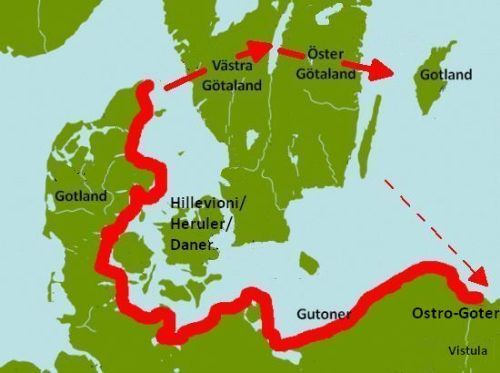
GOTLAND – HOME OF THE
VARANGIANS
CARRUTHERS ANCESTORS

*** Let us remember that the lighter color green along with the army green was Gutland/Gotland. The blue is the estuary of water that was a major tradeway highway of people. This is one reason they made the long boats. It ws easier to travel back and forth, from one end of their homeland to another on the long boats. ***
Gotland the home of the Varangians was an independent Merchant Farmers’ Republic, and the hub of the Baltic Sea region, which from time immemorial had its relations mainly east and south.
From the archaeological findings we can establish that trade relations between Gotland and the Roman Empire were intense. The early history is a piece of myth, oral tradition and fragmentary records. From all this can suddenly emerge a pattern, the outline of a process that may
not be scientifically inviolable, which it never really can be. Yet it is nearer the truth than you could ever reach with ‘scientific accuracy’.

If you take the Guta Saga, written down about 1220,and the Beowulf Epos, written down in the 700s, as serious as Snorri Sturluson’s ‘Nordiska kungasagor’, written down about 1220, has been honored – i.e. as evidence in lack of better sources, there will open up a new, breathtaking perspective regarding Gotlandic, Swedish and Scandinavian history during the Roman time of the emperors and the Migration Period. Yes also that of Europe.
Already in the Bronze Age and early Iron Age there are signs of Gotlandic trading Emporiums on the east coast of the Baltic Sea and all the way to the river Volga. Trade, especially amber trade, experiences in the Bronze Age a large bloom. The Gotlanders seem to have controlled the amber trade with trading Emporiums in the Kaliningrad-Vistula area.
The extensive trade relations convey inuences from outside. From southern cultural centers, Egypt, Crete, Mycenae, spiritual impulses stretched their effects also to the Baltic Sea region and Gotland. A new way of burial appears in the Lake Mälar area in the 500s, as well as the introduction of the Roman calendar.If we accept that the Heruli settle in the Lake Mälararea at this time, as mentioned by Procopius, it explains a lot. Actually this in fact explains the rise of the Vendelera, which in the Lake Mälar area starts first half of the 500s and continues until the beginning of the Middle Ages.
On Gotland it starts about 50 years earlier and is explained by the Gotlanders’ close contacts with Theoderic’s Gothic kingdom. With the discovery that the Beowulf epos is about the Gotlanders in combination with the Heruls immigration to the Lake Mälar area we have been able to shed new light on the Gotlandic history. Indeed the history of the whole Baltic Sea region has come in a whole new light. We now have a link between the Beowulf epos, Guta Saga and the archaeological finds from the 400s and 500s.
*** Some of these finds is where the first “Grouping” of Carruthers CTS11603 genome was found. Cinchester was one location that they know a group of Carruthers-Gotlanders came ashore, and then on the east coast of Ireland, and then to the Clyde River in Scotland. ***
Roman gold coins known as solidi have been found on the three Baltic Sea islands: Bornholm, 150,Öland 298, Gotland 270 + 47 on the Gotlandic market place Helgö in Mälaren. The latter have been intended as raw material and are according to the researchers most likely derived from Gotland. It is obvious here to see Helgö and then Birka as Gotlandic trading venues, as implied by the archaeological sources. Gotland’s importance for trade and culture in the
Baltic Sea region during the first millennium can also be illustrated by the coin ands in Gotland.
 King of the Goths or Gotland/Gutland
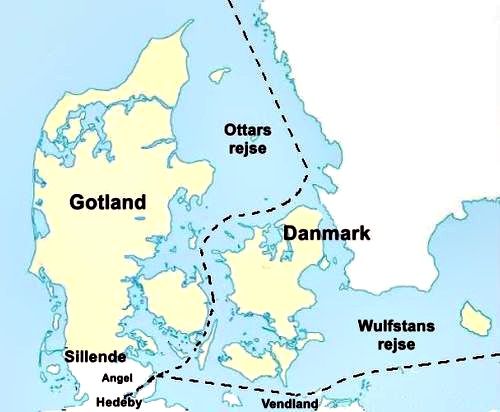
King of the Goths or Gotland/GutlandFrom the 500s until the 1000s the Gotlanders have, according to Swedish researchers, been considered to rarely be mentioned in ancient sources. They are, however, well known in Arabic and Byzantine sources as al-Rus’ and Varangian merchants.
The word Varangian was used by Arabs, Greeks and Kievan Rus’ for the merchants from the islandin the Baltic Sea region ( the Gotlanders ). It probably came from the old Norse word ‘vár’, which means‘ union through promise’, and was used by a group of men to keep them together in an association, and under oath observe certain obligations to support each other in good faith and to share the resulting profits.
It was a common word, when trading adventures were undertaken by Gotlandic tradesmen on the Russian rivers. They closed a business contract with each other and pledged to defend each other. Another meaning of the word was for the Gotlanders who acted as mercenary soldiers to the rulers ofKhazaria, Miklagarðr ( Constantinople ) and Garðaríki( Kievan Rus’). The Gotlandic Varangian Guard became an elite unit of the Byzantine army formed under emperor Basil II in 988.
At that time was also the official Christianization of the Kievan Rus’ by Vladimir I of Kiev. There were no Vikings in the Baltic Sea region. The word Viking is not known there. The Vikings were warriors from Denmark, the west of Sweden and Norway, and the Viking Age starts with the attackon Lindisfarne in 793. There is a clear line in the river Elbe between Vikings and Varangians .
East of the river Elbe there is no mention of Vikings, only Varangians. In the Baltic Sea region the Gotlanders, after the signing of the trade and peace treaty in the 550s,controlled the trade under Svea protection on the areas controlled by the Svear. End 700s when silver from the Islamic Caliphate started to flow, the Gotlanders entered the Russian rivers all the way to river Volga and the Kaspian Sea. The Gotlandic Merchant Farmers were on the Russian rivers called Varangians and al-Rus’ ( expeditions of rowing ships ). It is documented in Byzantine sources that from late 800s and forward there were larger Gotlandic contingents stationed in Miklagarðr. As mentioned above, it is only in the early 500s that sources start to talk about some powerful people in the Lake Mälar area, except for Tacitus Sitones who he considers degenerated as they were ruled by a woman.
1st. Prokopios tells us about the Heruli or Earls who settle next to the Gauti.
2nd. Snorri tells us about the Asia men who introduce a new religion and settle in Sigtuna.
The excavations at Old Sigtuna reveal major changes in the early 500s with large increase in people and horses.
3rd. The Beowulf epos talks about the conditions in the Baltic
Sea region and the antagonism betweenthe immigrant Svear and the Gotlanders.
The real name of the island in the Baltic Sea is Gutland or the island of the Gutar. In the trade treaties from the 1100s it is called ‘Gutniska kusten’( Gotlandish coast), and the people are called Gutar. The Couronians called the Gotlanders for Gudi. Jordanes talks about Gothi scandza as the linguists have translated with the ‘Gotlandic coast’, or the coast where the Gotlandic trading colonies were located on the southern shores of the Baltic Sea.
The word Scandza means just the coast, later ‘Gutniska kusten’, which is the island Gotland. The word Gotland is a Latin form that alludes to the Roman name for the Goths, who called them-selves Guthiuda and Gutans.
The Gotlanders were thus independent until the end of the 1300s and then self-governing
first under pirates ( including removed foreign kings ).From 1530 until 1645 Gotland was a tributary state under the Danish king. All that time the Gotlandic Merchant Farmers’ Republic functions de jure
The Gotlanders choose things judges and the large Gotlandic ‘national seal’ with the ewe is used until they later in the 1500s do not want to acknowledge a too uncomfortable Danish decision. Instead they explain that the seal has been lost. On paper the Gotlandic Merchant Farmers’ Re-public exists until the beginning of the 1600s but is gradually abolished.
The Gotlandic Merchant Farmers’ counted their birth position and their social class socially higher than burghers and peasants of other nations. The difference can obviously be explained, that they were aware, that they had a higher form of freedom, namely to be free from land lords and liability to taxation. The Gotlandic society before the 1600s was considered to be an ‘ethnie’, a group with a perceived common origin, language and history. The governor of Tobolsk, Siberia’s capital, Count Matjev Gagarin ( 1711-1719 ) was considered to be of Varangian origin and higher than Tsar Peter who was just a Romanov.
The Gotlanders had early close contact with the Byzantine Ortodox Church and a trade agreement was signed with the Emperor in Miklagarðr ( Constantinople ) dated in the year 911. The document was signed by the Emperor Leo VIand Karl, Ingjald, Farulf, Vermund, Hrollaf, Gun-nar, Harold, Kami, Frithleif, Hroarr, Angantyr, Throand, Leithulf, Fast, and Steinvith. The treaty regulates the status of the colony of the Gotlandic Varangian merchants in Constantinople.
The text testifies that they settled in the quarter of Saint Mamas. No one was able to force their will on the Gotlanders, not even the Catholic Church. The Gotlanders are one of the few peoples who themselves determined the conditions for the con-nection to the Pope and the Catholic Church.
It is important that we are aware that the Gotlanders had experience of many Christian and non-Christian doctrines of faith. Åke Ohlmarks, among others, believes that there is evidence of Arian-Christian graves on Gotland as early as the 500s. The Bishop in Linköping, who the Gotlanders con-cluded contracts with, “because he was closest to them”, seems not to have been able to interfere in the decision making in the Gotlandic Church. He was only contracted to perform dedication ceremonies and tours of inspection as required. He did not even have a say in the selection of priests, although he protested to Rome. Even the compensation, that the bishop received, was decided by the Gotlanders. As earlier mentioned the Gotlandic Merchant Farmers’ counted their birth position and their social class socially higher than burghers and peasants of other nations.

Preserving the Past, Recording the Present, Informing the Future
Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan Int Society
carruthersclan1@gmail.com carrothersclan@gmail.com

Tore Gannholm
Reviewed by Tammy Wise CHS
CLAN SEANACHAIDHI
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST
Information about Tore Gannholm, whose work has been valued by all researchers at Clan Carruthers CCIS
I have researched the Gotlandic history since 1990 when I came with my first book “Gutarnas historia”.At that time it said in Swedish history books: “Gotland is seldom mentioned in the written sources why it was considered that Gotland had no real history, as there lived only peasants.We still suffer badly from earlier generations ’‘Swedish – centered’ historical research. History was always written by the victors. The ‘history’ of the defeated and that of conquered territories is usually being ignored or even misinterpreted. This is true, not only for Gotland but for all those landscapes which were conquered in the 1600s and also, mutatis mutandis, for those parts of the old Sweden which were lost. Who now knows anything about the Middle Ages of Karelia or of Ingermanland or, for that matter, of Finland? When Gotland was annexed by Sweden in 1679 it was the winners history that became ruling. Gotlandic history became irrelevant. To understand the history of Gotland, one must fully realize that Gotland was an independent Merchant Farmers’ Republic, and the hub of the Baltic Sea region, which from time immemorial had its relations mainly east and south. The Gotlandic history is misleading and difficult to understand if it is bundled with the Swedish history, which so far has been done. They both have their separate history. There are some deadlocks in Swedish history which have blocked the view for a broader perspective. I here think of the Roman sources about the Baltic Sea region. In the 1600s when Sweden was a super-power they had to give it a story that matched its position in the world and when they in the Roman sources found peoples and places that started with an ‘S’ they immediately concluded that it must be ‘Svear’ and the ‘Scandinavian peninsula’. The Roman name for the Scandinavian peninsula was, however, still in the 500s THULE. This historical picture was created by Johannes Magnus, and continued by Olof Rudbeck in ‘Atlantica’. Still today many writers without thought are copying these old delusions that the Roman writers would have written about some mighty Svear at the beginning of our era.It is not possible to study Gotlandic history or Gotlandic world-uniqe churches in any Swedish university as there are no such subjects. However on internet I have over the years been able to discuss history with scholars in various countries. As regards the world-unique Gotlandic Medieval churches Professor Emeritus Jan Svanberg has been my mentor since early 1990s and I have followed him on various excursions to churches in Gotland, in Sweden, in Russia and in southern Europe. I have also arranged excursions with Jan as guide to Gotlandic churches. After the book-release of “Gotland the Pearl of the Baltic Sea” in august 2013 I started with the project of the Gotlandic churches with Jan Svanberg as my mentor. I realized something was wrong with the dating and could soon prove that they were up to 200 years older that available research showed. I worked 8 hours a day seven days a week for two years. I used three computers to access my research material that I had scanned and is available in pdf on my server. I had book release on ”The Gotlandic Merchant Republic and its Medieval Churches”.

You can find us on facebook at :
https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan/
https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClanLLC
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society




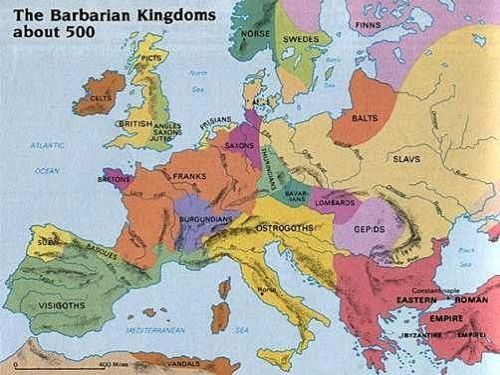
 From then on, until the disaster at Guadalete in Spain in 711 AD, when the Western Goths were defeated by invading Muslims, the climate was cold with snowy winters in northern and central Europe.
From then on, until the disaster at Guadalete in Spain in 711 AD, when the Western Goths were defeated by invading Muslims, the climate was cold with snowy winters in northern and central Europe.

 Right and left side of a lance head with runic inscription found near Kovel in the Northwest corner of Ukraine. The runic inscription to be read from right to left “Tilarids”. It has been identified as likely East Germanic, most likely Gothic because of the nominative s-suffix. It is from the beginning of the third century.
Right and left side of a lance head with runic inscription found near Kovel in the Northwest corner of Ukraine. The runic inscription to be read from right to left “Tilarids”. It has been identified as likely East Germanic, most likely Gothic because of the nominative s-suffix. It is from the beginning of the third century.