the Guta Saga takes their
existence for granted. The thing as an institution has been regarded as having
been dominated by small farmers, so that it remained independent of the great
landowners, since this is the picture inferred from the medieval laws (Brink
1998, p. 300; Vikstrand 2001, p. 412). Again, archaeology gives us a different
picture, in particular regarding the Viking period. Jarlabanke, a major landowner in central Sweden, inaugurated a thing site in the 11th century, as did
Arkil and his brothers some generations earlier to commemorate their father Ulf, also a great landowner (Nordén 1938; Lönnroth 1982; U 212, 225, 226).
TheÞingnes assembly place, Iceland’s first, was founded around 900 AD by the
‘supreme chieftain’, the Allsherjargodi, next to his house (Ólafsson 1987). Thus
archaeology shows us that an upper class of landowners took an active part in
developing the thing as an institution and influenced its location.
Is it plausible that the Gotland all-thing could actually have owned land
and been able to dispose of it as it wished? And if it did – why would the
all-thing give away as an endowment for a monastery the very spot that was
most central to its own activities – the assembly place itself? It appears more
likely that the endowment for the monastery was made by an individual great
landowner or chieftain in the area. To locate it in a setting which alluded to
older ritual behaviour and the great ancestors would comply better with what
we know about the nature of prehistoric power and the thing ideology. This
was the way of behaving and of displaying individual power in other areas of
Scandinavia. Likewise, the inauguration of a thing assembly place may well
have been influenced by individual members of the elite class who had external
connections and internal ambitions for power.
The Guta Saga and Guta Lagh regulate in detail other important matters of
concern to the community. The Christianization of the island, the first churches and their relation to the Church and the bishop are all mentioned, but
not the foundation of the monastery, which must have happened as part of the
same process (and at about the same time). This suggests that the latter was
not a matter of common concern. The name Gutnalia does not, as was suggested in the past, tell us that the monastery was founded by the all-thing, but
that it was once a sacred place of social distinction: the Al of Gotland.

PRESERVING OUR PAST, RECORDING OUR PRESENT,INFORMING OUR FUTURE
ANCIENT AND HONORABLE CARRUTHERS CLAN INT SOCIETY CCIS
CARROTHERSCLAN@GMAIL.COM CARRUTHERSCLAN1@GMAIL.COM

 Nanouschka Myrberg, University of Sweden
Nanouschka Myrberg, University of Sweden
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST
Article in Regner, E., von Heijne, C., Kitzler Åhfeldt, L. & Kjellström, A. (eds.). 2009. From Ephesos to Dalecarlia. Reflections on Body, Space and Time in Medieval and Early Modern Europe. The Museum of National Antiquities, Stockholm. Studies 11. Stockholm Studies in Archaeology 48. Stockholm. ISBN 978-91-89176-37-9
References
Andersson, G. 2003. Lunda – delområde E: “Lunden” – en plats för aktiviteter under förhistorisk och historisk tid. UV Mitt Dokumentation av fältarbetsfasen, 2003:6.
Stockholm
Andersson, G. 2004. Att föra gudarnas talan: figurinerna från Lunda. Stockholm
Blomkvist, T. & Jackson, P. 1999. Alt ir baugum bundit. Scaldic Poetry on Gotland in
a Pan-Scandinavian and Indo-European Context. Arkiv för nordisk filologi 114.
Brink, S. 1992. Har vi haft ett kultiskt *al i Norden? In Fellows-Jensen, G. & Holmberg, B. (eds.). Sakrale navne. Rapport fra NORNAs sekstende symposium i Gilleleje
30.11 – 2.12 1990. Uppsala
Brink, S. 1998. Land, bygd, distrikt och centralort i Sydsverige: några bebyggelsehistoriska nedslag. In Larsson, L. & Hårdh, B. (eds.). Centrala platser, centrala frågor:
samhällsstrukturen under järnåldern. En vänbok till Berta Stjernquist. Lund
Brink, S. 2002. Law and legal customs in Viking Age Scandinavia. In Jesch, J. (ed.).
The Scandinavians from the Vendel period to the tenth century – an ethnographic perspective. Woodbridge
Broberg, A. et al. 1990. Hallegårda i Halla – social stratifiering eller bara en tillfällighet? META 3/1990.
Caldwell, D. H. 2003. Finlaggan, Islay – stones and inauguration ceremonies. In Welander, R. et al. (eds.). The stone of destiny – artefact and icon. Edinburgh
Carlsson, A. 1983. Djurhuvudformiga spännen och gotländsk vikingatid. Stockholm
Domeij, M. 2000. Människor och silver: samhällsideologi och sociala strategier på Gotland
ca 700–1150. Lund
Driscoll, S. 2004. The archaeological context of assembly in early medieval Scotland
– Scone and its comparanda. In Pantos, A. & Semple, S. (eds.). Assembly places and
Practices in Medieval Europe. Dublin
Durrenberger, P. E. 1992. The Dynamics of Medieval Iceland. Political Economy & Literature. Iowa
Gannholm, T. 1984. Guta Lagh med Gutasagan. Stånga
Gurevich, A. J. 1985. Categories of medieval culture. London
Gustavson, H. 2003. Oklundainskriften sjuttio år efteråt. In Heizmann, W. & van
Nahl, A. (eds.). Runica – Germanica – Mediaevalia. Berlin
Habbe, P. 2005. Att se och tänka med ritual. Kontrakterande ritualer i de isländska släktsagorna. Lund
Hildeberg, S. 1999. Tuna offerplats på Gotland: ett folkvandringstida fynd i ny belysning.
Arkeologiska institutionen, Stockholms universitet. Stockholm
Holmgren, G. 1929. Ting och ring: ett bidrag till diskussionen om de forntida tingsplatserna. Rig 12.
Hyenstrand, Å. 1989. Socknar och stenstugor. Stockholm
Kyhlberg, O. 1991. Gotland mellan arkeologi och historia. Stockholm
Lindroth, H. 1915. Gutnal þing och Gutnalia. Från Filologiska föreningen i Lund.
Språkliga Uppsatser IV. Lund
Lindström, G. 1895. Anteckningar om Gotlands medeltid II. Stockholm
Lönnqvist, O. & Widmark, G. 1997. Den fredlöse och Oklundaristningens band.
Saga och sed 1996/97.
Lönnroth, E. 1982. Administration och samhälle i 1000-talets Sverige. Bebyggelsehistorisk Tidskrift 4/1982.
Meulengracht Sørensen, P. 1993. Fortælling og ære. Studier i islændingasagaerne. Aarhus
Moberg, I. 1938. Gotland um das Jahr 1700: eine kulturgeographische Kartenanalyse.
Stockholm
Myrberg, N. 2008. Room for All? Spaces and places for thing assemblies: the case of
the all-thing on Gotland, Sweden. Viking and Medieval Scandinavia 2008.
Nordén, A. 1938. Tingfjäl och bäsing. En studie över rätter tingstads inrättning. Fornvännen 1938.
Nyberg, T. 2000. Monasticism in north-western Europe, 800–1200. Aldershot
Ólafsson, G. 1987. Þingnes by Elliđavatn: The First Local Assembly in Iceland? In
Knirk, J.E. (ed.). Proceedings of the Tenth Viking Congress. Oslo
Ortved, E. 1933. Cistercieordenen og dens klostre i Norden. Bog 2, Sveriges klostre. København
Pernler, S.-E. 1977. Gotlands medeltida kyrkoliv. Biskop och prostar: en kyrkorättslig studie. Visby
Rafnsson, S. 1974. Studier i Landnámabók. Kritiska bidrag till den isländska fristatstidens historia. Lund
Ruthström, B. 1990. Oklunda-ristningen i rättslig belysning. Arkiv för nordisk filologi
1988.
Rönnby, J. 1995. Bålverket: om samhällsförändring och motstånd med utgångspunkt från
det tidigmedeltida Bulverket i Tingstäde träsk på Gotland. Stockholm
Sanmark, A. 2004. Tingsplatsen som arkeologiskt problem. Etapp I: Aspa: arkeologisk provundersökning, forskning: Raä 62, Aspa 2:11, Ludgo socken, Nyköpings
kommun. SAU rapport 2004:25. Uppsala
Sanmark, A. 2008. Tingsplatsen – scen för maktutövning. Populär arkeologi 2/2008.
Schmidt-Wiegand, R. 1967. Alach. Zur Bedeutung eines rechtstopografischen Begriffs der frankischen Zeit. Beiträge zur Namenforschung. NF 2.
Schmidt-Wiegand, R. 1989. Frühmittelalterliche Siedlungsbezeichnungen und Ortnamen im nordwestlichen Mitteleuropa. Studia Onomastica. Festskrift till Thorsten
Andersson den 23 februari 1989. Stockholm
Smith, K. P. 1995. Landnám: the settlement of Iceland in an archaeological and historical perspective. World Archaeology 26:3.
Steffen, R. 1943. Gotlands administrativa, rättsliga och kyrkliga organisation från äldsta
tider till år 1645. Lund
Svenska Dagbladet. Stockholm
Tagesson, G. 2002. Biskop och stad. Aspekter av urbanisering och sociala rum i medeltidens Linköping. Stockholm
U + nr = nr in UR
UR = Upplands runinskrifter. Granskade och tolkade av Elias Wessén och Sven B. F.
Jansson. 1940-58. (SRI. 6–9.) Stockholm
Vikstrand, P. 2001. Gudarnas platser. Förkristna sakrala ortnamn i Mälarlandskapen.
Uppsala
Wessén, E. & Jansson, S. B. F. 1940–58. Sveriges runinskrifter Bd 6 – 9, Upplands runinskrifter. Stockholm
Wilson, L. 1994. Runstenar och kyrkor. En studie med utgångspunkt från runstenar som
påträffats i kyrkomiljö i Uppland och Södermanland. Uppsala
Yrwing, H. 1940. Gotland under äldre medeltid: studier i baltisk-hanseatisk historia.
Lund
Yrwing, H. 1951. Gotlandskyrkan i äldre tid. In Hejneman, E. et al. (eds.). Visby stift i
ord och bild. Stockholm
Yrwing, H. 1978. Gotlands medeltid. Visby
Östergren, M. 1990. Det gotländska landstinget och cistercienserklostret i Roma.
META 3/1990.
Östergren, M. 1992. Det gotländska alltinget och cistercienserklostret i Roma. Gotländskt Arkiv 64.
Östergren, M. 2004. Det gotländska alltinget och cistercienserklostret i Roma. Gotland Vikingaön – Gotländskt Arkiv 76.
Abbreviations
ATA: Antiquarian-Topographical Archive (ATA), Stockholm.
DGK: Danmarks gamle købstadslovgivning. Erik Kroman 1951.
Dipl. Dal.: Diplomatarium Dalecarlicum: urkunder rörande landskapet Dalarne. Sam
lade och utgifne av C.G. Kröningssvärd & J. Lidén. Stockholm 1842–1853.
Dnr: Registration number.
DR+nr: Runic inscription in L. Jacobsen & E Moltke (eds.). Danmarks runeindskrifter. København 1941–42.
DS: Diplomatarium Suecanum. Utgivet af J. G. Liljegren m fl. 1828–. Stockholm
G+nr: Runic inscription in E. Brate och E. Wessén (eds.). Gotlands runinskrifter. Stockholm 1962.
GS: Guta Saga (The Gotlandic Saga), published in Gannholm, T. 1984. Guta
Lagh med Gutasagan. Stånga
GL: Guta Lagh (The Gotlandic law), published in Gannholm, T. 1984. Guta
Lagh med Gutasagan. Stånga
KHL: Kulturhistoriskt lexikon för nordisk medeltid från vikingatid till reformationstid. Malmö.
KMK: Kungl. Myntkabinettet (The Royal Coin Cabinet), Stockholm.
NE: Nationalencyklopedin. Höganäs 1993.
O.N.: Old Norse
RAp: Riksarkivet pergamentbrev. National Archive of Sweden, parchment letter.
RApp: Riksarkivet pappersbrev. National Archive of Sweden, letter.
RAÄ: The Swedish National Heritage Board
RAÄ+nr: Site nr in the Ancient monuments survey of the Swedish National Heri-
tage Board
SD: Svenskt Diplomatarium från och med år 1401 (täcker åren 1401–1420). Utg.
Av Riksarkivet och Kungl. Vitterhets- Historie- och Antikvitetesakademien. Stockholm 1875–1904.
SHM: Statens Historiska Museum (The Museum of National Antiquities), Stockholm.
277
INTRODUCTION
SML Nä: Sveriges Mynthistoria Landskapsinventeringen. Part 5, Närke. M. Golabiewski Lannby 1990. The Royal Coin Cabinet and the Numismatic Institute, Stockholm.
SRI: Sveriges runinskrifter. Utg. av Kungl. Vitterhets Historie och Antikvitets
Akademien 1–. 1900 ff. Stockholm.
SSAp: Stockholms stadsarkiv pergamentbrev. Municipal archive of Stockholm parchment letter.
Sö+nr: Runic inscription in E. Brate and E. Wessén, (eds.). Södermanlands runinskrifter. Stockholm 1924–36.
U+nr: Runic inscription in E. Wessén and S. B. F. Jansson, (eds.). Upplands runinskrifter. Stockholm 1940–58.
VG+nr: Runic inscription in H. Jungner and E Svärdström (eds). Västergötlands
runinskrifter. Stockholm 1940–1970
Webster: Webster´s Third New International Dictionary, 2000.
Ög+nr: Runic inscription in E. Brate, (ed.). Östergötlands runinskrifter. Stockholm
1911–18












 To read more on the Yggdrasil please follow the link :
To read more on the Yggdrasil please follow the link : 
























 The physical assembly place has thus often been connected with prehistoric
The physical assembly place has thus often been connected with prehistoric There are similar traditions attached to thing and assembly places in northern
There are similar traditions attached to thing and assembly places in northern During the negotiations the lord and his attendants would live on a larger island nearby, just off the shore, in a royal complex that included a monastery (Caldwell 2003). On
During the negotiations the lord and his attendants would live on a larger island nearby, just off the shore, in a royal complex that included a monastery (Caldwell 2003). On




 Nanouschka Myrberg, University of Sweden
Nanouschka Myrberg, University of Sweden












