
THE HERULS
The Heruli enjoys a prominent place in the Migration Age history. The name does not occur in the writings of the first two centuries AD, and it neither appears in sagas, Saxo or other Scandinavian sources. However, they are mentioned in the very first lines of the poem Beowulf. One can imagine that bards at the Dani court did not consider it opportune to sing about the country’s former rulers, whom Dani had displaced, and this is the reason for the absence of Heruls in sagas and skaldic verses. The Eddas, on the other hand, strongly emphasize on telling that the Jotuns were the first and the originals.

Most rock carvings with wheel cross in Denmark can be found at Lille Strandbygaard in Nylars on the island of Bornholm.
Jordanes mentions in his description of the peoples on the island of Scandia that Dani expelled Herulos from their settlements – perhaps in Scania, Halland, Blekinge or Sjælland, possibly around 200-300 AD. Procopius says that after a catastrophic defeat to the Longobards a very large part of the Heruli went back to Scandinavia, where they settled on the island of Thule that is the Scandinavian Peninsula “near the Goths” or “opposite the Goths.” Therefore, we believe that the Heruli originally came from Scandinavia, but since they are not mentioned in the Scandinavian historical sources, they must have been known there under a different name.
In fact, the opening lines of “Beowulf” mention King Skjold’s suppression of the “fearsome Herul” and other tribes beyond the “whale-road”:
“Listen! We – of the Spear-Danes in the days of yore,
of those clan-kings heard of their glory.
how those nobles performed courageous deeds.
Often Scyld, Scef’s son, from enemy hosts
from many peoples seized mead-benches;
and terrorised the fearsome Heruli (egsode Eorle) after first he was
found helpless and destitute, he then knew to recompense for that:-
he grew under the clouds, throve in honours,
until to him each of the bordering tribes
beyond the whale-road had to submit,
and yield tribute:- that was a good king!”
However, later in the poem, “Earle” is used in a way that can be understood as a title.
The archaeologist Johannes Brøndsted wondered about the lack of finds from the oldest iron age on Sjælland and in Skåne. Some have suggested that the Bronze Age lasted longer in this part of the country than in Jylland and on Fyn, it being understood that the Bronze Age culture here lasted long into the Iron Age. However, probably so that they largely used weapons of iron.
In Alvismal from the Elder Edda, it is told that the Elves called the sun Fager-wheel (Fager is an old Danish word for beautiful). There are thousands of rock carvings depicting wheel crosses, which we believe are sun symbols that we call wheel-crosses, all of which are carved by the bronze age people. They may have been the Elves or Alfs. Since the Bronze-culture probably existed for a longer time on Sjælland and in Scania than in the rest of the country, we can believe that the Heruls at the beginning of the Roman Iron Age was known as Elves or Alfs, and they were expelled by Dani.
One can also look into it so that Elves are the only names label from the Scandinavian mythology, which is vacant, besides from Jats and dwarfs, and thus speculatively attach them to the Heruls in Scandinavia.
 |
Single-edged sword from Lynghøjgaard in Salling adorned with a wheel cross. Foto Danmarks Oldtid by Johannes Brondsted.
Pliny mentions some names of seas, mountains and islands around Scandinavia: Amalchian sea, Morimarusa, Rubeas, Cronian Sea, Baltia; which names they were called according to “the language of these races.” These names do not sound like Gothic or Germanic names. If not the ancient writers explicitly had written that thus they are called on the natives’ own language, we would probably think that they came from Latin. Therefore, we may believe that the language of some of “these races” was a language close to an original Proto-Indo-European language, which reminded of Latin that the Bronze Age people alias Elves alias Heruls may have spoken; and it was in that language that the inner Danish waters was called Codanus.
Ancient sources, including Zosimus and Dexippo, say that Goths and Heluroi from Crimea around the year 200 AD, sailed across the Black Sea and captured the great city of Trebizond, from which they took a big booty and abducted a large number of prisoners. The same fate befell large and splendid cities of Bithynia like Chalcedon and Nicomedia. It is also said that in emperor Gallienus’ reign, 260-268 AD the Goths and Heruls sailed with a large fleet through Bosphorus and Hellespont. They plundered Athens and many other cities. They landed in Greece, where the campaign’s leaders began to quarrel among themselves, and one of the Heruli leaders named Naulobatus, went in Roman service together with all his men. He was very well received of the emperor, who gave him a rank of consul.
Jordanes tells about the Heruli at the shore of the Black Sea around 360 AD: “But though famous for the submission of so many races, he (Hermanaric, king of the Eastern Goths) gave himself no rest until he had slain the majority of the tribe of the Arulos (gentem Erulorum), whose chief was Alaricus, and reduced the rest to his domination. Now the aforesaid race, as the historian Ablabius tells us, dwelt near the Sea of Asov in marshy places, which the Greeks call ele hence they were named Eluri. They were a people swift of foot, and on that account were the more swollen with pride. Indeed, there was at that time no race that would not have chosen from them its light-armed troops for battle. But though their quickness often outmaneuvered others, who frequently engaged in war, yet they were overthrown by the steadiness and slowness of the Goths; and the lot of fortune brought it to pass that they, as well as the other tribes, had to serve Ermanaric, king of the Goths (Gothorum regi Ermanarico). After the slaughter of the Eruli, this same Ermanaric (Ermanaricus) took arms against the Wenethos.”

Thor in dialog with the dwarf Alvis. Illustration in Alvismal by W. G. Collingwood.
The author believes that the Goths were a collective term for various groups, which understood each other because of their shared Gothic language and culture. However, if Heruls was simply another Germanic or Gothic migration people, why did the antique sources write “Goths and Heruls”. They could have contented themselves with writing only “Goths”. There must have been qualitative differences between Goths and Heruls, for example, different languages, culture and physical appearance.
In his report on the Vandal War, Procopius listed the Gothic nations: “There were many Gothic nations in earlier times, just as also at the present, but the greatest and most important of all are the Goths, Vandals, Visigoths, and Gepaedes. In ancient times, however, they were named Sauromatae and Melanchlaeni; and there were some too who called these nations Getic.” Procopius was general Belisarius’ secretary through three wars, namely against the Persians, Vandals and Goths, and in all campaigns, Heruls had been part of the Roman army. He must have had quite a good knowledge of Heruls, and when he did not count them among the Gothic nations, so it must have been because they precisely were not Goths.
Sidonius Apollinaris wrote about the Heruls: ” – Here strolls the Herulian with his glaucous cheeks, inhabitant of Ocean’s furthest shore, and of one complexion with its weedy deeps.”
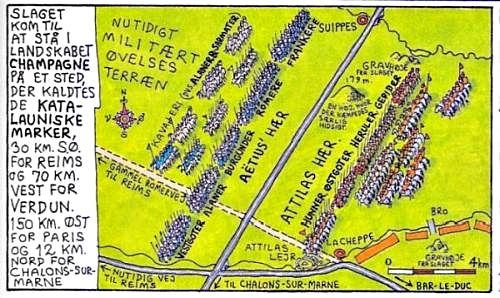 |
Claus Deleurans Description of the famous battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451 AD. From “Danmarkshistorie for Folket”.
The Heruli fought with Attila in the battle on the Catalaunian Plains in 451 AD. After Attila’s death and the showdown with his sons in the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD, they tore free from the Huns. They established their own kingdom and joined Odoacer in Italy. Odovacar was a Sciri, who was commander of the imperial troops, who deposed the last Western Roman Emperor, Romulus Augustulus, in 476 AD.
Jordanes tells about the confrontation with the Huns by the river Nedao: “For then, I think, must have occurred a most remarkable spectacle, where one might see the Goth fighting with pikes, the Gepides raging with his sword, the Rugians breaking off missiles in his own wound, the Swevian as foot soldier, the Hun taking the initiative with his bow, the Alan forming a of heavy battle line, the Erulum one of light armor.”
Paul the Deacon tells that Heruli was part of Odovacar army in Italy: ” – Odoacar then, having collected together the nations, which were subject to his sovereignty, that is the Turcilingi and the Heroli and the portion of the Rugii he already possessed and also the peoples of Italy, came into Rugiland and fought with the Rugii.”
Further, Paul tells in his Historia Langobardorum that the Herulian king was called Rotholf. The king’s brother visited the Longobards to negotiate a peace. After completing the mission he was about to return home, but was invited to a glass of wine by a Longobard Princess, who, however, looked down at him because he was rather small: ” – and because he was small in stature, the girl looked down upon him in contemptuous pride and uttered against him mocking words.” She arranged that her servants killed the little man with a spear from behind through a window, while he drank wine.
 |
The last stand of Rolf Krake and his household troops. Hrodwulf, Rudolf, Rudolf and Rodolphus appear as names of Herulian kings, so it is tempting to believe that Rolf was a traditional Herulian king’s name, like we today have Frederik and Christian as traditional Danish King names. The philologist Niels Lukman suggested in 1943 that Rolf Krake could have been a Herulian king named Rodulf. The legend of Rolf Krake thus becomes a kind of Scandinavian King Arthur legend. Drawing by Louis Moe.
King Rudolf sent his hardened veterans against the Longobards. Paulus tells: “The Heroli were indeed at that time well trained in martial exercises, and already very famous for their many victories. And either to fight more freely or to show their contempt for a wound inflicted by the enemy, they fought naked, covering only the shameful things of the body.” King Rudolf himself did not participate in the fight; he awaited the outcome of the battle in the shade of a tree, as he felt sure of Herulian victory. Too late, he was told that the Longobards had progress, and he fell along with the greater part of his army. Paul tells only that the King’s brother was small in stature, but that sort of things runs in the family, so the king himself has probably not been a giant. A Herulian king, who left his people and sought refuge in Constantinople, was also called Rodolphus, indicating that it has been a traditional name for Herulian kings. This brings to mind the Scandinavian legend of Rolf Krake, who also was small in stature.
Paulus Diaconus continued: “- And now from that time all the courage of the Heroli so decayed that thereafter they had no king over them in any way.”
The Danish scholar Niels Lukman suggested in his doctoral thesis in 1943 that Rolf Krake could have been a Herulian king named Rodulf. The legend of Rolf Krake thus becomes a kind of Scandinavian King Arthur legend, loved by bards.
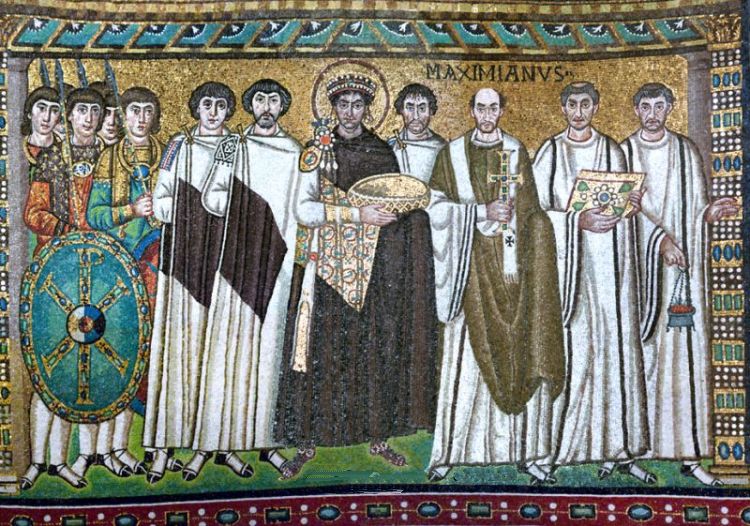 |
Emperor Justinian and his entourage as mosaic in the Basilica of San Vitale in Ravenna. The bearded gentleman by the emperor’s right hand is believed to be Procopius’ superior, General Belisarius. He was in charge of the Justinian attempts to recapture the Western Roman Empire. The man at the Emperor’s left is thought to be the eunuch Narses, who succeeded Belisarius as commander in Italy. Photo Wikipedia.
As General Belisarius secretary Procopius participated in the Eastern Roman Empire’s war against the Persians in 531 AD, against the Vandals in 532 AD, and against the Goths in Italy 535 AD. He wrote a very descriptive report on the course of the wars. Along with many other barbaric peoples, the Heruls were part of the imperial army in all three wars, and Procopius mentions them many times.
Before an important battle in the Persian war, he says: “The extremity of the left straight trench which joined the cross trench, as far as the hill which rises here, was held by Bouzes with a large force of horsemen and by Pharas the Erulian with three hundred of his nation.” Apparently, the Heruls here were light infantry supporting the cavalry. Procopius uses the term “his nation”, indicating that Heruls really were a people, a race, with their own culture and most likely own language.
Before the battle the following day Pharas got a creative idea: “Then Pharas came before Belisarius and Hermogenes, and said: “It does not seem to me that I shall do the enemy any great harm if I remain here with the Eruli; but if we conceal ourselves on this slope, and then, when the Persians have begun the fight, if we climb up by this hill and suddenly come upon their rear, shooting from behind them, we shall in all probability do them the greatest harm.”
Which they did: “But first the three hundred Eruli under Pharas from the high ground got in the rear of the enemy and made a wonderful display of valorous deeds against all of them and especially the Cadiseni.”
Heruls was only one of many barbarous people in the Roman army. About preparations for another battle it is said: “And he arranged the soldiers as follows. On either side of the tent were Thracians and Illyrians, with Goths beyond them, and next to these Eruli, and finally Vandals and Moors. And their line extended for a great distance over the plain.”
 |
Painting depicting Procopius and Belisarius. Perhaps it is the artist’s idea that Procopius is the elderly bearded man, but the author believes that Procopius was a young man, eager but a little naive, when he followed the armies and wrote his reports. Only a young man could have had the physique to work as a war correspondent for so long time. Unknown artist – from mikeaztec.wordpress.com.
In a battle, the Heruls became too eager and pushed too far forward: “And then Narses urged his men forward and pressed still harder upon the enemy, and the rest of the Romans joined in the action. But all of a sudden the men who were in ambush, as has been said, came out from the cabins along the narrow alleys, and killed some of the Eruli, falling unexpectedly upon them” – “And the Persians, shooting into great masses of the enemy in the narrow alleys, killed a large number without difficulty, and particularly of the Eruli who had at the first fallen upon the enemy with Narses and were fighting for the most part without protection. For the Eruli have neither helmet nor corselet nor any other protective armour, except a shield and a thick jacket, which they gird about them before they enter a struggle. And indeed the Erulian slaves go into battle without even a shield, and when they prove themselves brave men in war, then their masters permit them to protect themselves in battle with shields. Such is the custom of the Eruli.”
In 532 AD the so-called Nika revolt against Emperor Justinian broke out in Constantinople. Procopius says that thousands of rebels had gathered in the Hippodrome to crown a new emperor. They were all cut down by professional soldiers under the command of the generals Belisarius and Moundos. Belisarius was followed by his lifeguard, which included Thracian Goths, and the Gepide prince Moundos “had some Eroulian barbarians with him.” The two generals attacked the poorly armed crowd from each end of the Hippodrome and cut them down indiscriminately. It was the bloodiest revolt ever in Constantinople, some historians assume that up to 30,000 to 35,000 people lost their lives before the rebellion was quelled.
The Heruls also participated in the Roman emperor’s following war against the Vandals in North Africa: “And there followed with them also four hundred Eruli, whom Pharas led.”
Romans and Procopius did not have great expectations of the Heruli, but Pharas was a positive surprise by the capture of the Vandal king, Gelimer: ” – and so he chose out soldiers, with Pharas as their leader, and set them to maintain the siege of the mountain. Now this Pharas was energetic and thoroughly serious and upright in every way, although he was an Erulian by birth. And for an Erulian not to give himself over to treachery and drunkenness, but to strive after uprightness, is no easy matter and merits abundant praise. But not only was it Pharas, who maintained orderly conduct, but also all the Erulians who followed him. This Pharas, then, Belisarius commanded to establish himself at the foot of the mountain during the winter season and to keep close guard, so that it would neither be possible for Gelimer to leave the mountain nor for any supplies to be brought in to him. And Pharas acted accordingly.”

Emperor Constantine is monitoring that Arian heretics are forced to burn their books. From MS CLXV, Biblioteca Capitolare, Vercelli, 9th century. – Wikimedia Commons.
Emperor Justinian was a very devout Catholic and allowed no deviations in the Christian faith, and this was a contributing factor to a mutiny among the Roman troops after the victory over the Vandals: “In the Roman army there were, as it happened, not less than one thousand soldiers of the Arian faith; and the most of these were barbarians, some of these being of the Erulia nation.” Maybe it was especially the Heruli, who were Arian Christians.
In Procopius’ section on the Gothic war, Heruls are first mentioned somewhat late in the war. Maybe there was Heruls in Belisarius’ army from the beginning, but we do not hear much about them. But in the army, which the emperor sent 538 AD led by Narses there was a large group: “And about two thousand of the Erulian nation also followed him, commanded by Visandus and Aluith and Phanitheus.”
Procopius tells about Narses’ attack on Caesena (Cesena), in which Heruls participated: “But since the barbarians defended themselves manfully, many fell in the fight and among them Phanitheus, the leader of the Eruli”.
“Now as to who in the world the Eruli are, and how they entered into alliance with the Romans, I shall forthwith explain.” Procopius wrote in “History of the Wars – Book XIV”:
“They used to dwell beyond the Ister River from of old, worshipping a great host of gods, whom it seemed to them holy to appease even by human sacrifices. And they observed many customs which were not in accord with those of other men. For they were not permitted to live either when they grew old or when they fell sick, but as soon as one of them was overtaken by old age or by sickness, it became necessary for him to ask his relatives to remove him from the world as quickly as possible. And these relatives would pile up a quantity of wood to a great height and lay the man on top of the wood, and then they would send one of the Eruli, but not a relative of the man, to his side with a dagger; for it was not lawful for a kinsman to be his slayer. And when the slayer of their relative had returned, they would straightway burn the whole pile of wood, beginning at the edges. And after the fire had ceased, they would immediately collect the bones and bury them in the earth. And when a man of the Eruli died, it was necessary for his wife, if she laid claim to virtue and wished to leave a fair name behind her, to die not long afterward beside the tomb of her husband by hanging herself with a rope. And if she did not do this, the result was that she was in ill repute thereafter and an offence to the relatives of her husband. Such were the customs observed by the Eruli in ancient times.”

Burned spot grave at Storup on the island of Mors. The digging spoon gives an idea of the size. Burned spot grave appears that after cremation, the survivors scraped the burned bones and the remains of the fire together in a hole in the ground, and covered it. If this has been the burial custom in eastern Denmark in the early Iron Age it will explain the striking emptiness of finds of graves on Sjælland and Skåne. In cultivated areas, where farmers have sown and plowed through more than a millennium since then, such graves must have been made completely invisible. – Excavated by Mors Arkæologisk Forening.
Such burial method would only leave some very simple cremation graves that it would be almost impossible to find after one and a half thousand years; and this may explain the emptiness of finds of graves in Sjælland and Scania from the early Iron Age.
We must believe that Procopius had his information from the newly arrived Heruls themselves. Maybe because they recently had converted to Christianity, they seem to have had a rather critical, almost ironic attitude to their own pagan past: “But as time went on they became superior to all the barbarians who dwelt about them both in power and in numbers, and, as was natural, they attacked and vanquished them severally and kept plundering their possessions by force. And finally they made the Lombards, who were Christians, together with several other nations, subject and tributary to themselves, though the barbarians of that region were not accustomed to that sort of thing; but the Eruli were led to take this course by love of money and a lawless spirit. When, however, Anastasius took over the Roman empire, the Eruli, having no longer anyone in the world whom they could assail, laid down their arms and remained quiet, and they observed peace in this way for a space of three years. But the people themselves, being exceedingly vexed, began to abuse their leader Rodolphus without restraint, and going to him constantly they called him cowardly and effeminate, and railed at him in a most unruly manner, taunting him with certain other names besides. And Rodolphus, being quite unable to bear the insult, marched against the Lombards, who were doing no wrong, without charging against them any fault or alleging any violation of their agreement, but bringing upon them a war which had no real cause.”

The holy priest and martyr Maximus and more than 50 colleagues are being hung in Salzburg in modern Austria by Heruls under King Odovacer perhaps around 480 AD. Odovacer was an Arian Christian, but it is said that he rarely intervened in religious matters, but maybe he did a few times – Engraving from 1716 in the “Bavaria Sancta”.
The following battle was a catastrophic defeat for the Heruli.
“For this reason, the Eruli were no longer able to tarry in their ancestral homes, but departing from there as quickly as possible they kept moving forward, traversing the whole country which is beyond the Ister River, together with their wives and children. But when they reached a land where the Rogi dwelt of old, a people who had joined the Gothic host and gone to Italy, they settled in that place. But since they were pressed by famine, because they were in a barren land, they removed from there not long afterward, and came to a place close to the country of the Gepaedes.”
“And at first the Gepaedes permitted them to dwell there and be neighbours to them since they came as suppliants. But afterwards for no good reason, the Gepaedes began to practise unholy deeds upon them. For they violated their women and seized their cattle and other property, and abstained from no wickedness whatever, and finally began an unjust attack upon them. And the Eruli, unable to bear all this any longer, crossed the Ister River and decided to live as neighbours to the Romans in that region”.

The 55 martyrs from Salzburg killed by Heruls under King Odovacer perhaps around 480 AD – Engraving from 1716 in the “Bavaria Sancta.
First of the emperor greeted them welcome, but before long it came to fighting between Heruls and Romans: “But when Justinian took over the empire, he bestowed upon them good lands and other possessions, and thus completely succeeded in winning their friendship and persuaded them all to become Christians.” We remember that Heruls took part in the Arian mutiny in Belisairus’ army in Africa, so some Heruls were Arians. But Justinian was fanatical Catholic and must have converted them to Catholic Christianity. There may have been religious divisions among Heruli, such that some were Catholics, and others were Arians and this can have contributed to their final disappearance as a people.
Procopius was very fascinated by the stories of the midnight sun and the dark winter on the island of Thule (Scandinavian peninsula), which shows that he was an inquisitive and curious young man: “And although I was eager to go to this island and become an eye-witness of the things I have told, no opportunity ever presented itself. However, I made enquiry from those who come to us from the island as to how in the world they are able to reckon the length of the days since the sun never rises nor sets there at the appointed times. And they gave me an account which is true and trustworthy.”
The Scandinavian soldiers told Procopius on the Nordic Christmas: “When, however, the time of the nights arrives, they always take note of the courses of the moon and stars and thus reckon the measure of the days. And when a time amounting to thirty-five days has passed in this long night, certain men are sent to the summits of the mountains for this is the custom among them and when they are able from that point barely to see the sun, they bring back word to the people below that within five days the sun will shine upon them. And the whole population celebrates a festival at the good news, and that too in the darkness. And this is the greatest festival, which the natives of Thule have.”

Wheel cross petroglyphs which very much looks like a wheel with four spokes from Fossum in Skien – Photo Telemark Fylkeskommune.
Forty days of darkness will place them well north of the Arctic Circle, and it is not likely that others than scattered hunters and reindeer herders lived there in the Iron Age. There must have been some, who made a little fun with Procopius. But the story says nevertheless that there were men in the army, which were believed to have come from Scandinavia. In the Bronze Age religion, which probably originally also had been the Heruli’s, played the Sun a big role, and we celebrate still Christmas (“jul” in Danish, which is similar to “hjul”, which means wheel) so many years later.
But we notice that it is not a midwinter festival, which they describe, as darkness lasts 40 days, and after 35 days they will watch for the sun, which will be in the middle of January, and only then comes the festival, which one must assume took place late January. It brings to mind the Chinese New Year, also known as Spring Festival, which takes place in late January or early February.
The whole long and detailed report on the nature and the people on the island of Thule in connection with his report on Heruls indicates that at least some Heruls really came from Scandinavia – though he did not write it directly and unambiguously.

The man at the emperor’s right side on a mosaic in the Church of San Vitale in Ravenna are thought to be Belisarius. He was Procopius’ superior through three wars. In all of these Heruls were part of the army. He is believed to have been born in 505 AD in modern Bulgaria in a family with Gothic roots. As early as 527 AD, when he was in his early twenties, he was appointed as army commander in Syria in the war against the Persians. His success in many campaigns aroused the emperor’s jealousy, and he was withdrawn from the war in Italy in 540 A.D. and later replaced by the eunuch Narses.
Procopius was also a somewhat simple-minded young man, who in good faith wrote down, what Heruli’s enemies had to say about them: “They are still, however, faithless toward them (the Romans), and since they are given to avarice, they are eager to do violence to their neighbours, feeling no shame at such conduct. And they mate in an unholy manner, especially men with asses, and they are the basest of all men and utterly abandoned rascals.” Maybe it was a contribution from his superior, Belisarius, who did not like Heruls.
Procopius says that when the Emperor heard what the Goths had done in Milan – namely destroyed the city, killed all the men and given the women to the Burgundians – he pulled Narses back from Italy and made Belisarius commander: “But the Eruli seeing that Narses was departing from Italy, refused to remain there any longer, although Belisarius promised that they would receive many benefits from both himself and from the emperor, if they remained; but they all packed up their luggage and withdrew going first to Liguria. There they happened upon the army of Uraias, and they sold all the slaves and all the animals they were taking with them to the enemy and , having thus acquired a great amount of money, they took an oath that they would never array themselves Goths or do battle with them. Thus they made their withdrawal in peace and came into the land of the Veneti. But upon meeting Vitalius there, they forthwith began to repent of the wrong they had done the emperor Justinian. And seeking to clear themselves of the charge against them, they left there Visandus, one of their commanders, with his forces, but all the rest betook themselves to Byzantium under the leadership of Aluith and Philemuth, the latter having taken the command after Phanitheus was killed at Caesena.”
But things went badly for the remaining Heruls in Italy: “While the other commanders were remaining quiet on account of this situation (the arrival of imperial tax collectors) Vitalius alone (for he happened to have in Venetia a numerous army comprising with others a great throng of barbarian Eruli) had the courage to do battle with Ildibadus, fearing, as actually happened, that at a later time, when his power had grown greatly they would be no longer able to check him. But in the fierce battle, which took place near the city of Tarbesium (Treviso) Vitalius was badly defeated and fled saving some few men, but losing the most of them there. In this battle, many Eruli fell and among them, Visamdus, the leader of the Eruli, was killed.”
The Heruls lived in the Balkans near the town of modern Belgrade: “Other towns of Dacia also, about the city of Singidunum (Belgrad) had been taken over by the Eruli as a gift from the emperor, and here they are settled at present time, overrunning and plundering Illyricum and the Thracian towns very generally. Some of them have even become Roman soldiers serving among the foederati, as they are called. So whenever envoys of the of the Eruli are sent to Byzantium, representing the very men, who are plundering Roman subjects, they collect all their contribution from the emperor without the least difficulty and carry them off home.”
The emperor sent Narses to the Heruls again to recruit them for the war in Italy: “The emperor also sent Narses the eunuch to the rulers of the Eruli, in order to persuade most of them to march to Italy. And many of the Eruli followed him, commanded by Philemuth and certain others, and they came with him into the land of Thrace. – And it so fell out during this journey they unexpectedly rendered a great service to the Romans. for a great throng of barbarians Schlaveni, had, as it happened, recently crossed the river Ister, plundering the adjoining county and enslaved a very great number of Romans. Now the Eruli suddenly came upon these barbarians and joined battle with them, and, although far outnumbered, they unexpectedly defeated them, and some they slew, and the captives they released one and all to go to their homes.”
Procopius also tells the story of how the Heruls killed their king and sent word to Scandinavia for a new one “The Eruli, displaying their beastly and fanatical character against their own “rex,” one Ochus by name, suddenly killed the man for no good reason at all, laying against him no other charge than that they wished to be without a king thereafter. And yet even before this, while their king did have the title, he had practically no advantage over any private citizen. But all claimed the right to sit with him and eat with him, and whoever wished insulted him without restraint; for no men in the world are less bound by convention or more unstable than the Eruli. Now when the evil deed had been accomplished, they were immediately repentant. For they said that they were not able to live without a ruler and without a general; so after much deliberation, it seemed to them best in every way to summon one of their royal family from the island of Thule. And the reason for this I shall now explain.”

The man at the Emperor’s left side on the mosaic in San Vitale in Ravenna is thought to be the eunuch Narses, who in 551 AD arrived in Italy at the head of the largest army, the Emperor ever had sent against the Goths, he was reportedly about 80 years old, but still sound of mind. The army included a large group Heruls. However, the man in the picture does not look like an eighty-years-old.
Procopius took up the thread again after the description of the island of Thule: “On the present occasion, therefore, the Eruli who dwelt among the Romans, after the murder of their king had been perpetrated by them, sent some of their notables to the island of Thule to search out and bring back whomsoever they were able to find there of the royal blood. And when these men reached the island, they found many there of the royal blood, but they selected the one man who pleased them most and set out with him on the return journey. But this man fell sick and died when he had come to the country of the Dani. These men, therefore, went a second time to the island and secured another man, Datius by name. And he was followed by his brother Aordus and two hundred youths of the Eruli in Thule. But since much time passed while they were absent on this journey, it occurred to the Eruli in the neighbourhood of Singidunum that they were not consulting their own interests in importing a leader from Thule against the wishes of the Emperor Justinian. They, therefore, sent envoys to Byzantium, begging the emperor to send them a ruler of his own choice. And he straightway sent them one of the Eruli who had long been sojourning in Byzantium, Suartuas by name. At first, the Eruli welcomed him and did obeisance to him and rendered the customary obedience to his commands; but not many days later a messenger arrived with the tidings that the men from the island of Thule were near at hand. And Suartuas commanded them to go out to meet those men, his intention being to destroy them, and the Eruli, approving his purpose, immediately went with him. But when the two forces were one day’s journey distant from each other, the king’s men all abandoned him at night and went over of their own accord to the newcomers, while he himself took to flight and set out unattended for Byzantium. Thereupon the emperor earnestly undertook with all his power to restore him to his office, and the Eruli, fearing the power of the Romans, decided to submit themselves to the Gepaedes. This, then, was the cause of the revolt of the Eruli”
In the following fighting, it seems like Heruls fought against Heruls: “They (the Romans) also took with them as allies fifteen hundred Eruli, commanded by Philemuth and others. For except for these the whole nation of the Eruli to the number of three thousand were arrayed with the Gepaedes, since they had revolted against the Romans not long before.”
“Now a detachment of the Romans, who were marching to join the Lombards as allies, unexpectedly chanced upon some of the Eruli with Aordus, the brother of their ruler. And a fierce battle ensued in which the Romans were victorious, and they slew both Aordus and many of the Eruli.”
 |
Claus Deleuran’s depiction of the last Herul in history. I do not know from where he has it.
Some Roman units, which included Heruls, under general John rested on the laurels at a place called Lucania in Italy after an easy victory over a group of Goths. They failed to keep effective guard and were overrun in a subsequent nightly Gothic counter-attack: “And once outside the camp they ran up into the mountains, many of which rise close by, and thus were saved. Among these were John himself and Arufus, the leader of the Eruli. Of the Romans about a hundred perished.”
The emperor sent one army after another against the Goths in Italy, including a platoon Heruls under Verus: “Later he (the emperor) sent Verus with three hundred Eruli, and Varazes an Armenian by birth, and he recalled from his post Valerian, the general of Armenia, and ordered him to go to Italy with his attendants spearmen and guards, who numbered more than a thousand. Now Verus was the first to put in at Dryus, and he left his ships there, being quite unwilling to remain in that place, where John’s army was and went forward on horseback with his command. for this man was not of a serious temper, but he was utterly addicted to the disease of drunkenness, and consequently, he was always possessed by a spirit of reckless daring. And when they had come close to the city of Brundisium, they made camp and remained there.”
“And when Totila learned this, he said: “Verus has one of two things, either a powerful army or a very silly head. Let us proceed against him instantly, that either we must make trial of the man’s army, or that he may realize his own silliness”. So Totila with these words marched against him with a numerous army; and the Eruli, spying the enemy already at hand, took refuge in a wood, which was close by. And the enemy surrounded them and killed more than two hundred, and was about to lay hands on Verus himself and the rest of the force, who were hiding among the thorn-bushes, but fortune came to their aid and saved them unexpectedly. For the ships, in which Varazes and the Armenians under him were sailing, suddenly put up on the shore there. Now when Totila saw this, supposing the hostile army to be more numerous, than it really was, he immediately set out and marched away from there, while Verus and his men were glad to reach their ships on the run.”
One of the last times in history, we hear about Heruls was when they fought on the Roman side in the decisive battle of the Gothic war in Italy, which was the battle of Gualdo Tadino in 552 AD, also known as the Battle of the Gallic tombstones. It was between the Roman army under Narses and the Goths under their young king, Totila “Three thousand Heruls fought on horseback under Philemuth, their own chief, and the noble Aratus”; on the Roman side fought also 5,000 Langobards and 400 gepids, it is said.
Gibbons tells about the Heruls, who around 553 AD appeared in written history; I do not know, from where he got it: “The vanguard of the Roman army was stationed near Po, under the leadership of Fulkaris, a brave Herul, who hastily thought that personal bravery was a commander’s only duty and qualification. When he without order or caution marched along the Aemilian Road, suddenly, an ambush of Franks broke forward from Parma amphitheater, his troops were surprised and driven away, but their leader refused to flee stating in the last minute that death was less horrible than meeting Narses’ anger.”
 |
The battle between Caesar and Ariovist in the video “1-5 Germanic Tribes 1 – Barbarians Against Romans”, showing that the Germans attacked in wedge-formations. It is stated that Arovist’s Germans attacked in seven spear-head formations – in Germanic tradition called “svinefylkning”. Though, it can not be confirmed by Caesar’s “War in Gaul”, which simply states: ” – and the enemy stormed forward so suddenly and quickly that there was no time to throw spears at them. They, (the Romans) therefore, threw their spears away, and fought with swords in melee.” – perhaps it is mentioned in another source.
John Bagnell Bury confirms that there could be reasons for Heruls to fear Narses: “The course of the battle of Capua 554 AD was affected by an accident. One of the Herul captains killed his servant for some delinquency, and when Narses called him to account, he asserted that masters had the power of life and death over their slaves and that he would do the same thing again. He was put to death by the command of Narses, to the great indignation of the Heruls, who withdrew from the camp and said they would not fight. Narses drew up his line of battle without them.”
It sounds like Narses made a Cannae on the Franks, showing the limitation of the wedge-formation: “Meanwhile, two Heruls had deserted to the enemy, and persuaded Buccelin that his chance was to attack at once, as the Romans were in consternation at the defection of the Herul troops. Buccelin had drawn up his army, which consisted entirely of infantry, in the shape of a deep column, which should penetrate like a wedge through the hostile lines. In this array, the Franks arrived, armed with missile lances, swords, and axes, confident that they would sweep all before them at the first rush. They penetrated into the central space which was to have been occupied by the Heruls, dislodging the outer ranks of the Roman infantry on either side. Narses quietly issued orders to his wings to face about, and the enemy was caught between the crossfire of the cavalry, who were all armed with bows.” – “Their ranks were gradually mown down, and then Sindual and his Heruls appeared upon the scene.”

OFFICIAL AND REGISTEREDL CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
SCOTTISH CLAN – IRISH CLAN – NORSE CLAN
Preserving Our Past! Recording Our Present! Informing Our Future!
The Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society LLC
CLANCARRUTHERS1@GMAIL.COM

CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST

You can find us on our main facebook pages at :
SILVER WINGS-https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClanLLC/
GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Socie


