Ragnar Lodbrok and His Wives and Sons
CARRUTHERS ANCESTORS
 The old sagas, or hero tales of the north, are full of stories of enchantment and strange marvels. We have told one of these tales in the record of King Rolf ( Rollo ) and Princess Torborg. We have now to tell that of Ragnar Lodbrok, a hero king of the early days, whose story is full of magical incidents. That this king reigned and was a famous man in his days there is no reason to doubt, but around his career gathered many fables, as was apt to be the case with the legends of great men in those days. To show what these tales were like we take from the sagas the marvellous record of Ragnar and his wives.
The old sagas, or hero tales of the north, are full of stories of enchantment and strange marvels. We have told one of these tales in the record of King Rolf ( Rollo ) and Princess Torborg. We have now to tell that of Ragnar Lodbrok, a hero king of the early days, whose story is full of magical incidents. That this king reigned and was a famous man in his days there is no reason to doubt, but around his career gathered many fables, as was apt to be the case with the legends of great men in those days. To show what these tales were like we take from the sagas the marvellous record of Ragnar and his wives.
In East Gothland in the ancient days there lived a mighty jarl, or earl, named Herröd, who was descended from the gods. He had a daughter named Tora, who was famed for her beauty and virtue, but proved as hard to win for a wife as Princess Torborg had been. She dwelt in a high room which had a wall built around it like a castle, and was called Castle Deer, because she surpassed all other women in beauty as much as the deer surpasses all other animals.
Her father, who was very fond of her, gave her as a toy a small and wonderfully beautiful snake which he had received in a charmed egg in Bjarmaland. It proved to be an unwelcome gift. The snake was at first coiled in a little box, but soon grew until the box would not hold it, and in time was so big that the room would not hold it. So huge did it become in the end that it lay coiled in a ring around the outer walls, being so long that its head and tail touched.
It got to be so vicious that no one dared come near it except the maiden and the man who fed it, and his task was no light one, for it devoured an ox at a single meal. The jarl was sorry enough now that he had given his daughter such a present. It was one not easy to get rid of, dread of the snake having spread far and wide, and though he offered his daughter with a great dower to the man who should kill it, no one for a long time ventured to strive for the reward. The venom which it spat out was enough to destroy any warrior.
At length a suitor for the hand of the lovely princess was found in Ragnar, the young son of Sigurd Ring, then one of the greatest monarchs of the age, with all Sweden and Norway under his sway, as the sagas tell. Ragnar, though still a boy, had gained fame as a dauntless warrior, and was a fit man to dare the venture with the great snake, though for a long time he seemed to pay no heed to the princess.
But meanwhile he had made for himself a strange coat. It was wrought out of a hairy hide, which he boiled in pitch, drew through sand, and then dried and hardened in the sun. The next summer he sailed to East Gothland, hid his ships in a small bay, and at dawn of the next day proceeded toward the maiden’s bower, spear in hand and wearing his strange coat.
There lay the dreaded serpent, coiled in a ring round the wall. Ragnar, nothing daunted, struck it boldly with his spear, and before it could move in defence struck it a second blow, pressing the spear until it pierced through the monster’s body. So fiercely did the snake struggle that the spear broke in two, and it would have destroyed Ragnar with the venom it poured out if he had not worn his invulnerable coat.
The noise of the struggle and the fierceness of the snake’s convulsions, which shook the whole tower, roused Tora and her maids, and she looked from her window to see what it meant. She saw there a tall man, but could not distinguish his features in the grey dawn. The serpent was now in its death throes, though this she did not know, and she called out:
“Who are you, and what do you want?”
Ragnar answered in this verse:
| “For the maid fair and wise
I would venture my life. The scale-fish got its death wound From a youth of fifteen!” |
Then he went away, taking the broken handle of the spear with him. Tora listened in surprise, for she learned from the verse that a boy of fifteen had slain the great monster, and she marvelled at his great size for his years, wondering if he were man or wizard. When day came she told her father of the strange event, and the jarl drew out the broken spear from the snake, finding it to be so heavy that few men could have lifted it.
Who had killed the serpent and earned the reward? The jarl sent a mandate throughout his kingdom, calling all men together, and when they came he told them the story of the snake’s death, and bade him who possessed the handle of the spear to present it, as he would keep his word with any one, high or low.

Ragnar and his men stood on the edge of the throng as the broken head of the spear was passed round, no one being able to present the handle fitting it. At length it came to Ragnar, and he drew forth the handle from his cloak, showing that the broken ends fitted exactly. A great feast for the victor was now given by Jarl Herröd, and when Ragnar saw the loveliness of Tora, he was glad to ask her for his queen, while she was equally glad to have such a hero for her spouse. A splendid bridal followed and the victor took his beautiful bride home.
This exploit gave Ragnar great fame and he received the surname of Lodbrok, on account of the strange coat he had worn. Ragnar and Tora lived happily together but not to old age, for after some years she took sick and died, leaving two sons, Erik and Agnar, who grew up to be strong and beautiful youths. Ragnar had loved her greatly and after her death said he would marry no other woman. Nor could he comfort himself at home but began to wander abroad on warlike voyages, that he might drive away his sorrow.
Leaving Ragnar Lodbrok to his travels, let us take up the strange story of another fair maiden, who was to have much to do with his future life. She was named Aslög and was the daughter of King Sigurd Fafnisbane, of Germany. Soon after she was born enemies of her father killed him and her mother and all of his race they could find. Her life was saved by Heimer, foster-father to her mother, who to get her away from the murderers had a large harp made with a hollow frame, in which he hid the child and all the treasure he could find.
Then he wandered far as a travelling harper, letting the child out when they came to solitary woods, and when she wept and moaned silencing her by striking the strings of the harp. After long journeying he came to a cottage in Norway called Spangerhed, where lived a beggar and his wife. Seeing a gold bracelet under Heimer’s rags, and some rich embroidery sticking from the harp, the beggar and his wife killed him during the night and broke open the harp. They found in it the wealth they sought, but the discovery of the pretty little girl troubled them.
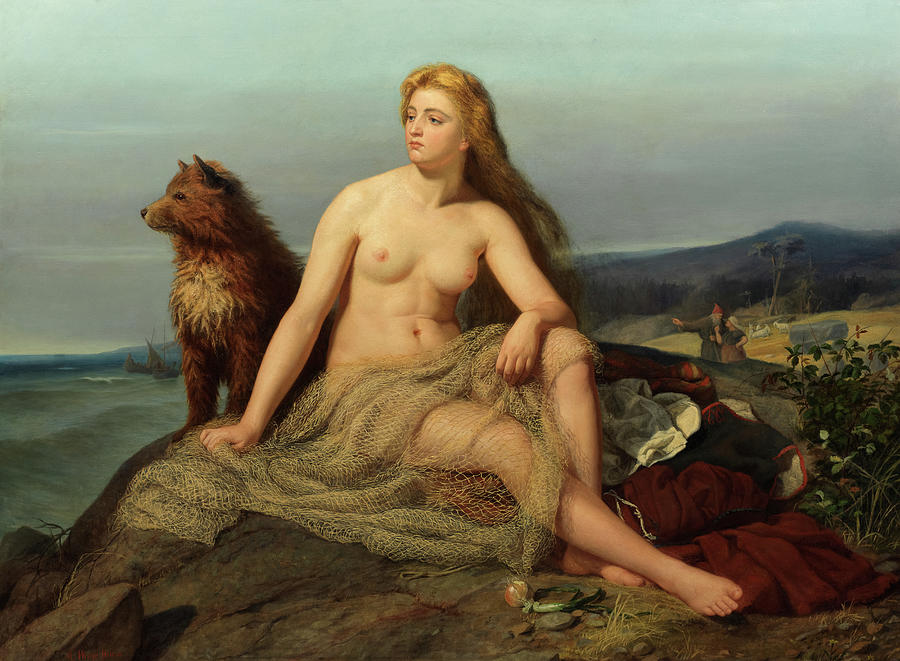

KRAKA
“What shall we do with this child?” he asked.
“We will bring her up as our own, and name her Kraka, after my mother,” said his wife.
“But no one will believe that ugly old people like us can have so fair a daughter.”
“Let me manage it,” said the wife. “I will put tar on her head so that her hair will not be too long, and keep her in ragged clothes and at the hardest work.”
This they did and little Aslög grew up as a beggar’s child. And as she kept strangely silent, never speaking, all people thought her dumb.
One day, when Aslög was well grown, Ragnar Lorbrok came that way, cruising along the Norway coast. The crew was out of bread and men were sent ashore to bake some at a house they saw in the distance. This house was Spangerhed, where Kraka dwelt.
She had seen the ships come up and the men land, and was ashamed to be seen by strangers as she was, so she washed herself and combed her hair, though she had been bidden never to do so. So long and thick had her hair grown that it reached to the ground and covered her completely.
When the cooks came to bake their bread they were so surprised at the beauty of the maiden that they let the loaves burn while looking at her, and on being blamed for this carelessness on their return to the ship said they could not help it, for they had been bewitched by the face of the loveliest maiden they had ever gazed upon.
“She cannot be as lovely as Tora was,” said Ragnar.
“There was never a lovelier woman,” they declared, and Ragnar was so struck by their story that he sent messengers ashore to learn if they were telling the truth. If it were so, he said, if Kraka were as beautiful as Tora, they were bidden to bring her to him neither dressed nor undressed, neither fasting nor satisfied, neither alone nor in company. The messengers found the maiden as fair as the cooks had said and repeated the king’s demand.
“Your king must be out of his mind, to send such a message,” said the beggar’s wife; but Kraka told them that she would come as their king wished, but not until the next morning.
The next day she came to the shore where the ship lay. She was completely covered with her splendid hair, worn like a net around her. She had eaten an onion before coming, and had with her the old beggar’s sheep dog; so that she had fulfilled Ragnar’s three demands.
Her wit highly pleased Ragnar and he asked her to come on board, but she would not do so until she had been promised peace and safety. When she was taken to the cabin Ragnar looked at her in delight. He thought that she surpassed Tora in beauty, and offered a prayer to Odin, asking for the love of the maiden. Then he took the gold-embroidered dress which Tora had worn and offered it to Kraka, saying in verse, in the fashion of those times:
| “Will you have Tora’s robe? It suits you well.
Her white hands have played upon it. Lovely and kind was she to me until death.” |
Kraka answered, also in verse:
| “I dare not take the gold-embroidered robe which adorned Tora the fair.
It suits not me. Kraka am I called in coal-black baize. I have ever herded goats on the stones by the sea-shore.” |
“And now I will go home,” she added. “If the king’s mind does not change he can send for me when he will.”
Then she went back to the beggar’s cottage and Ragnar sailed in his ship away.
Of course every one knows without telling what came from such an invitation. It was not long before Ragnar was back with his ship and he found Kraka quite ready to go with him. And when they reached his home a splendid entertainment was given, during which the marriage between Ragnar and Kraka took place, everything being rich and brilliant and all the great lords of the kingdom being present. It will be seen that, though the Princess Aslög pretended to be dumb during her years of youthful life in the beggar’s cottage, she found her voice and her wits with full effect when the time came to use them.

She was now the queen of a great kingdom, and lived for many years happily with her husband Ragnar. And among her children were two sons who were very different from other men. The oldest was called Iwar. He grew up to be tall and strong, though there were no bones in his body, but only gristle, so that he could not stand, but had to be carried everywhere on a litter. Yet he was very wise and prudent. The second gained the name of Ironside, and was so tough of skin that he wore no armor in war, but fought with his bare body without being wounded. To the people this seemed the work of magic. There were two others who were like other men.
Since the older brothers, the sons of Tora, had long been notable as warriors, the younger brothers, when they grew up, became eager to win fame and fortune also, and they went abroad on warlike expeditions, fighting many battles, winning many victories, and gaining much riches.

IWAR THE BONELESS
But Iwar, the boneless one, was not satisfied with this common fighting, but wanted to perform some great exploit, that would give them a reputation everywhere for courage. There was the town of Hvitaby (now Whitby, in Yorkshire, England), which many great warriors had attacked, their father among them, but all had been driven back by the power of magic or necromancy. If they could take this stronghold it would give them infinite honor, said Iwar, and to this his brothers agreed.
To Hvitaby they sailed, and leaving their younger brother Ragnwald in charge of the ships, because they thought him too young to take part in so hard a battle, they marched against the town. The place was ably defended, not only by men but by two magical heifers, their charm being that no man could stand before them or even listen to their lowing. When these beasts were loosed and ran out towards the troops, the men were so scared by the terrible sound of their voices that Ironside had all he could do to keep them from a panic flight, and many of them fell prostrate. But Iwar, who could not stand, but was carried into battle upon shields, took his bow and sent his arrows with such skill and strength that both the magic heifers were slain.

Then courage came back to the troops and the townsmen were filled with terror. And in the midst of the fighting Ragnwald came up with the men left to guard the ships. He was determined to win some of the glory of the exploit and attacked the townsmen with fury, rushing into their ranks until he was cut down. But in the end the townsmen were defeated and the valiant brothers returned with great honor and spoil, after destroying the castle. Thus it was that the sons of Kraka gained reputation as valiant warriors.
But meanwhile Kraka herself was like to lose her queenly station, for Ragnar visited King Osten of Upsala who had a beautiful daughter named Ingeborg. On seeing her, his men began to say that it would be more fitting for their king to have this lovely princess for his wife, instead of a beggar’s daughter like Kraka. Ragnar heard this evil counsel, and was so affected by it that he became betrothed to Ingeborg. When he went home he bade his men to say nothing about this betrothal, yet in some way Kraka came to know of it. That night she asked Ragnar for news and he said he had none to tell.
“If you do not care to tell me news,” said Kraka, “I will tell you some. It is not well done for a king to affiance himself to one woman when he already has another for his wife. And, since your men chose to speak of me as a beggar’s daughter, let me tell you that I am no such thing, but a king’s daughter and of much higher birth than your new love Ingeborg.”
“What fable is this you tell me?” said Ragnar. “Who, then, were your parents?”
“My father was King Sigurd Fafnisbane and my mother was the Amazon Brynhilda, daughter of King Budle.”
“Do you ask me to believe that the daughter of these great people was named Kraka and brought up in a peasant’s hut?”
The queen now told him that her real name was Aslög and related all the events of her early life. And as a sign that she spoke the truth, she said that her next child, soon to be born, would be a son and would have a snake in his eye.
It came out as she said, the boy, when born, having the strange sign of which she had spoken, so that he was given a name that meant Sigurd Snake-in-Eye. So rejoiced was Ragnar at this that he ceased to think of Ingeborg and all his old love for Kraka, or Aslög as she was now called, came back.
The remainder of the lives of Ragnar and Aslög and of their warlike sons is full of valiant deeds and magic arts, far too long to be told here, but which gave them a high place in the legendary lore of the north, in which Ragnar Lodbrok is one of the chief heroes. At length Ragnar was taken prisoner by King Ethelred of England and thrown into a pit full of serpents, where he died. Afterwards Iwar and his brothers invaded England, conquered that country, and avenged their father by putting Ethelred to death by torture. Iwar took England for his kingdom and the realms of the north were divided among his brothers, and many more were the wars they had, until death ended the career of these heroes of northern legend.

OFFICIAL AND REGISTEREDL CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS SINCE 1983-CLAN OF OUR ANCESTORS
SCOTTISH CLAN – IRISH CLAN – NORSE CLAN
Preserving Our Past! Recording Our Present! Informing Our Future!
The Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society LLC
carruthersclan1@gmail.com carrothersclan@gmail.com

CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST

You can find us on our main facebook pages at :
SILVER WINGS-https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClanLLC/
GOLD WINGS – https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
CLAN CARRUTHERS FAMILY HISTORY – https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan
CLAN CARRUTHERS CCIS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/3878691252182714
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY- https://www.facebook.com/groups/394653845137709
CLAN CARRUTHERS – BORDER REIVERS – https://www.facebook.com/groups/434959914239094
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Societ