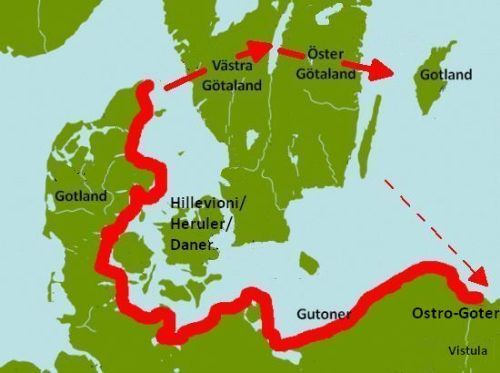
THE GOTS AND GOTLAND IN 500 AD
Who were the Goths?
The Goths were a number of Germanic tribes in the Migration Period, which appeared in written history in the third century in the areas north of the Black Sea between the rivers Danube and Don. Except for frequent raids, they invaded the Roman Empire first time in 268 AD, and later in 376 AD. The Western Goths settled a few years in the Garonne valley in France until they conquered a kingdom, which included Spain and the South of France. In France, they were displaced by the Franks after a few years, and Spain was in 711 AD conquered by Muslim invaders – but the Goths descendants took the country back in the Middle Ages. The Eastern Goths established a thriving kingdom in Italy, but after only 67 years, they were defeated by armies sent by the emperor in Constantinople.
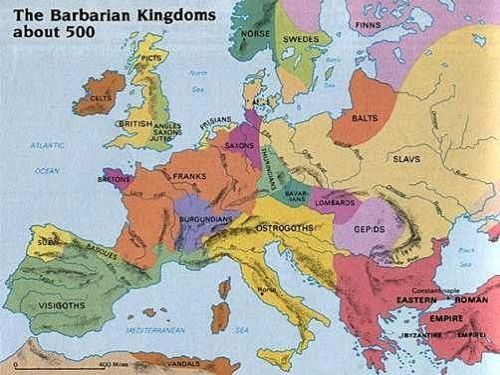
A map of Europe showing the Germanic kingdoms that were established after the downfall of the Western Roman Empire. After numerous battles and long migrations, the Western Goths managed to settle in Spain and the Eastern Goths to take possession of Italy. However, it did not last forever. From ancientweb.org.
Bottom: An artistic reconstruction of the Western Goths in battle with Attila’s Huns at Chalons. From ancientweb.org.
When the first Goths arrived at the northern coast of the Black Sea about 170 AD, the climate was still influenced by the Roman Warm Period, which, however, ended about 400 AD. The Vandals crossed the frozen Rhine new year’s eve 406 AD, thus commencing the Migration time and heralding the downfall of the Western Roman Empire. The fact that the Rhine was frozen, testifies to a rather cold climate. I do not recall the Rhine has been frozen in modern times.
 From then on, until the disaster at Guadalete in Spain in 711 AD, when the Western Goths were defeated by invading Muslims, the climate was cold with snowy winters in northern and central Europe.
From then on, until the disaster at Guadalete in Spain in 711 AD, when the Western Goths were defeated by invading Muslims, the climate was cold with snowy winters in northern and central Europe.
Goths can be traced further back in history to today’s northern Poland, and even in the distant past to their origins in Scandinavia and the Baltic area. Thus Jutland through thousand years was called Gotland.
Paul the Deacon tells about how the Langobards migrated from their original island in the ocean: “Now when the people living there had multiplied to such a number that they could no longer live together, they divided, it is told, their whole people into three parts and decided by casting lots, which of those, who were to leave the homeland and seek new places of residence.” Dudo confirmed many years later that it was a traditional way of solving problems of overpopulation in Scandinavia.
Also, the Gotland Gute Saga says that some of the people were taken for emigration by casting lot: “After a long time, the people have so increased that the country was not able to feed them all. So the land was distributed, on which every third tilled, each of these was allowed to keep and bring and take away everything, which he in his life had acquired.”
Pliny the Elder (23-79 AD) wrote: “Pytheas says that the Gutones, a people of Germania, inhabits the shores of an estuary of the Ocean called Mentonomon, their territory extending a distance of six thousand stadia; that, at one day’s sail from this territory, is the Isle of Abalus, upon the shores of which, amber is thrown up by the waves in spring, it being an excretion of the sea in a concrete form; as, also, that the inhabitants use this amber by way of fuel, and sell it to their neighbours, the Teutones.”
Pytheas wrote: “Pytheas says that the Gutones, a people of Germany, inhabit the shores of an estuary of the Ocean called Mentonomon, their territory extending a distance of six thousand stadia.” Other ancient writers also believed that the Baltic Sea and inner Danish waters was a major estuary.
Procopius wrote about the returning Heruls: “After these, they passed by the nations of the Dani, without suffering violence at the hands of the barbarians there. Coming thence to the ocean, they took to the sea, and putting in at Thule, remained there on the island.” – “And one of their most numerous nations is the Gauti, and it was opposite (next to?) them that the incoming Eruli settled at the time in question.” We must believe that Procopius shared the ancient authors believe that the Danish waters and the Baltic Sea was a large estuary, in which case it “opposite the Goths” can be understood: on the opposite side of the estuary. Alternatively, it should be translated “next to the Goths.” However, in both cases, suggesting that the Heruls were Goths.
There is some uncertainty about how long a stadium was, the proposals vary between 160 and 192 m. That means that the coastline, which was inhabited by Gutones, was between 960 and 1.152 km. long. That gives a range from Skagen to the Vistula estuary at Gdansk.
It suits very well with that the Jutland peninsula before the Viking Age was called Gotland, as it is the case in Ottar’s travelogue, added in Alfred the Great’s translation of Orosius’ Roman history from about 850 AC: “When he sailed there from Skíringssal (at Oslo), Denmark was on the port side and to starboard for three days was the open sea. And then, two days before he came to Hedeby, Gotland was to starboard (him wæs on þæt steorbord Gotland), and Sillende and many islands. The Angles dwelt in that area before they came here to this land.”
Since the area was inhabited by Gutones in time before Christ – according to Pytheas – and as part of it still was called Gotland 800-900 AD, it is reasonable to assume that at least the coast along Kattegat and the Baltic Sea were the Goth’s original homeland.
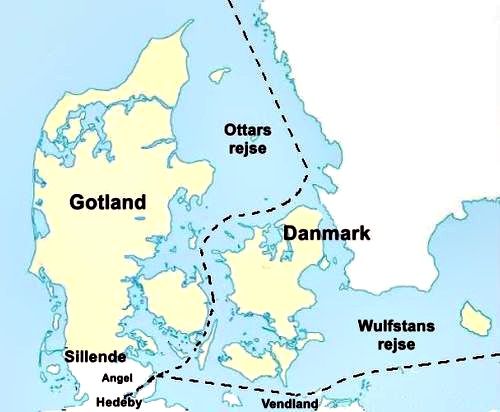
Ottar’s and Wulfstan’s travels according to additions in Alfred the Great’s translation of Orosius’ Roman history. Both Jutland and the island in the Baltic Sea are called Gotland. (The island of Gotland is not shown on this map).
That will indicate that Cimbri, Teutons, Angles and all other tribes, who lived along this coastline, and whose names we are not sure about, all originally have thought of themselves as kinds of Goths speaking the same language, namely Gothic.
Some believe that the Gutones on the densely populated Jutland east coast very early crossed the Kattegat and gradually populated West and East Gøta Land – and from there the island of Gotland in the Baltic Sea.
In Alfred the Great’s translation of Orosius’ Roman history is also added Wulfstan’s travel report from a voyage from Hedeby to Truso in Vistula’s delta from about 850 AC, which reads: “Wulfstan said that he traveled from Hedeby, and that he was in Truso in seven days and nights, and that the ship all the way went under sail. Wendland was on his starboard side and to port, he had Langeland, Lolland, Falster and Scania. These countries all belong to Denmark. So we had Bornholm to port, and they have their own king. So after Bornholm we had the countries named first Blekinge, More, Oland and Gotland to port (and Gotland on bæcbord), and these countries belong to the Swedes. And we had Wendland to starboard all the way to the Vistula river mouth.” By Gotland is here obviously meant the island of Gotland or maybe the coast of Eastern Gøtaland.

Gothic cross found in Spain perhaps from 700’s.
Ptolemy placed the people Goutai on the island of Skandia and the Gudones by the Vistula river.
The Roman historian Cornelius Tacitus described the location of the Gotones as: “Beyond the Lugii is the monarchy of the Gotones: The hand upon the reins closes somewhat tighter here than among the other tribes of Germans, but not so tight yet as to destroy freedom. Then immediately following them and on the ocean are the Rugii and Lemovii. The distinguishing features of all these tribes are round shields, short swords, and a submissive bearing before their kings.” This means that Gotones, who was ruled by powerful kings, lived north or northeast of the Lugii and further inland than the Rugii and Lemovii, which he explicitly stated as residing at the sea. Perhaps Gotones lived at the Vistula river.
Jordanes located the peoples Ostro-Goths, Ewa-Greutingis and Gaiti-Goths on the island of Scandia. Gauti-Goths were “a race of men bold and quick to fight”, he wrote, and further, “But still another race dwells there, the Sweans, who like the Thuringos, having splendid horses.” With the term “another race” he must have meant that they were not Goths. “All these nation surpassed the Germans in size and spirit, and fought with the cruelty of wild beasts”, he concluded the description of the peoples on the Scandinavian peninsula.
 Right and left side of a lance head with runic inscription found near Kovel in the Northwest corner of Ukraine. The runic inscription to be read from right to left “Tilarids”. It has been identified as likely East Germanic, most likely Gothic because of the nominative s-suffix. It is from the beginning of the third century.
Right and left side of a lance head with runic inscription found near Kovel in the Northwest corner of Ukraine. The runic inscription to be read from right to left “Tilarids”. It has been identified as likely East Germanic, most likely Gothic because of the nominative s-suffix. It is from the beginning of the third century.
He mentions different tribes of Goths, who lived on the island of Skandia, including Greutingis and Ostro-Goths, which names we later recognize for Gothic peoples on the Danube and in Italy. This makes it likely that it is true that the Goths, who attacked the Roman Empire, originally came from Scandinavia and the coasts of the Baltic Sea. Furthermore, there are several areas of southern Scandinavia, which have been called, or still are named as Gotland with different spellings, which also support the theory that this region was the original homeland of the Goths. In his report on the Gothic war in Italy, Procopius mentions the Rugi, as part of the Goths in Italy; they are also referred to by Jordanes as one of Skandia’s indigenous tribes. They are also mentioned in other ancient sources.
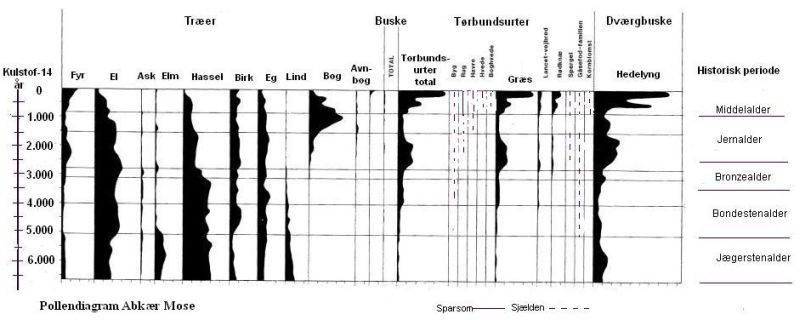
Pollen analysis from Abkjær Mose at Vojens. It appears that forest, especially beech, increases sharply and herbs typical of open land, grass and heather decrease immediately after the migration time around 500 AD indicating that the forest returned to areas that previously were pastures for cattle. Similar studies in other parts of the country show the same pattern. It is reasonable to interpret that this could be due to emigration.
Also, Procopius reports on the returning Heruls suggests that Scandinavia was quite thinly populated. For how could they just “settle down”, as if they came to an untouched prairie? If not the country had been relatively sparsely populated.
However, when large parts of the original population had turned their back to good pastures, it may not only have been hunger and misery that drove them to emigrate.
It is known that for several hundred years of the late Imperial time the Roman legions were mostly populated with various Germanic soldiers since the Roman Empire’s own citizens did not seem to have been suitable. You could say that every Roman legion was a sort of Foreign Legion, in which also many young men from the South Scandinavian region must have served. Therefore the tribes around the Baltic Sea may have concluded that they were the best and the bravest – and therefore deserved to rule. Such attitudes among the Germanic tribes were most likely critical to the doom of the Western Roman Empire.
All these ancient authors wrote before official correct spelling was invented; they wrote in different languages with different alphabets and over a period of several hundred years. They reproduced words for Goths that often for them were in an unfamiliar language, besides most likely Gothic by this time had already developed in several dialects. It is quite understandable that they spelled it in so many different ways, and we do not have to connect any deeper meaning in the different spellings.

The Goths lived spread out over farmland in small villages with each may be about 8-10 houses and farms.
In Book III of Justinian’s wars, Procopius wrote about the Goths’ early history: “Now while Honorius was holding the imperial power in the West, barbarians took possession of his land; and I shall tell, who they were and in what manner, they did so. There were many Gothic nations in earlier times, just as also at the present, but the greatest and most important of all are the Goths, Vandals, Visigoths, and Gepaedes. In ancient times, however, they were named Sauromatae and Melanchlaeni; and there were some too, who called these nations Getic. All these, while they are distinguished from one another by their names, as has been said, do not differ in anything else at all. For they all have white bodies and fair hair and are tall and handsome to look upon, and they use the same laws and practice a common religion. For they are all of the Arian faith, and have one language called Gothic; and, as it seems to me, they all came originally from one tribe, and were distinguished later by the names of those who led each group.”
Procopius is undoubtedly correct that most Germanic migrations peoples were a kind of Goths; they resembled each other and spoke largely the same language. But then they must originally have come from the same tribe, as he wrote. That is, we must believe that they all came more or less directly from the original Gothic area along the Baltic Sea, the Danish waters and from the southern part of the Scandinavian Peninsula. Procopius believed that also the Vandals and Gepids were kinds of Goths, although they were not generally named as such.
Moreover, in Denmark are clear indications of a big drop in population density in Germanic Iron Age relative to the Roman Iron Age, which indicates a considerable migration.

Preserving the Past, Recording the Present, Informing the Future
Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan Int Society
carruthersclan1@gmail.com carrothersclan@gmail.com

Dr Patricia Carrothers
Reviewed by Tammy Wise CHS
CLAN SEANACHAIDHI
CLAN CARRUTHERS INT SOCIETY CCIS HISTORIAN AND GENEALOGIST

You can find us on facebook at :
https://www.facebook.com/carrutherscarrothers.pat.9
https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClan/
https://www.facebook.com/CarruthersClanLLC
Disclaimer Ancient and Honorable Carruthers Clan International Society